
UGC NET 16 June 2023 Question Paper Exam Analysis : Check the subject-wise exam analysis of the NTA UGC NET 2023 online exam held on June 16, 2023. Download the type of questions asked in Paper-1 and Paper-2, their difficulty level, and the number of good attempts.
| UGC NET 16 June 2023 Question Paper Exam Analysis | ||
| Category | Number of Questions asked | Difficulty Level /Good Attempts) |
| Teaching Aptitude | 5-6 | Easy to Moderate |
| Research Aptitude | 6-7 | Moderate |
| Reading Comprehension | 5 | Easy to Moderate |
| Communication | 3 to 4 | Easy to Moderate |
| Maths | 4 to 5 | Moderate |
| Logical Reasoning | 5 to 6 | Moderate |
| Data Interpretation | 5 | Moderate to tough |
| Information & Communication Technology (ICT) | 4 to 5 | Moderate |
| People & Environment | 3 to 4 | Moderate |
| Higher Education System: Governance, Polity & Administration & Current Affairs | 4 to 5 | Moderate to Difficult |
UGC NET 16 June 2023 Question Paper & Exam analysis
| UGC NET Paper-1: June 16, 2023 (Shift-1 ) | ||
| Category | Number of Questions asked | Difficulty Level /Good Attempts) |
| Teaching Aptitude | 5-6 | Easy to Moderate |
| Research Aptitude | 6-7 | Moderate |
| Reading Comprehension | 5 | Easy to Moderate |
| Communication | 3 to 4 | Easy to Moderate |
| Maths | 4 to 5 | Moderate |
| Logical Reasoning | 5 to 6 | Moderate |
| Data Interpretation | 5 | Moderate to tough |
| Information & Communication Technology (ICT) | 4 to 5 | Moderate |
| People & Environment | 3 to 4 | Moderate |
| Higher Education System: Governance, Polity & Administration & Current Affairs | 4 to 5 | Moderate to Difficult |
Sunandani Chawariya, [16-06-2023 12:24]
Ma’am RRR
Recycle Resume Reduce
What is RRR in environment?
Reduce, Reuse, Recycle.
What is the 3R formula?
The 3Rs are used to refer to the three terms that are – Reduce, Reuse and Recycle. While recycling is easily using the material again, once it is finished, reusing is discovering a new, alternate way to utilize the trash instead of discarding it.
3R फॉर्मूला क्या है?
3Rs का उपयोग तीन शब्दों को संदर्भित करने के लिए किया जाता है – कम करें, पुन: उपयोग करें और रीसायकल करें। जबकि पुनर्चक्रण आसानी से सामग्री का फिर से उपयोग कर रहा है, एक बार जब यह समाप्त हो जाता है, तो पुन: उपयोग करना कचरे को हटाने के बजाय उसका उपयोग करने का एक नया, वैकल्पिक तरीका खोज रहा है।
Sunandani Chawariya, [16-06-2023 12:25]
Rubrics in Evaluation
What is a rubric in evaluation?
Assessment & Evaluation. A rubric is a type of scoring guide that assesses and articulates specific components and expectations for an assignment. Rubrics can be used for a variety of assignments: research papers, group projects, portfolios, and presentations.
मूल्यांकन में रूब्रिक क्या है?
आंकलन मूल्यांकन। एक रूब्रिक एक प्रकार की स्कोरिंग गाइड है जो एक असाइनमेंट के लिए विशिष्ट घटकों और अपेक्षाओं का आकलन और स्पष्ट करता है । रूब्रिक का उपयोग विभिन्न कार्यों के लिए किया जा सकता है: शोध पत्र, समूह परियोजनाएं, पोर्टफोलियो और प्रस्तुतियां।
Sunandani Chawariya, [16-06-2023 12:25]
On 210
Off 340 h toh set ky hoga
Sunandani Chawariya, [16-06-2023 12:26]
Uniyam sankendran
Madhuri, [16-06-2023 12:26]
Di percentage and ratio se related tha , comprehension easy tha, EVS me photochemical smog,green house pe statement based questions tha, eutrophication se related question tha
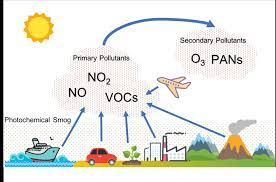
Photochemical smog is a resultant of the reaction among
- NO2, O3 and peroxyacetyl nitrate in the presence of sunlight
- CO, O2 and peroxyacetyl nitrate in the presence of sunlight
- CO, CO2 and NO2 at low temperature
- high concentration of NO2, O3 and CO in the evening
फोटोकेमिकल स्मॉग के बीच की प्रतिक्रिया का परिणाम है
- सूर्य के प्रकाश की उपस्थिति में NO2 , O3 और पेरोक्सीएसीटाइल नाइट्रेट
- सूर्य के प्रकाश की उपस्थिति में CO, O2 और पेरोक्सीएसीटाइल नाइट्रेट
- कम तापमान पर CO, CO 2 और NO 2
- शाम को NO2, O3 और CO की उच्च सांद्रता
विकल्प 1: सूर्य के प्रकाश की उपस्थिति में NO2 , O3 और पेरोक्सीएसीटाइल नाइट्रेट
सूर्य के प्रकाश की उपस्थिति में सही उत्तर NO2 , O3 और पेरोक्सीएसीटाइल नाइट्रेट है ।
प्रमुख बिंदु
- स्मॉग एक द्वितीयक प्रदूषक है, जो स्मोक और फॉग से बना है।
- परंपरागत रूप से, स्मॉग धुएं और सल्फर डाइऑक्साइड के मिश्रण के कारण एक क्षेत्र में बड़ी मात्रा में कोयले के जलने से उत्पन्न हुआ है ।
- आजकल, वाहन उत्सर्जन और औद्योगिक उत्सर्जन जो सूरज से पराबैंगनी प्रकाश द्वारा वायुमंडल में द्वितीयक प्रदूषक बनाने के लिए कार्य किया जाता है जो प्राथमिक उत्सर्जन के साथ मिलकर फोटोकैमिकल स्मॉग बनाते हैं।
- फोटोकैमिकल स्मॉग में प्रमुख रासायनिक प्रदूषक NO, NO2 , वाष्पशील कार्बनिक यौगिक, ओजोन और PAN (पेरोक्सीसेटाइल नाइट्रेट) हैं ।
- NO2 पीले रंग के कारण दृश्यता कम कर देता है ।
- अतः विकल्प 1 सही है।
।अतिरिक्त जानकारी
- स्टेट ऑफ़ ग्लोबल एयर 2020 रिपोर्ट:
- इसके अनुसार, भारत ने दुनिया में सबसे अधिक प्रति व्यक्ति प्रदूषण जोखिम (83.2 μg/घन मीटर) का सामना किया।
- 2019 में, गंभीर वायु प्रदूषण के संपर्क में आने के कारण जन्म के एक महीने के भीतर भारत में 116,000 से अधिक शिशुओं की मृत्यु हो गई।
- रिपोर्ट यह भी बताती है कि गर्भावस्था के दौरान प्रदूषित हवा के संपर्क में आने से कम वजन और समय से पहले जन्म होता है।
- इसके अलावा, यह नोट किया गया कि 2019 में भारत में बाहरी और घरेलू वायु प्रदूषण के लंबे समय तक संपर्क में रहने से स्ट्रोक, दिल का दौरा, मधुमेह, फेफड़ों के कैंसर, पुरानी फेफड़ों की बीमारियों और नवजात रोगों से 1.67 मिलियन से अधिक वार्षिक मौतें हुईं।
- इसके अनुसार, भारत ने दुनिया में सबसे अधिक प्रति व्यक्ति प्रदूषण जोखिम (83.2 μg/घन मीटर) का सामना किया।
- प्रदूषकों का स्वास्थ्य पर प्रभाव
- सार्वजनिक स्वास्थ्य चिंता के सबसे मजबूत सबूत वाले प्रदूषकों में पार्टिकुलेट मैटर (PM), ओजोन (O3 ) , नाइट्रोजन डाइऑक्साइड (NO2 ) और सल्फर डाइऑक्साइड (SO2 ) शामिल हैं।
- ये प्रदूषक फेफड़े के मार्ग में गहराई तक प्रवेश करने और रक्तप्रवाह में प्रवेश करने में सक्षम होते हैं, जिससे कार्डियोवैस्कुलर, सेरेब्रोवास्कुलर और श्वसन प्रभाव होते हैं।
Option 1 : NO2, O3 and peroxyacetyl nitrate in the presence of sunlight
The correct answer is NO2, O3, and peroxyacetyl nitrate in the presence of sunlight.
Key Points
- Smog is a secondary pollutant, which has made up of Smoke and Fog.
- Traditionally, the smog has resulted from large amounts of coal burning in an area caused by a mixture of smoke and sulfur dioxide.
- Nowadays, the Vehicle emissions and Industrial emissions that are acted on in the atmosphere by ultraviolet light from the sun to form secondary pollutants that also combine with the primary emissions to form photochemical smog.
- The major chemical pollutants in Photochemical smog are NO, NO2, volatile organic compounds, Ozone, and PAN (Peroxyacetyl Nitrate).
- NO2 decreases visibility due to yellowish colour.
- Hence option 1 is correct.
Additional Information
- State of Global Air 2020 Report:
- According to it, India faced the highest per capita pollution exposure (83.2 μg/cubic metres) in the world.
- In 2019, over 116,000 infants in India died within a month after birth due to exposure to severe air pollution.
- The report also suggests exposure to polluted air during pregnancy is linked to low weight and premature birth.
- Further, it noted that long-term exposure to outdoor and household air pollution contributed to over 1.67 million annual deaths from stroke, heart attack, diabetes, lung cancer, chronic lung diseases, and neonatal diseases in India in 2019.
- According to it, India faced the highest per capita pollution exposure (83.2 μg/cubic metres) in the world.
- Pollutants Causing Effect on Health
- Pollutants with the strongest evidence for public health concern include particulate matter (PM), Ozone (O3), Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and Sulphur dioxide (SO2).
- These pollutants are capable of penetrating deep into lung passageways and entering the bloodstream causing cardiovascular, cerebrovascular and respiratory impacts.
