
One liner questions on CTET CDP Important & Expected for All TET Exams .