Sunandani Chawariya, [16-06-2023 12:27]
Di percentage nd ratio
evs h bht sare the green house
- Greenhouse gases are gases that absorb and emit radiant energy within the thermal infrared range causing the greenhouse effect.
- The following are the primary greenhouse gases in the earth atmosphere:
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
- Methane (CH4)
- Nitrous Oxide (N2O)
- Ozone (O3).
- The greenhouse gases are also present in the atmosphere of Venus, Mars, and Titan (satellite of Saturn).
- The major non-greenhouse gases present in the earth’s atmosphere are Nitrogen (78%), Oxygen (21%), and Argon (0.9%).
- The greenhouse gas Carbon dioxide is present in the atmosphere is very high quantities.
- When fossil fuels are burned the number of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere increases.
- Chlorofluorocarbon is the most potent Greenhouse Gas in terms of efficiency.
- Life on the earth is possible only because of the Greenhouse effect.
- The greenhouse effect is the natural process that helps in maintaining the earth’s temperature.
- The more is the emission of greenhouse gases, the more is the temperature of the earth’s atmosphere.
- ग्रीनहाउस गैसें ऐसी गैसें हैं जो थर्मल इन्फ्रारेड रेंज के भीतर विकिरण ऊर्जा को अवशोषित और उत्सर्जित करती हैं जिससे ग्रीनहाउस प्रभाव पैदा होता है ।
- पृथ्वी के वायुमंडल में प्राथमिक ग्रीनहाउस गैसें निम्नलिखित हैं:
- कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड (सीओ 2 )
- मीथेन (सीएच 4 )
- नाइट्रस ऑक्साइड ( N2O )
- ओजोन (ओ 3 ) ।
- शुक्र, मंगल और टाइटन (शनि के उपग्रह) के वातावरण में भी ग्रीनहाउस गैसें मौजूद हैं ।
- पृथ्वी के वायुमंडल में मौजूद प्रमुख गैर–ग्रीनहाउस गैसें नाइट्रोजन (78%), ऑक्सीजन (21%), और आर्गन (0.9%) हैं ।
- वातावरण में मौजूद ग्रीनहाउस गैस कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड बहुत अधिक मात्रा में है ।
- जब जीवाश्म ईंधन जलाया जाता है तो वातावरण में ग्रीनहाउस गैसों की संख्या बढ़ जाती है ।
- दक्षता के मामले में क्लोरोफ्लोरोकार्बन सबसे शक्तिशाली ग्रीनहाउस गैस है ।
- पृथ्वी पर जीवन ग्रीनहाउस प्रभाव के कारण ही संभव है।
- ग्रीनहाउस प्रभाव प्राकृतिक प्रक्रिया है जो पृथ्वी के तापमान को बनाए रखने में मदद करती है ।
- ग्रीनहाउस गैसों का उत्सर्जन जितना अधिक होगा, पृथ्वी के वायुमंडल का तापमान उतना ही अधिक होगा ।
Sunandani Chawariya, [16-06-2023 12:28]
Baki yaad aayege toh bataungi
Madhuri, [16-06-2023 12:29]
Square of opposition se 2 se 3 question tha,
Bihar me kon sa ancient University h ye pucha tha,
What is the name of ancient university in Bihar?
Ancient alanda University
Nalanda is an ancient center of higher learning in Bihar, India from 427 to 1197. Nalanda was established in the 5th century AD in Bihar, India.
बिहार के प्राचीन विश्वविद्यालय का क्या नाम है ?
नालंदा बिहार, भारत में 427 से 1197 तक उच्च शिक्षा का एक प्राचीन केंद्र है। नालंदा की स्थापना 5 वीं शताब्दी ईस्वी में बिहार, भारत में हुई थी।
1857 kon si University bni thi jese Calcutta, Bombay and madras
Who established new universities in Calcutta Bombay and Madras in 1857?
The Universities of Calcutta, Bombay and Madras were established by Sir Charles Wood’s Despatch in the year 1857. He had an excellent impact on disseminating education in India
1857 में कलकत्ता बॉम्बे और मद्रास में नए विश्वविद्यालयों की स्थापना किसने की?
कलकत्ता, बॉम्बे और मद्रास विश्वविद्यालयों की स्थापना सर चार्ल्स वुड के डिस्पैच द्वारा वर्ष 1857 में की गई थी। भारत में शिक्षा के प्रसार पर उनका उत्कृष्ट प्रभाव था।
HARSHITA RATHORE, [16-06-2023 12:32]
Comprehension kis topic p tha do uh remember
Madhuri, [16-06-2023 12:32]
Industrial revolution ka impact
Madhuri, [16-06-2023 12:34]
Ma’am ne Jo bhi pyq solve krwa rkha usko ache practice kr lo direct indirect question
wahi se bn rha h
Madhuri, [16-06-2023 12:35]
ICT se approx 2 question
ssh80 HUS, [16-06-2023 12:37]
Sdg aur Mdg se question aaye the ya nhi
Madhuri, [16-06-2023 12:37]
No
ssh80 HUS, [16-06-2023 12:38]
Indian fallacy se
Madhuri, [16-06-2023 12:40]
Nyaya aur Aristotle statement form me question tha.. nyaya is only inductive and material 2nd statement tha Aristotle se deductive only
Is the Nyaya syllogism deductive or inductive?
deductive-inductive
the Nyaya syllogism is deductive-inductive and formal-material. the Nyaya syllogism recognizes the fact that verbal form is not the essence of inference and is required only to convince others.
न्यायवाक्य निगमनात्मक है या आगमनात्मक?
निगमनात्मक प्रेरक
न्याय न्यायवाक्य निगमनात्मक-आगमनात्मक और औपचारिक-सामग्री है। न्याय न्यायवाक्य इस तथ्य को स्वीकार करता है कि मौखिक रूप अनुमान का सार नहीं है और केवल दूसरों को समझाने के लिए आवश्यक है।
Is Aristotle’s syllogism deductive or inductive?
Aristotle focused much of his work in logic on a particular type of deductive argument called the syllogism, which is defined in terms of a certain structure. Aristotle syllogism consists of three successive assertions; the first two are the premises, and the third is the conclusion.
अरस्तू का न्यायवाक्य निगमनात्मक है या आगमनात्मक?
अरस्तू ने तर्कशास्त्र में अपने अधिकांश कार्य को एक विशेष प्रकार के निगमनात्मक तर्क पर केंद्रित किया जिसे न्यायवाक्य कहा जाता है, जिसे एक निश्चित संरचना के संदर्भ में परिभाषित किया गया है। अरस्तू के न्यायवाक्य में लगातार तीन अभिकथन होते हैं; पहले दो परिसर हैं, और तीसरा निष्कर्ष है।
Madhuri, [16-06-2023 12:42]
1992 education se ekk question tha 4 statement the elimination se solve ho jata
What was the 1992 education policy?
The main objective of the National Policy of Education of 1986 and Programme of Action, 1992 was to establish a national system of education that implies that all students irrespective of caste, creed, sex, and religion have access to education of comparable quality. Special emphasis was given to women’s education.
1992 की शिक्षा नीति क्या थी?
1986 की शिक्षा की राष्ट्रीय नीति और 1992 की कार्य योजना का मुख्य उद्देश्य शिक्षा की एक राष्ट्रीय प्रणाली स्थापित करना था जिसका अर्थ है कि जाति, पंथ, लिंग और धर्म के बावजूद सभी छात्रों को तुलनीय गुणवत्ता की शिक्षा तक पहुंच प्राप्त है। स्त्री शिक्षा पर विशेष बल दिया गया।
Madhuri, [16-06-2023 12:43]
Independent India ki first education commission ya policy
Which was the first education commission set up after independence?
The Union government established the University Education Commission (1948–1949), the Secondary Education Commission (1952–1953), University Grants Commission and the Kothari Commission (1964–66) to develop proposals to modernise India’s education system.
स्वतंत्रता के बाद स्थापित पहला शिक्षा आयोग कौन सा था?
केंद्र सरकार ने भारत की शिक्षा प्रणाली को आधुनिक बनाने के प्रस्तावों को विकसित करने के लिए विश्वविद्यालय शिक्षा आयोग (1948-1949), माध्यमिक शिक्षा आयोग (1952-1953), विश्वविद्यालय अनुदान आयोग और कोठारी आयोग (1964-66) की स्थापना की।
Madhuri, [16-06-2023 12:44]
Panini se matching me question tha
ssh80 HUS, [16-06-2023 12:45]
Book thi ya university se maching tha
Madhuri, [16-06-2023 12:47]
Kis field se related h ekk Panini,bartihari, baratha sb ka pucha tha
Madhuri, [16-06-2023 12:56]
Research se internal and external validity se tha
Internal validity examines whether the study design, conduct, and analysis answer the research questions without bias. External validity examines whether the study findings can be generalized to other contexts.
आंतरिक वैधता इस बात की जांच करती है कि क्या अध्ययन डिजाइन, आचरण और विश्लेषण बिना किसी पूर्वाग्रह के अनुसंधान प्रश्नों का उत्तर देते हैं। बाहरी वैधता जांच करती है कि क्या अध्ययन के निष्कर्षों को अन्य संदर्भों में सामान्यीकृत किया जा सकता है।
B2 ::::::, [16-06-2023 12:57]
ON -210 ,OFF-540,SET?
Adii, [16-06-2023 12:58]
Malware, education commission, indian logic se tha questions
Ashu, [16-06-2023 12:59]
Ancient University se
Sunandani Chawariya, [16-06-2023 13:00]
Freeware se tha ma’am ek question
Adii, [16-06-2023 13:01]
Experimental research, judgemental research se tha questions
Vîháàñ Yâdūvãñßhî, [16-06-2023 13:02]
1900 tha ma’am
M H, [16-06-2023 13:03]
Mam air pollution k bare me bhi aaya tha
NTA-UGC NET /JRF Paper-1 Preparation ���������, [16-06-2023 13:06]
Ok on = 15×14=210
NTA-UGC NET /JRF Paper-1 Preparation ���������, [16-06-2023 13:06]
Off =6×6×15
Madhuri, [16-06-2023 13:06]
Also Check –Ugc Net 13 June 2023 Question Paper & Exam Analysis
Other name of judgemental research??
NTA-UGC NET /JRF Paper-1 Preparation ���������, [16-06-2023 13:06]
=540
Madhuri, [16-06-2023 13:07]
Plagiarism if 42% hoga to konsa level hoga?
HARSHITA RATHORE, [16-06-2023 13:07]
No purposive sampling
NTA-UGC NET /JRF Paper-1 Preparation ���������, [16-06-2023 13:08]
Purposive sampling✅
HARSHITA RATHORE, [16-06-2023 13:09]
3rd level 40 – 60 % of plagiarism
nincompoop, [16-06-2023 13:13]
Red ka code diya tha or blue ka bhi Diya tha shyd
Black ka code pucha tha
Kal wale me
Sunandani Chawariya, [16-06-2023 13:14]
Or ma’am channel aaye the matching me chnl no 4 5 6 7 matching me aaye the
ssh80 HUS, [16-06-2023 13:15]
Binary and decimal hexa decimal and octal se bhi aaya tha kya
Mind Mapping
M.J Thakor, [16-06-2023 13:22]
1,6,14,40,108,296,808
Madhuri, [16-06-2023 13:28]
Mind map ka importance kya h ye bhi statement k form me question pucha tha
ssh80 HUS, [16-06-2023 13:28]
2208 ans h
Sunandani Chawariya, [16-06-2023 13:44]
Mind mapping ka question tha
Sunandani Chawariya, [16-06-2023 13:45]
Wed page pr tha question or fare ware ka tha
Kk Inderk, [16-06-2023 13:51]
5.5,11,18.5, 3o,49.5, 8o…eh v sum tha
���Anshu Chaudhary Indian army ���, [16-06-2023 13:52]
152.5
Kk Inderk, [16-06-2023 13:53]
152.5
Kk Inderk, [16-06-2023 13:55]
Red=360..black=796..blue=
Kk Inderk, [16-06-2023 13:56]
Sry black 792
@nkit m@ury@ ❤, [16-06-2023 13:58]
Ye reasoning hai
| UGC NET June 16 Question Paper Analysis 2023 Shift 1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Particulars | Paper 1 | Paper 2 (History) | Paper 2 (Management) |
| Overall Difficulty | Easy to Moderate | ||
| Paper Difficulty | Easy to Moderate | Easy to Moderate | Moderate |
| Important Topics | Environmental Soil Pollutants Greenhouse gases Global WarmingLogical ReasoningWestern LogicResearch AptitudePlagirism Act, 2016 Sampling Method (Judgemental Sampling) HypothesisData InterpretationPercentage RatioHigher EducationSwayam Prabha Channels Ancient University NEP changes in 1990 CommissionsICTMalware Web Browser | Ancient IndiaMegolithic Kanishka Inscription Temples Chronology Post Gupta Dynasties Chalukyas Ancient Ports Buddhist Philosophy Sakha Philosophy Rig Vedic Period Gupta Period Port Locations Ancient Philosophy Grihasutras Archeology DatingMedieval IndiaVijayangar Sher Shah Dahasala Akbar City of Mughal Jahangir and Shah Jahan Early Medieval Dynasty Razia Bahaman Capital Transfer Alberune Dynasties of kashmir Passage of Sikh Nathumanin Passage on conflict between Pallavas and ChalukyasModern IndianPre congress association B R Ambedkar Consistutional Assembly Subhas Chandra Bose and INA Films Newspapers Bal Gangadhar Tilak National Movements Chronology Kuka Movement Mahendra Lal Government 1857 revolt Marathas and East India Company Anglo Afghan – Burma War Gandhi Vivekanand | Organisational Structure Organisational Design Micro Economics Production National Income Ethics Mangement theories GDP & Unemployment curve Workforce diversity Hoftead Framework Motivation theory StressEmployee involvement EPRG framework Human Resource development Staffing Job Evaluation Appraisal Technology Extramural Act IHRMNPV IRR Accounting Standards Break Even Ratio PV ratio Contribution FormulaGreenmail Cap budgeting ARR Walter’s Model EPS ROEVIRO (Internal Analysis) Marketing Research Techniques 7S Framework RetrenchmentPassage on Blue Ocean Stratergy Consumer Buying Behaviour Nicosia Model IMC Brand Equity CRMPassage on ERP GANTT chart Kaizen Type 2 error Line balancingLientoff Paradox BOP SCHEMA in RCBMS IMF AIRural Enterprises Innovation Udyami Yojana Women Entrepreneurship SIDBI |
UGC NET Paper I Exam Analysis Overall Shift 1 & 2
Here is a detailed analysis of the UGC NET Paper 1 Exam Analysis 2023 . Candidates will find all the topics asked in the question paper along with the number of questions asked from each section and their difficulty level. Overall, the difficulty level of the question paper was easy to moderate.
| UGC NET Paper I Exam Analysis Overall | ||
| Subjects | Level | Number of Questions |
| Teaching Aptitude | Easy-Moderate | 5 |
| Research Aptitude | Easy-Moderate | 7-8 |
| Comprehension | Moderate | 5 |
| Logical Reasoning | Moderate | 5-6 |
| Data Interpretation | Easy-Moderate | 4-5 |
| Maths | Moderate | 5 |
| Communication | Easy-Moderate | 7 |
| Environment | Easy-Moderate | 8 |
| People & Development | Easy-Moderate | 2-3 |
| Higher Education | Easy-Moderate | 3 |
| Information Technology | Easy-Moderate | 5 |
| Total | Easy-Moderate | 35-40 |
UGC NET 2023 Paper Analysis has been mentioned in below article subject wise. UGC NET paper I will include 11 sections which include Teaching Aptitude, Research Aptitude, Comprehension, Logical Reasoning, Data Interpretation, Maths, Communication, Environment, People & Development, Higher Education and Information Technology. UGC NET 2023 Paper Analysis for Shift 1 and Shift 2 topic wise and asked question has been mentioned below.
| Subjects | UGC NET Paper 1 | |
| Teaching Aptitude | Learner Characteristic, Levels of Teaching, Teaching Skills, NEP Changes, Cognitive Theory | |
| Research Aptitude | Plagiarism Act, Sampling Method, research methodology, Steps of Hypothesis, you shouldn’t speak in favour when you eat meat. identify the fallacy, Null Hypothesis, | |
| Comprehension | Unseen passage on Environment Issue | |
| Logical Reasoning | Western Logic, Informal Fallacies, Argument Based Questions, Directions, Coding Decoding, Immediate Interference, Syllogism, inductive and deductive, Opposition | |
| Data Interpretation | Data comparison between two Data | |
| Maths | find distance, Number series, Time and work | |
| Communication | Mass Media, Media Tools | |
| People & Development, Environment | air pollution, Green House Gas, Global Warming, Soil, Uranium, Smog | |
| Higher Education | Universities in bihar, 1999 what changes happened in NEP, Dispatch Bill, Swayam Prabha Channel, Ancient University, education commission after independence, Kothari Commission | |
| Information Technology | Malware, Virus, Number System Conversion, Web Browser, Search engine, equation question, L+M=N , find value of m when L and n was given in binary, chatbox cookies |
Sonam,
Ict me se www pucha gya tha
Communication
Green house gas
2nd paper bhut Hard tha
A,B,C,D की उम्र 45 hai or ABCDE ki 48 hai to E ki age kitni hogi
Jeetu HR Dahiya,
4*45=180
5*48=240
240-180=60 ans.
HARSHITA RATHORE,
Fallacy se question tha
VOC se question tha
CFC se question tha
Ma’am research se scales p Aaya survay p Aaya plagiarism p Aaya
Teaching se colleborative learning p Aaya
मनोवैज्ञानिक सर्वे पूछा था
मनोवैज्ञानिक सर्वेक्षण क्या है?
जैसा कि नाम से पता चलता है, मनोविज्ञान सर्वेक्षण उत्तरदाताओं से उनकी विचार प्रक्रियाओं और मानसिक स्थिति को समझने के लिए पूछे गए प्रश्नों की एक श्रृंखला है। मनोवैज्ञानिक सर्वेक्षण उत्तरदाताओं में विभिन्न लक्षणों, व्यवहारों और स्थितियों को सामने लाते हैं जो उनके कार्यों को सबसे अधिक प्रभावित कर सकते हैं।
What is a psychological survey?
As the name suggests, psychology surveys are a series of questions asked to the respondents in order to understand their thought processes and mental state. Psychological surveys bring out the various traits, behaviors, and conditions in respondents that can affect their actions the most.
सर्वेक्षण करने के 7 चरण क्या हैं?
वांछित परिणाम लाने वाले सर्वेक्षण के संचालन के 7 चरण
- अपने लक्षित दर्शकों की पहचान करें। …
- सर्वेक्षण प्रश्नों पर निर्णय लें। …
- अपने सर्वेक्षण में प्रश्न शाखाओं को जोड़ें। …
- सर्वेक्षण करने के लिए सही समय चुनने के लिए ट्रिगर सेट करें। …
- सर्वेक्षण डिजाइन चुनें और सर्वेक्षण को परिनियोजित करें। …
- परिणामों का विश्लेषण करें। …
- कार्रवाई करें।
What are the 7 steps to conduct a survey?
7 Steps to Conduct a Survey That Brings Desired Results
- Identify Your Target Audience. …
- Decide on the Survey Questions. …
- Add Question Branching to Your Survey. …
- Set Triggers to Pick the Right Moment to Conduct the Survey. …
- Choose the Survey Design and Deploy the Survey. …
- Analyze the Results. …
- Take Actions.
Income expenditure profit% ke base per thi
Calulative tha lekin saare question ke answer aa ja rahe the
Number Series -5 7 9 11
Factors affecting Learning
Which of the following is teacher related factor affecting learning?
- Maturation & Motivation
- The socio-emotional climate of the class
- Structure of the discipline
- Leadership style of teacher
निम्नलिखित में से कौन-सा शिक्षक से संबंधित अधिगम को प्रभावित करने वाला कारक है?
- परिपक्वता और प्रेरणा
- कक्षा का सामाजिक-भावनात्मक वातावरण
- अनुशासन की संरचना
- शिक्षक की नेतृत्व शैली
Option 4 : शिक्षक की नेतृत्व शैली
सीखना एक प्रक्रिया है जिसके द्वारा व्यवहार को या तो संशोधित किया जाता है या अनुभव या प्रशिक्षण के माध्यम से बदला जाता है। इस प्रकार सीखना प्रतिक्रिया क्षमता में अपेक्षाकृत स्थायी परिवर्तन है जो प्रबलित अभ्यास के कार्य के रूप में होता है।
प्रमुख बिंदु
सीखने को प्रभावित करने वाले शिक्षक संबंधी कारक:
- विषय वस्तु पर शिक्षक का ज्ञान : जो शिक्षक अपने विषय ज्ञान में दृढ़ता से निहित हैं वे स्पष्ट प्रस्तुतीकरण करते हैं और छात्रों की कठिनाइयों को आसानी से पहचानते हैं। उसे अनुप्रयोग-उन्मुख शिक्षण भी करने में सक्षम होना चाहिए।
- शिक्षक द्वारा अपनाई गई नेतृत्व शैली चाहे वह अधिनायकवादी, लोकतांत्रिक, परोपकारी, या उदासीन हो, बहुत प्रभावित करती है कि छात्र कैसे प्रतिक्रिया देंगे और खुद को सीखने के कार्यों में शामिल करेंगे।
- शिक्षकों का अपने छात्रों के साथ जो संबंध होता है, वह कक्षा के स्वर और वातावरण को भी निर्धारित करता है।
- शिक्षकों द्वारा मौखिक या लिखित रूप में की जाने वाली मूल्यांकनात्मक टिप्पणियों का भी विद्यार्थियों के अधिगम पर बहुत प्रभाव पड़ता है। उनके पास प्रेरित करने और प्रोत्साहित करने या दबाने और हतोत्साहित करने की शक्ति है।
- उम्मीदों के अलावा, शिक्षकों से जुड़ी कई अन्य विशेषताएँ हैं जो उनके शिक्षार्थियों और सीखने-सिखाने की प्रक्रिया को प्रभावित करती हैं। इनमें से सबसे महत्वपूर्ण मॉडलिंग, उत्साह, देखभाल और सकारात्मक अपेक्षाएं हैं ।
- अनुसंधान इंगित करता है कि शिक्षक जो जानकारी को उत्साहपूर्वक प्रस्तुत करते हैं , शिक्षार्थियों की आत्म-प्रभावकारिता, प्रयास और क्षमता के गुण, आत्मविश्वास और उपलब्धि को बढ़ाते हैं।
- एक शिक्षक का देखभाल करने वाला रवैया और वह इसे कैसे संप्रेषित करता है, यह एक अन्य महत्वपूर्ण कारक है, देखभाल एक शिक्षक की अपने शिक्षार्थियों के संरक्षण और विकास पर जोर देने और निवेश करने की क्षमता को संदर्भित करता है।
अतिरिक्त जानकारी
- शिक्षार्थी संबंधित :
- परिपक्वता (सीखने की तैयारी)
- प्रेरणा
- स्व अवधारणा
- लक्ष्य
- शिक्षक संबंधी
- शिक्षक का व्यक्तित्व
- विषय-वस्तु पर महारत
- संचार
- शिक्षक की नेतृत्व शैली
- शिक्षार्थियों के साथ शिक्षक के पारस्परिक संबंध।
- शिक्षण शैलियों
- कार्य संबंधी
- विधियों का प्रयोग किया
- कार्य की प्रकृति
- शिक्षण सहायक सामग्री का प्रयोग किया
- अनुशासन की संरचना
- पर्यावरण संबंधी
- भौतिक वातावरण (जलवायु/आराम)
- कक्षा का सामाजिक-भावनात्मक वातावरण
संकेत देना
- बैठने की उचित व्यवस्था, शिक्षण-अधिगम संसाधनों की उपलब्धता, विषयवस्तु की प्रकृति या सीखने के अनुभव कक्षा से संबंधित कारक हैं जो सीखने को प्रभावित करते हैं।
Option 4 : Leadership style of teacher
Learning is a process by which behaviour is either modified or changed through experience or training. Learning is thus a relatively permanent change in response potentiality which occurs as a function of reinforced practice.
Key Points
Teacher-related factors affecting learning:
- Teacher’s Knowledge over the subject matter: Teachers who are firmly rooted in their subject knowledge make clearer presentations and recognize students’ difficulties readily. He/she should be able to undertake application-oriented teaching as well.
- The leadership style adopted by the teacher in terms of whether it is authoritarian, democratic, benevolent, or indifferent greatly influences how the students will respond and involve themselves in the learning tasks.
- The relationship which teachers have with their students also sets the tone and climate of the classroom.
- The evaluative comments that teachers make either verbally or in writing also have a great bearing on students learning. They have the power to motivate and encourage or stifle and discourage.
- Apart from expectations, there are many other characteristics related to teachers that influence their learners and the teaching-learning process. The most significant among these are modeling, enthusiasm, caring, and positive expectations.
- Research indicates that teachers who present information enthusiastically, increase learners’ self-efficacy, attributions of effort and ability, self-confidence, and achievement.
- The caring attitude of a teacher and how he/she communicates it is another important factor, Caring refers to a teacher’s ability to emphasize and invest in the protection and development of her learners.
Additional Information
- Learner related:
- Maturation (Readiness to learn)
- Motivation
- Self-concept
- Goals
- Teacher Related
- Teacher’s Personality
- Mastery over the subject-matter
- Communication
- Leadership style of teacher
- Interpersonal relationships of the teacher with the learners.
- Teaching styles
- Task Related
- Methods used
- Nature of Task
- Teaching aids used
- Structure of the discipline
- Environment Related
- Physical environment (climate/comfort)
- The socio-emotional climate of the class
Hint
- Proper seating arrangement, Availability of teaching-learning resources, Nature of the content or learning experiences are the classroom related factors affecting learning.
From the above, we can conclude that mastery over the subject-matter is a teacher-related factor affecting learning.
Hypothesis Testing
परिकल्पना परीक्षण की प्रक्रिया इस प्रकार है:
- सेटअप नल और वैकल्पिक परिकल्पना
- महत्व स्तर का चयन करें
- टेस्ट सांख्यिकी का चयन करें
- निर्णय नियम स्थापित करें
- प्रदर्शन संगणना
- परिणाम निकालना
Process of Hypothesis Testing are as follows:
- Setup Null and Alternate Hypothesis
- Select the Significance Level
- Select Test Statistics
- Establish the Decision Rule
- Performance Computations
- Draw Conclusions
फिट की अच्छाई:
- फिट टेस्ट की अच्छाई एक सांख्यिकीय परिकल्पना परीक्षण है , यह देखने के लिए कि नमूना डेटा सामान्य वितरण के साथ आबादी से वितरण के लिए कितनी अच्छी तरह फिट बैठता है ।
- अलग तरीके से कहें तो, यह परीक्षण दिखाता है कि क्या आपका नमूना डेटा उस डेटा का प्रतिनिधित्व करता है जिसे आप वास्तविक जनसंख्या में खोजने की उम्मीद करेंगे या यदि यह किसी तरह तिरछा है।
- गुडनेस-ऑफ़-फिट देखे गए मूल्यों और सामान्य वितरण मामले में मॉडल से अपेक्षित मूल्यों के बीच विसंगति को स्थापित करता है ।
- अच्छाई का निर्धारण करने के लिए कई तरीके हैं। आँकड़ों में उपयोग की जाने वाली कुछ सबसे लोकप्रिय विधियों में ची–स्क्वायर, कोलमोगोरोव–स्मिर्नोव परीक्षण, एंडरसन–डार्लिंग परीक्षण और शापिरो–विल्क परीक्षण शामिल हैं।
- अच्छाई-की-फिट परीक्षण अक्सर व्यावसायिक निर्णय लेने में उपयोग किए जाते हैं। ची-स्क्वायर अच्छाई-की-फिट की गणना करने के लिए, पहले शून्य परिकल्पना और वैकल्पिक परिकल्पना को बताना आवश्यक है, एक महत्व स्तर चुनें (जैसे α = 0.5) और महत्वपूर्ण मान निर्धारित करें।
- सबसे आम अच्छाई–की–फिट परीक्षण ची–स्क्वायर परीक्षण है , आमतौर पर असतत वितरण के लिए उपयोग किया जाता है।
- ची-स्क्वायर परीक्षण विशेष रूप से कक्षाओं (डिब्बे) में डाले गए डेटा के लिए उपयोग किया जाता है, और सटीक परिणाम उत्पन्न करने के लिए पर्याप्त नमूना आकार की आवश्यकता होती है।
- गुडनेस-ऑफ-फिट टेस्ट आमतौर पर अवशिष्टों की सामान्यता के परीक्षण के लिए या यह निर्धारित करने के लिए उपयोग किया जाता है कि समान वितरण से दो नमूने एकत्र किए गए हैं या नहीं।
1. टी–टेस्ट :
- टी-परीक्षण आपको बताता है कि समूहों के बीच के अंतर कितने महत्वपूर्ण हैं; दूसरे शब्दों में, यह आपको बताता है कि क्या वे अंतर (माध्यमों में मापे गए) संयोग से हो सकते हैं।
- टी-टेस्ट सांख्यिकी में परिकल्पना परीक्षण के प्रयोजन के लिए उपयोग किए जाने वाले कई परीक्षणों में से एक है।
2. एफ टेस्ट :
- शोधकर्ता द्वारा एफ सांख्यिकी के आधार पर एफ-परीक्षण किया जाता है।
- एफ सांख्यिकी को दो स्वतंत्र ची–स्क्वायर चर के बीच के अनुपात के रूप में परिभाषित किया गया है जो उनकी स्वतंत्रता की संबंधित डिग्री से विभाजित हैं।
- F-परीक्षण स्नेडेकोर के F-वितरण का अनुसरण करता है। दो जनसंख्या प्रसरणों की समानता के लिए परीक्षण करने के लिए एक शोधकर्ता द्वारा एफ-परीक्षण का उपयोग किया जाता है।
- यदि एक शोधकर्ता यह परीक्षण करना चाहता है कि समान परिवर्तनशीलता वाली सामान्य जनसंख्या से दो स्वतंत्र नमूने लिए गए हैं या नहीं, तो वह आम तौर पर एफ-परीक्षण का उपयोग करता है।
- एफ-टेस्ट का उपयोग शोधकर्ता द्वारा यह निर्धारित करने के लिए भी किया जाता है कि जनसंख्या प्रसरण के दो स्वतंत्र अनुमान प्रकृति में सजातीय हैं या नहीं।
3. जेड टेस्ट :
- Z-परीक्षण एक प्रकार का परिकल्पना परीक्षण है—आपके लिए यह पता लगाने का एक तरीका है कि किसी परीक्षण के परिणाम मान्य हैं या दोहराए जा सकते हैं।
- उदाहरण के लिए, अगर किसी ने कहा कि उन्हें कैंसर का इलाज करने वाली एक नई दवा मिल गई है, तो आप यह सुनिश्चित करना चाहेंगे कि यह शायद सच है।
- एक परिकल्पना परीक्षण आपको बताएगा कि क्या यह शायद सच है, या शायद सच नहीं है। AZ परीक्षण का उपयोग तब किया जाता है जब आपका डेटा लगभग सामान्य रूप से वितरित होता है (अर्थात जब आप इसे ग्राफ़ करते हैं तो डेटा में बेल कर्व का आकार होता है)।
The goodness of fit:
- The goodness of fit test is a statistical hypothesis test to see how well sample data fit a distribution from a population with a normal distribution.
- Put differently, this test shows if your sample data represents the data you would expect to find in the actual population or if it is somehow skewed.
- Goodness-of-fit establishes the discrepancy between the observed values and those that would be expected of the model in a normal distribution case.
- There are multiple methods for determining goodness-of-fit. Some of the most popular methods used in statistics include the chi-square, the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test, the Anderson-Darling test, and the Shapiro-Wilk test.
- Goodness-of-fit tests are often used in business decision making. In order to calculate a chi-square goodness-of-fit, it is necessary to first state the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis, choose a significance level (such as α = 0.5) and determine the critical value.
- The most common goodness-of-fit test is the chi-square test, typically used for discrete distributions.
- The chi-square test is used exclusively for data put into classes (bins), and it requires a sufficient sample size in order to produce accurate results.
- Goodness-of-fit tests are commonly used to test for the normality of residuals or to determine whether two samples are gathered from identical distributions.
1. T-Test:
- The t-test tells you how significant the differences between groups are; In other words it lets you know if those differences (measured in means) could have happened by chance.
- The t-test is one of many tests used for the purpose of hypothesis testing in statistics.
2. F Test:
- An F-test is conducted by the researcher on the basis of the F statistic.
- The F statistic is defined as the ratio between the two independent chi-square variates that are divided by their respective degree of freedom.
- The F-test follows the Snedecor’s F- distribution. The F-test is used by a researcher in order to carry out the test for the equality of the two population variances.
- If a researcher wants to test whether or not two independent samples have been drawn from a normal population with the same variability, then he generally employs the F-test.
- The F-test is also used by the researcher to determine whether or not the two independent estimates of the population variances are homogeneous in nature.
3. Z Test:
- A Z-test is a type of hypothesis test—a way for you to figure out if results from a test are valid or repeatable.
- For example, if someone said they had found a new drug that cures cancer, you would want to be sure it was probably true.
- A hypothesis test will tell you if it’s probably true, or probably not true. A Z test is used when your data is approximately normally distributed (i.e. the data has the shape of a bell curve when you graph it).
NIOR Scale
The scale of measurement:
- A scale is a device or an object used to measure or quantify any event or another object.
- In Statistics, the variables or numbers are defined and categorized using different scales of measurements.
- Each level of measurement scale has specific properties that determine the various use of statistical analysis.
- There are five scales of measurement
- Nominal scale
- Ordinal scale
- Interval scale
- Ratio scale
- Attitude scale
| Type of scale | Characteristics | Example |
| Nominal scale | When a value has two or more sub-categories it can be measure in nominal scaleNominal means where the name of the variable considers onlyClassification only | In an application form, you have to select your gender |
| Ordinal scale | It is also known as the ranking scaleIt measures quantitative and qualitative variablesThere the measurements usually done dividing the data into classes or in absolute valueIt is not necessary that the interval between two class should be equalClassification and order | The income group can be divided into threeLower-income groupMiddle-income groupHigher-income groupIt can also be measured based on the annual family income like 150000/annum |
| Interval scale | It has quite similar to the ordinal scaleInterval scale refers to the level of measurement in which the attributes composing variables are measured on specific numerical scores or valuesThere are equal distances between attributes.The distance between any two adjacent attributes is called an interval, and intervals are always equal.The scale attached with a thermometer is a kind of interval scaleClassification, order, and equal unit | Likert ScaleNet Promoter Score (NPS)Bipolar Matrix Table |
| Ratio scale | The ratio scale of measurement is similar to the interval scale in that it also represents the quantity and has equality of units.However, this scale also has an absolute zero (no numbers exist below zero).It indicates differences between two variable, their amount of differences, and the direction of differencesClassification, order, equal unit, and zero | What is the weight of an iron rod in Kgs?0 – 5 kgs5 – 10 kgs10 – 15 kgs15 – 20 kgsMore than 20 kgs |
Attitude scales:
- It provides a quantitative measurement of attitudes, opinions, or values by summarizing numerical scores given by researchers to people’s responses to sets of statements exploring dimensions of an underlying theme.
- In qualitative research, this scale is very important
Ph Value
pH is a measure of how acidic/basic water is. The range goes from 0 – 14, with 7 being neutral. pHs of less than 7 indicate acidity, whereas a pH of greater than 7 indicates a base. pH is really a measure of the relative amount of free hydrogen and hydroxyl ions in the water
पीएच इस बात का पैमाना है कि पानी कितना अम्लीय/क्षारीय है। सीमा 0 – 14 से जाती है, जिसमें 7 तटस्थ होता है । 7 से कम पीएच अम्लता को इंगित करता है, जबकि 7 से अधिक पीएच एक आधार को इंगित करता है। पीएच वास्तव में पानी में मुक्त हाइड्रोजन और हाइड्रॉक्सिल आयनों की सापेक्ष मात्रा का एक उपाय है।
Plagriasm
Symbol in communication
Examples of symbol-based communication:
प्रतीक आधारित संचार
प्रतीक–आधारित संचार क्या है?
संवर्धित और वैकल्पिक संचार (एएसी) में प्रतीक आधारित संचार ” विकल्प ” है। एएसी के तत्वों पर करीब से नजर डालने से हमें यह देखने की अनुमति मिलती है कि इस संदर्भ में प्रतीक-आधारित संचार कहां फिट बैठता है:
- संवर्द्धन का अर्थ है जोड़ना या बढ़ाना। लगभग सभी वक्ता और गैर वक्ता आंख दिखाकर, बोलकर, इशारों और शरीर की भाषा का उपयोग करके भाषण में वृद्धि करते हैं।
- वैकल्पिक का अर्थ है प्रतिस्थापन या स्थानापन्न। भाषण के एक विकल्प में प्रतीकों की ओर इशारा करना या टकटकी लगाना, हस्ताक्षर करना या वर्तनी शामिल है।
- संचार का अर्थ कम से कम एक अन्य व्यक्ति के साथ संदेश भेजना और प्राप्त करना है।
प्रतीक-आधारित संचार अक्सर उन व्यक्तियों द्वारा उपयोग किया जाता है जो अकेले भाषण का उपयोग करने में असमर्थ होते हैं और जो अभी तक विकसित नहीं हुए हैं, या साक्षरता कौशल विकसित करने में कठिनाई होती है। प्रतीक किसी शब्द या विचार का दृश्य प्रतिनिधित्व प्रदान करते हैं।
“तात्कालिक लक्ष्य छात्रों के लिए उन सभी प्रतीकों का उपयोग करना नहीं है जिन्हें हमने कार्यात्मक रूप से उनके स्वयं के संचार में पेश किया है, बल्कि उनके लिए उन अन्य लोगों के साथ बातचीत करना है जो संचार के लिए प्रतीक–आधारित दृष्टिकोणों का अनुकरण कर रहे हैं।“ -करेन एरिकसन
प्रतीक–आधारित संचार से किन छात्रों को लाभ होगा?
जिन छात्रों का भाषण है:
- विकसित करने के लिए धीमा
- समझने में मुश्किल (बैक अप के रूप में)
- बहुत सीमित या अस्तित्वहीन
प्रतीक–आधारित संचार से छात्र कैसे लाभान्वित हो सकते हैं?
जिन छात्रों को सीखने और रहने के वातावरण में प्रतीक-आधारित प्रणाली का उपयोग करके संवाद करने के लिए प्रामाणिक और सार्थक अवसर प्रदान किए जाते हैं, वे कई तरह से लाभान्वित होते हैं, जिनमें शामिल हैं:
- भाषा कौशल का विकास
- साक्षरता कौशल का विकास
- अधिक लोगों से अधिक कहना
- रिश्तों और जुड़ाव और अपनेपन का निर्माण
- हताशा / व्यवहार में कमी
- उनके आसपास की दुनिया की बेहतर समझ विकसित करना
- व्यक्तिगत रूप से सार्थक अनुरोध, विकल्प और निर्णय लेना
- पर्यावरण में बढ़ती भागीदारी
- रचनात्मकता और आत्म अभिव्यक्ति का निर्माण
प्रतीक–आधारित संचार के उदाहरण:
संचार बोर्ड भाषा को दृश्यमान और सुलभ बनाते हैं। कोर शब्दावली का उद्देश्य सभी वातावरणों और भाषा क्षमता के स्तरों में उपयोग किया जाना है।
फ्लिप बुक एक संचार पुस्तक है जिसमें आसान नेविगेशन के लिए टैब होते हैं। शब्दावली श्रेणियों द्वारा व्यवस्थित की जाती है, जो टैब पर इंगित की जाती हैं।
लो-टेक कम्युनिकेशन बोर्ड विकल्पों के लिए टेम्प्लेट के लिए इस संसाधन को देखें:
आई–गेज़ (जिसे आई-पॉइंटिंग के रूप में भी जाना जाता है) किसी अन्य व्यक्ति के ध्यान को निर्देशित या पुनर्निर्देशित करने के लिए किसी की आँखों का उपयोग करने का कार्य है। प्रभावी दृष्टि से देखने के लिए छात्र और संचार भागीदार दोनों की भागीदारी की आवश्यकता होती है। छात्र इच्छित संदेश की दिशा में अपनी टकटकी लगाता है। उदाहरण के लिए, यदि कोई छात्र बाहर जाना चाहता है, तो वह अपनी दृष्टि दरवाजे पर लगा सकता है।
ई –ट्रान , या आई गेज़ कम्युनिकेशन बोर्ड, एक वर्टिकली होल्ड/माउंटेड बोर्ड है, जो प्लेक्सीग्लास या मज़बूत कागज़ से बना होता है, जिसके बीच में एक खिड़की कटी होती है, जो छात्रों को बोर्ड पर प्रदर्शित चयनित वस्तुओं पर अपनी दृष्टि केंद्रित करके संवाद करने में सक्षम बनाता है। . आइटम किसी भी कॉन्फ़िगरेशन में प्रदर्शित किए जा सकते हैं और प्रत्येक बोर्ड पर अधिक विकल्प प्रदान करने के लिए एन्कोड किए जा सकते हैं। छात्र पार्टनर असिस्टेड स्कैनिंग के माध्यम से ETran तक पहुँचते हैं।
यह व्यावहारिक रूप से आधारित संचार पृष्ठ सेट विशेष रूप से विभिन्न प्रकार के विषयों और जरूरतों के बारे में सरल बातचीत करने में उपयोगकर्ताओं की मदद करने के लिए बनाया गया है।
एक आईपैड संचार ऐप उपयोगकर्ता को सीधे उन प्रतीकों का चयन करने की अनुमति देता है जो किसी विशिष्ट विषय का समर्थन करने के लिए व्यवस्थित होते हैं या एक संवादात्मक कार्य करते हैं। उदाहरण के लिए, यह पृष्ठ वर्णानुक्रम में क्रियाओं की एक सूची है- ढूंढें, उड़ें, दें, सहायता करें। कई ऐप्स के पृष्ठ गतिशील होते हैं, जिसका अर्थ है कि एक बार जब उपयोगकर्ता किसी संदेश का चयन कर लेता है, तो ऐप अगले तार्किक पृष्ठ पर चला जाएगा।
Communication boards make language visible and accessible. Core vocabulary is intended to be used across all environments and levels of language competence.
A flip book is a communication book with tabs for easy navigation. Vocabulary is arranged by categories, which are indicated on the tabs.
Check out this resource for templates for Low-tech Communication Board options:
Eye-gaze (also known as eye-pointing) is the act of using one’s eyes to direct or redirect the attention of another person. Effective eye-gaze requires participation of both the student and the communication partner. The student fixes their gaze in the direction of the intended message. For example, if a student wants to go outside, they may set their gaze on the door.
An e-tran, or an eye gaze communication board, is a vertically held/mounted board, made of plexiglass or sturdy paper with a window cut in the middle, that enables students to communicate by focusing their gaze on selected items displayed on the board. Items can be displayed in any configuration and can be encoded to provide more choices on each board. Students access the ETran via Partner Assisted Scanning.
This pragmatically based communication page set is specifically made to help eye gaze users hold simple conversations around a variety of topics and needs.
An iPad communication app allows the user to directly select symbols that are arranged to support a specific topic or serve a communicative function. For example, this page is a list of verbs in alphabetical order- find, fly, give, help. The pages on many apps are dynamic, meaning once the user selects a message, the app will jump to the next logical page.
Spyware
Ms Excel Formula
DI -Income Expenditure % Based
Rc on Environment
Waste Management
- अपशिष्ट अनुपयोगी सामग्री है। अपशिष्ट कई रूपों में आता है।
- अपशिष्ट को इस प्रकार वर्गीकृत किया जा सकता है:
- ठोस अपशिष्ट (सब्जी के छिलके, कचरे के डिब्बे और ऐसे अन्य नगरपालिका अपशिष्ट),
- तरल अपशिष्ट (उद्योगों से पानी का निर्वहन, खेतों से हानिकारक अपवाह आदि),
- और गैसीय अपशिष्ट (उद्योगों से निकलने वाली हानिकारक गैसें)।
- शहरी, औद्योगिक और ग्रामीण क्षेत्रों में अपशिष्ट प्रबंधन एक ज्वलंत समस्या है।
- अपशिष्ट प्रबंधन में निम्नलिखित कदम शामिल हैं:
- कचरे का संग्रह
- कचरे का पृथक्करण
- कचरे का परिवहन
- कचरे का प्रसंस्करण
- कचरे का निपटान
प्रमुख बिंदु
कचरे का प्रसंस्करण:
- अपशिष्ट प्रसंस्करण और उपचार में बहुत सारी विभिन्न प्रक्रियाएँ शामिल हैं।
- प्रसंस्करण, परिभाषा के अनुसार, भौतिक उपचार के शीर्षक के अंतर्गत आता है।
- यह कचरे की संरचना और चरित्र को बदलने के लिए भौतिक तकनीकों का उपयोग करता है।
- इसमें पुनर्चक्रण और छंटाई शामिल है।
- प्रत्येक रीसाइक्लिंग प्रक्रिया सामग्री के रूपांतरण का प्रतिनिधित्व करती है।
- अतः पुनर्चक्रण की प्रक्रिया भी नई सामग्री के उत्पादन की एक प्रक्रिया है।
- यह द्वितीयक कच्चे माल के उत्पादन की प्रक्रिया का वर्णन करता है।
- इन सभी गतिविधियों से लैंडफिल में जाने वाले कचरे की मात्रा कम हो जाती है।
- इस पुनर्चक्रण प्रक्रिया में महत्व यह है कि अपशिष्ट प्रसंस्करण पृथक्करण से शुरू होता है।
- प्रक्रिया की शुरुआत में कचरे को अलग करने से कचरे के उपचार में मदद मिलती है और कचरे से निपटने वाली सुविधाओं की दक्षता बढ़ाने में मदद मिलती है।
- Waste is unusable material. Waste comes in many forms.
- Waste can be categorized as:
- solid waste (vegetable peels, trash cans and other such municipal waste),
- liquid waste (water discharge from industries, harmful runoff from fields etc),
- and gaseous waste (harmful gases released from industries).
- Waste management is a burning problem in urban, industrial and rural areas.
- Wastes management involves the following steps:
- Collection of wastes
- Segregation of wastes
- Transportation of waste
- Processing of wastes
- Disposal of waste
Key Points
Processing of waste:
- Waste processing and treatment includes a lot of different processes.
- Processing, by definition, falls under the heading of physical treatment.
- It uses physical techniques for changing the composition and character of the waste.
- It includes recycling and sorting.
- Every recycling process represents a conversion of the material.
- So the process of recycling is also a process of production of new materials.
- It describes the process of producing secondary raw material.
- All these activities conduce to reduce the amount of waste which has to landfill.
- Of significance in this recycling process is that waste processing starts with separation.
- Separation of waste at the beginning of the process supports the treatment of the waste and helps to raise the efficiency of the facilities which deals with the waste.
Scaffolding in Teaching
Nep 2020
Ancient Education
Consider following statements:
(a) Chlorofluorocarbons are responsible for ozone layer depletion.
(b) Green house effect is responsible for global warming.
(c) Ozone layer does not permit infrared radiation from sun to reach the earth.
(d) Acid rain is mostly because of oxides of nitrogen and sulphur.
Correct statements are:
- (a), (b) and (c)
- (b), (c) and (d)
- (a), (c) and (d)
- (a), (b) and (d)
निम्नलिखित कथनों पर विचार करें:
(ए) ओजोन परत की कमी के लिए क्लोरोफ्लोरोकार्बन जिम्मेदार हैं।
(b) ग्लोबल वार्मिंग के लिए ग्रीन हाउस प्रभाव जिम्मेदार है।
(सी) ओजोन परत सूर्य से अवरक्त विकिरण को पृथ्वी तक पहुंचने की अनुमति नहीं देती है।
(d) अम्लीय वर्षा मुख्यतः नाइट्रोजन और सल्फर के ऑक्साइड के कारण होती है।
सही कथन हैं:
- (ए), (बी) और (सी)
- (बी), (सी) और (डी)
- (ए), (सी) और (डी)
- (ए), (बी) और (डी)
विकल्प 4 : (ए), (बी) और (डी)
व्याख्या:
- क्लोरोफ्लोरोकार्बन (सीएफसी) वास्तव में ओजोन परत के क्षरण के लिए जिम्मेदार हैं। सीएफसी सिंथेटिक यौगिक हैं जो आमतौर पर रेफ्रिजरेंट, एयरोसोल प्रोपेलेंट और अन्य औद्योगिक अनुप्रयोगों में उपयोग किए जाते थे। वातावरण में छोड़े जाने पर, सीएफसी समताप मंडल तक पहुंच सकते हैं जहां उन्हें पराबैंगनी (यूवी) विकिरण द्वारा तोड़ा जा सकता है। यह प्रक्रिया क्लोरीन परमाणुओं को छोड़ती है, जो ओजोन अणुओं के साथ प्रतिक्रिया कर सकती है, जिससे ओजोन परत का क्षरण हो सकता है।
- ग्लोबल वार्मिंग के लिए ग्रीनहाउस प्रभाव जिम्मेदार है।
- ग्रीनहाउस प्रभाव एक प्राकृतिक प्रक्रिया है जिसमें कुछ गैसें, जैसे कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड (CO2), मीथेन (CH4), और जल वाष्प, पृथ्वी के वायुमंडल में गर्मी को रोक लेती हैं।
- ये गैसें सूर्य के प्रकाश को गुजरने देती हैं, लेकिन वे ऊष्मा ऊर्जा को अवशोषित और पुन: विकीर्ण करती हैं, जिससे इसे वापस अंतरिक्ष में जाने से रोका जा सकता है।
- यह घटना पृथ्वी के तापमान में क्रमिक वृद्धि की ओर ले जाती है, जिसे ग्लोबल वार्मिंग के रूप में जाना जाता है।
- कथन (सी) गलत है। ओजोन परत मुख्य रूप से सूर्य से हानिकारक पराबैंगनी (यूवी) विकिरण को अवशोषित करती है।
- हालांकि, यह इन्फ्रारेड विकिरण (गर्मी) को पृथ्वी की सतह तक पहुंचने से रोकता या रोकता नहीं है।
- इन्फ्रारेड विकिरण ओजोन परत से काफी हद तक अप्रभावित है और पृथ्वी के तापमान नियमन में एक भूमिका निभाता है।
- अम्ल वर्षा वास्तव में ज्यादातर नाइट्रोजन (NOx) और सल्फर (SOx) के ऑक्साइड के कारण होती है।
- ये गैसें मुख्य रूप से मानवीय गतिविधियों जैसे कि जीवाश्म ईंधन को जलाने, औद्योगिक प्रक्रियाओं और वाहन उत्सर्जन से वातावरण में छोड़ी जाती हैं।
- जब ये गैसें वायुमंडलीय नमी के साथ मिलकर क्रमशः नाइट्रिक एसिड और सल्फ्यूरिक एसिड बनाती हैं।
- ये अम्ल फिर अम्लीय वर्षा के रूप में पृथ्वी पर वापस गिर सकते हैं, जो पारिस्थितिक तंत्र, जल निकायों और बुनियादी ढांचे पर हानिकारक प्रभाव डाल सकते हैं।
सही कथन हैं:
- ओजोन परत के क्षरण के लिए क्लोरोफ्लोरोकार्बन जिम्मेदार हैं।
- ग्लोबल वार्मिंग के लिए ग्रीनहाउस प्रभाव जिम्मेदार है।
- अम्लीय वर्षा मुख्यतः नाइट्रोजन और सल्फर के ऑक्साइड के कारण होती है।
गलत कथन है:
- ओजोन परत सूर्य से अवरक्त विकिरण को पृथ्वी तक नहीं पहुंचने देती है।
तो, यहाँ (ए), (बी) और (डी) सही उत्तर हैं।
Option 4 : (a), (b) and (d)
Air and Noise Pollution Question 1 Detailed Solution
- Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) are indeed responsible for ozone layer depletion. CFCs are synthetic compounds that were commonly used in refrigerants, aerosol propellants, and other industrial applications. When released into the atmosphere, CFCs can reach the stratosphere where they can be broken down by ultraviolet (UV) radiation. This process releases chlorine atoms, which can react with ozone molecules, leading to the depletion of the ozone layer.
- The greenhouse effect is responsible for global warming.
- The greenhouse effect is a natural process in which certain gases, such as carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and water vapor, trap heat in the Earth’s atmosphere.
- These gases allow sunlight to pass through, but they absorb and re-radiate the heat energy, preventing it from escaping back into space.
- This phenomenon leads to a gradual increase in the Earth’s temperature, known as global warming.
- Statement (c) is incorrect. The ozone layer primarily absorbs harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun.
- However, it does not block or prevent infrared radiation (heat) from reaching the Earth’s surface.
- Infrared radiation is largely unaffected by the ozone layer and plays a role in the Earth’s temperature regulation.
- Acid rain is indeed mostly caused by oxides of nitrogen (NOx) and sulfur (SOx).
- These gases are released into the atmosphere primarily from human activities such as burning fossil fuels, industrial processes, and vehicle emissions.
- When these gases combine with atmospheric moisture, they form nitric acid and sulfuric acid, respectively.
- These acids can then fall back to Earth as acid rain, which can have detrimental effects on ecosystems, water bodies, and infrastructure.
The correct statements are:
- Chlorofluorocarbons are responsible for ozone layer depletion.
- The greenhouse effect is responsible for global warming.
- Acid rain is mostly caused by oxides of nitrogen and sulfur.
The incorrect statement is:
- Ozone layer does not permit infrared radiation from the sun to reach the Earth.
So, here (a), (b) and (d) is the correct answer.
Volatile organic compounds are organic compounds that have a high vapor pressure at room temperature. High vapor pressure correlates with a low boiling point, which relates to the number of the sample’s molecules in the surrounding air, a trait known as volatility.
वाष्पशील कार्बनिक यौगिक या वे कार्बनिक रसायन है जिनमे कमरे के समान्य ताप पर भी उच्च वाष्प दाब होता है। इनका उच्च वाष्प दाब, उनके कम क्वथनांक की वजह से garmi अधिक अणुओं के ठोस या द्रव वाष्पीकृत या ऊर्ध्वपतित होकर यौगिक बनाने व आस पास की वायु में मिलने के कारण होता है https://t.me/Ugcnetpaper1Preparation
CHANNELS 01-10 ARE MANAGED BY CEC-UGC, NEW DELHI. NATIONAL COORDINATOR IS
PROF. JAGAT BHUSHAN NADDA, DIRECTOR, CEC, NEW DELHI.
| CHANNEL NO. | CHANNEL NAME | ROUTE/PARENT | COORDINATOR NAME | DESCRIPTION | VIEW | |
| 1 | Channel 01: VAGEESH: CEC/UGC: Humanities- 1, Language and Literature | EFL University, EMRC EFLU | director.emmrc.eflu@gmail.com, sreekumartt@efluniversity.ac.in | Prof. T T Sreekumar Director I/C | The Swayamprabha Humanities Ch…Read More | |
| 2 | Channel 02: SANSKRITI: CEC/UGC: Humanities- 2, History, Culture & Philosophy | CEC, New Delhi | additionaldirector.cec@gmail.com | Prof. Rajnish Shrivastava | ÔÇ£Learn as if you are goin…Read More | |
| 3 | Channel 03: PRABODH: CEC/UGC: Social Science -1, Social & Behavioral Sciences | Jai Narayan Vyas University, EMRC Jodhpur | director.emmrc.jnvu@gmail.com | Prof. Sunil Sharma | Learning gives creativity, cre…Read More | |
| 4 | Channel 04: SAARASWAT: CEC/UGC: Social Science – 2, Education, Psychology, Home Science and related subjects | CEC, New Delhi | additionaldirector.cec@gmail.com | Prof. Rajnish Shrivastava | ÔÇ£You can teach a student …Read More | |
| 5 | Channel 05: PRABANDHAN: CEC/UGC: Social Science – 3, Management, Library Science, Information Science and related subjects | Jamia Milia University, MCRC Jamia | mcrc@jmi.ac.in, sghosh@jmi.ac.in | Dr. Shohini Ghosh | ÔÇ£Learning gives creativit…Read More | |
| 6 | Channel 06: VIDHIK: CEC/UGC: Social Science – 4, Law, Legal Studies, Human Rights and related subjects | Punjabi University, EMRC Patiala | emmrc.patiala@gmail.com, directormediacentre@gmail.com | Dr. Daljit Ami Director I/C | The Swayam Prabha DTH Channel …Read More | |
| 7 | Channel 07: KAUTILYA: CEC/UGC: Economics, Commerce and Finance | Gujarat University, EMRC Ahmadabad | emrcabadad1@bsnl.in, diremrc@gujaratuniversity.ac.in | Prof. Naresh J Dave Director I/C | Swayam Prabha DTH Channel 7, E…Read More | |
| 8 | Channel 08: ARYABHATT: CEC/UGC: Physical sciences, Mathematics, Physics, Chemistry and related Subjects | Calicut University, EMRC Calicut | emmrccalicut@yahoo.co.in, damodar.prasad@gmail.com | Dr. D. Damodar Prasad Director | The Channel-08- Swayam Prabha …Read More | |
| 9 | Channel 09: SPANDAN: CEC/UGC: Life Sciences, Botany, Zoology, Bio-Science and related subjects | Kashmir University, EMRC Srinagar | salimaemrc@gmail.com | Dr. Salima Jan Director I/C | The vision of the channel is t…Read More | |
| 10 | Channel 10: DAKSH: CEC/UGC: Applied Sciences, Allied Physical and Chemical sciences and related subjects | Anna University, EMRC Chennai | emmrcchennai@annauniv.edu | Dr. C.D. ANURADHA Director I/C | The SWAYAM Prabha DTH Channel…Read More | |
| 21 | Channel 21: Vyas (CEC) | CEC | drsunilmehru@gmail.com | Dr. Sunil Mehru JD (S/W) | – |
CHANNELS ARE MANAGED BY NPTEL. NATIONAL COORDINATOR
| CHANNEL NO. | CHANNEL NAME | ROUTE/PARENT | COORDINATOR NAME | DESCRIPTION | VIEW | |
| 11 | Channel 11: NPTEL: Mechanical Engineering & related branches | IIT Kanpur | bhattacs@iitk.ac.in | Prof. Shantanu Bhattacharya | The SWAYAMPRABHA Chemical Engi…Read More | |
| 12 | Channel 12: NPTEL: Civil Engineering & related branches | matsagar@civil.iitd.ac.in | Prof. Vasant Matsagar | – | ||
| 13 | Channel 13: NPTEL: Computer / IT & related branches | IIT Kharagpur | sudipm@iitkgp.ac.in | Prof. Sudip Mishra | The Swayam Prabha Computer Sci…Read More | |
| 14 | Channel 14: NPTEL: Electrical, Electronics and Communication & related branches | IIT Delhi | kannan@iitb.ac.in | Prof. Kannan Moudgalya | Channel 14 is dedicated to Ele…Read More | |
| 15 | Channel 15: NPTEL : Engineering Sciences & related subject | IIT Madras | arunkt@iitm.ac.in, arunkt@dth.ac.in | Prof. Arun K. Tangirala | The Swayam Prabha Channel 15 D…Read More | |
| 16 | Channel 16: NPTEL: Humanities, Management & other branches | IIT Kanpur | mjha@iitk.ac.in | Prof. Munmun Jha | Channel 16 is funded by MHRD a…Read More | |
| 22 | Channel 22: IIT PAL | IIT PAL 4, IIT Delhi | joby@physics.iitd.ac.in | Prof. Joby Joseph | The Swayam Prabha Physics Chan…Read More |
CHANNELS ARE MANAGED BY IGNOU NEW DELHI. THE NATIONAL COORDINATOR IS PROF. UMA KANJILAL, IGNOU, NEW DELHI
| CHANNEL NO. | CHANNEL NAME | ROUTE/PARENT | COORDINATOR NAME | DESCRIPTION | VIEW | |
| 17 | Channel 17: IGNOU: Social Sciences and Humanities | IGNOU, New Delhi | archana@ignou.ac.in | Dr. Archana Shukla | Introduction:Liberal arts educ…Read More | |
| 18 | Channel 18: IGNOU:Basic and Applied Sciences | IGNOU, New Delhi | drsgupta@ignou.ac.in | Dr. Sanjay Gupta | Agriculture sector plays an im…Read More | |
| 19 | Channel 19: Professional and Vocational Education | IGNOU, New Delhi | skesharwani@ignou.ac.in | Dr. Subodh Kesharwani | – | |
| 20 | Channel 20: IGNOU: State Open Universities and Teacher Education | IGNOU, New Delhi | gmythili@ignou.ac.in | Dr. G. Mythili | Channel-20 IGNOU: State Open U…Read More |
CHANNELS ARE MANAGED BY PRIMARY EDUCATION
| CHANNEL NO. | CHANNEL NAME | ROUTE/PARENT | COORDINATOR NAME | DESCRIPTION | VIEW | |
| 23 | Class-1 PMeVIDYA | NCERT, New Delhi | dth.class1@ciet.nic.in | Class 1 | – | |
| 24 | Class-2 PMeVIDYA | NCERT, New Delhi | dth.class2@ciet.nic.in | Class 2 | – | |
| 25 | Class-3 PMeVIDYA | NCERT, New Delhi | dth.class3@ciet.nic.in | Class 3 | – | |
| 26 | Class-4 PMeVIDYA | NCERT, New Delhi | dth.class4@ciet.nic.in | Class 4 | – | |
| 27 | Class-5 PMeVIDYA | NCERT, New Delhi | dth.class5@ciet.nic.in | Class 5 | – | |
| 28 | Class-6 PMeVIDYA | NCERT, New Delhi | dth.class6@ciet.nic.in | Class 6 | – | |
| 29 | Class-7 PMeVIDYA | NCERT, New Delhi | dth.class7@ciet.nic.in | Class 7 | – | |
| 30 | Class-8 PMeVIDYA | NCERT, New Delhi | dth.class8@ciet.nic.in | Class 8 | – |
CHANNELS ARE MANAGED BY SECONDARY EDUCATION
| CHANNEL NO. | CHANNEL NAME | ROUTE/PARENT | COORDINATOR NAME | DESCRIPTION | VIEW | |
| 31 | Class-9 PMeVIDYA | NCERT, New Delhi | dth.class9@ciet.nic.in | Class 9 | – | |
| 32 | Class-10 PMeVIDYA | NCERT, New Delhi | dth.class10@ciet.nic.in | Class 10 | – |
CHANNELS ARE MANAGED BY HIGHER SECONDARY EDUCATION
| CHANNEL NO. | CHANNEL NAME | ROUTE/PARENT | COORDINATOR NAME | DESCRIPTION | VIEW | |
| 33 | Class-11 PMeVIDYA | NCERT, New Delhi | dth.class11@ciet.nic.in | Class 11 | – | |
| 34 | Class-12 PMeVIDYA | NCERT, New Delhi | dth.class12@ciet.nic.in | Class 12 | – |
Which of the following is NOT a commonly used fuel for nuclear power plants?
- Pu – 236
- U – 238
- Pu – 244
- U – 235
निम्नलिखित में से कौन सा परमाणु ऊर्जा संयंत्रों के लिए आमतौर पर इस्तेमाल किया जाने वाला ईंधन नहीं है?
- पु – 236
- यू – 238
- पु – 244
- यू – 235
विकल्प 3 : पु – 244
सही उत्तर विकल्प 3 है):( पु – 244 )
अवधारणा:
- पु-236 प्लूटोनियम का समस्थानिक है
- यूरेनियम -238 प्रकृति में पाया जाने वाला यूरेनियम का सबसे आम समस्थानिक है, जिसकी सापेक्ष बहुतायत 99% है। यूरेनियम -235 के विपरीत, यह गैर-विखंडनीय है, जिसका अर्थ है कि यह थर्मल-न्यूट्रॉन रिएक्टर में श्रृंखला प्रतिक्रिया को बनाए नहीं रख सकता है।
- प्लूटोनियम -244 प्लूटोनियम का सबसे स्थिर समस्थानिक है
- प्लूटोनियम के कई औद्योगिक उपयोग हैं, खासकर परमाणु उद्योग में। प्लूटोनियम -239 मुख्य रूप से परमाणु रिएक्टरों को बिजली देने के लिए ईंधन के रूप में उपयोग किया जाता है।
अतिरिक्त जानकार
परमाणु ऊर्जा प्लांट:
एक जनरेटिंग स्टेशन जिसमें परमाणु ऊर्जा को विद्युत ऊर्जा में परिवर्तित किया जाता है, परमाणु ऊर्जा स्टेशन के रूप में जाना जाता है।
परमाणु ऊर्जा स्टेशनों में, यूरेनियम (U 235 ) या थोरियम (Th 232 ) जैसे भारी तत्वों को रिएक्टर के रूप में जाने वाले एक विशेष उपकरण में परमाणु विखंडन के अधीन किया जाता है।
इस प्रकार जारी ऊष्मा ऊर्जा का उपयोग उच्च तापमान और दबाव पर भाप बनाने में किया जाता है।
भाप भाप टरबाइन को चलाती है जो भाप ऊर्जा को यांत्रिक ऊर्जा में परिवर्तित करती है। टरबाइन अल्टरनेटर को चलाता है जो यांत्रिक ऊर्जा को विद्युत ऊर्जा में परिवर्तित करता है।
परमाणु ऊर्जा स्टेशन की योजनाबद्ध व्यवस्था:
एक परमाणु ऊर्जा स्टेशन की योजनाबद्ध व्यवस्था को चित्र में दिखाया गया है। पूरी व्यवस्था को निम्नलिखित मुख्य चरणों में विभाजित किया जा सकता है:
(i) परमाणु रिएक्टर
(ii) हीट एक्सचेंजर
(iii) स्टीम टर्बाइन
(iv) अल्टरनेटर
(i) परमाणु रिएक्टर: यह एक उपकरण है जिसमें परमाणु ईंधन (यू 235 ) परमाणु विखंडन के अधीन है। यह श्रृंखला प्रतिक्रिया को नियंत्रित करता है जो विखंडन के बाद शुरू होती है।
यदि श्रृंखला प्रतिक्रिया को नियंत्रित नहीं किया जाता है, तो जारी ऊर्जा में तेजी से वृद्धि के कारण विस्फोट होगा।
दाबित पानी रिएक्टर (पीडब्ल्यूआर), उबलते पानी रिएक्टर (बीडब्ल्यूआर), उन्नत गैस-कूल्ड रिएक्टर (एजीआर), हल्का पानी ग्रेफाइट-मॉडरेटेड रिएक्टर (एलडब्ल्यूजीआर), फास्ट न्यूट्रॉन रिएक्टर (एफएनआर), परमाणु ऊर्जा संयंत्र में प्रयुक्त ब्रीडर रिएक्टर प्रकार परमाणु रिएक्टर .
(ii) हीट एक्सचेंजर: शीतलक हीट एक्सचेंजर को गर्मी देता है जिसका उपयोग भाप को ऊपर उठाने में किया जाता है। गर्मी छोड़ने के बाद, शीतलक को फिर से रिएक्टर में भेजा जाता है।
(iii) स्टीम टर्बाइन: हीट एक्सचेंजर में उत्पन्न होने वाली भाप को वाल्व के माध्यम से स्टीम टर्बाइन तक ले जाया जाता है। टर्बाइन में उपयोगी कार्य करने के बाद भाप संघनित्र में समाप्त हो जाती है। संघनित्र भाप को संघनित करता है जिसे फीडवाटर पंप के माध्यम से हीट एक्सचेंजर को खिलाया जाता है।
(iv) अल्टरनेटर: स्टीम टरबाइन अल्टरनेटर को चलाता है जो यांत्रिक ऊर्जा को विद्युत ऊर्जा में परिवर्तित करता है। अल्टरनेटर से आउटपुट को ट्रांसफॉर्मर, सर्किट ब्रेकर और आइसोलेटर्स के माध्यम से बस बार तक पहुंचाया जाता है।
आरेख से, योजनाबद्ध व्यवस्था है:
परमाणु रिएक्टर → हीट एक्सचेंजर → स्टीम टर्बाइन → अल्टरनेटर
Option 3 : Pu – 244
The correct answer is option 3):(Pu – 244 )
Concept:
- Pu – 236 is an isotope of plutonium
- Uranium-238 is the most common isotope of uranium found in nature, with a relative abundance of 99%. Unlike uranium-235, it is non-fissile, which means it cannot sustain a chain reaction in a thermal-neutron reactor.
- Plutonium-244 is the most stable isotope of plutonium
- Plutonium has several industrial uses, particularly in the nuclear industry. Plutonium-239 is primarily used as a fuel to power nuclear reactors.
Additional Information
Nuclear Power Plant:
A generating station in which nuclear energy is converted into electrical energy is known as a nuclear power station.
In nuclear power stations, heavy elements such as Uranium (U235) or Thorium (Th232) are subjected to nuclear fission in a special apparatus known as a reactor.
The heat energy thus released is utilized in raising steam at high temperatures and pressure.
The steam runs the steam turbine which converts steam energy into mechanical energy. The turbine drives the alternator which converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Schematic Arrangement of Nuclear Power Station:
The schematic arrangement of a nuclear power station is shown in Fig. The whole arrangement can be divided into the following main stages :
(i) Nuclear reactor
(ii) Heat exchanger
(iii) Steam turbine
(iv) Alternator
(i) Nuclear Reactor: It is an apparatus in which nuclear fuel (U235) is subjected to nuclear fission. It controls the chain reaction that starts once the fission is done.
If the chain reaction is not controlled, the result will be an explosion due to the fast increase in the energy released.
Pressurized water reactor (PWR), Boiling water reactor (BWR), Advanced gas-cooled reactor (AGR), Light water graphite-moderated reactor (LWGR), Fast neutron reactor (FNR), Breeder reactor type Nuclear Reactor used in Nuclear Power Plant.
(ii) Heat exchanger: The coolant gives up heat to the heat exchanger which is utilized in raising the steam. After giving up heat, the coolant is again fed to the reactor.
(iii) Steam turbine: The steam produced in the heat exchanger is led to the steam turbine through a valve. After doing useful work in the turbine, the steam is exhausted to the condenser. The condenser condenses the steam which is fed to the heat exchanger through a feedwater pump.
(iv) Alternator: The steam turbine drives the alternator which converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. The output from the alternator is delivered to the bus bars through the transformer, circuit breakers, and isolators.
From the diagram, the schematic arrangement is:
Nuclear reactor → heat exchanger → steam turbine → alternator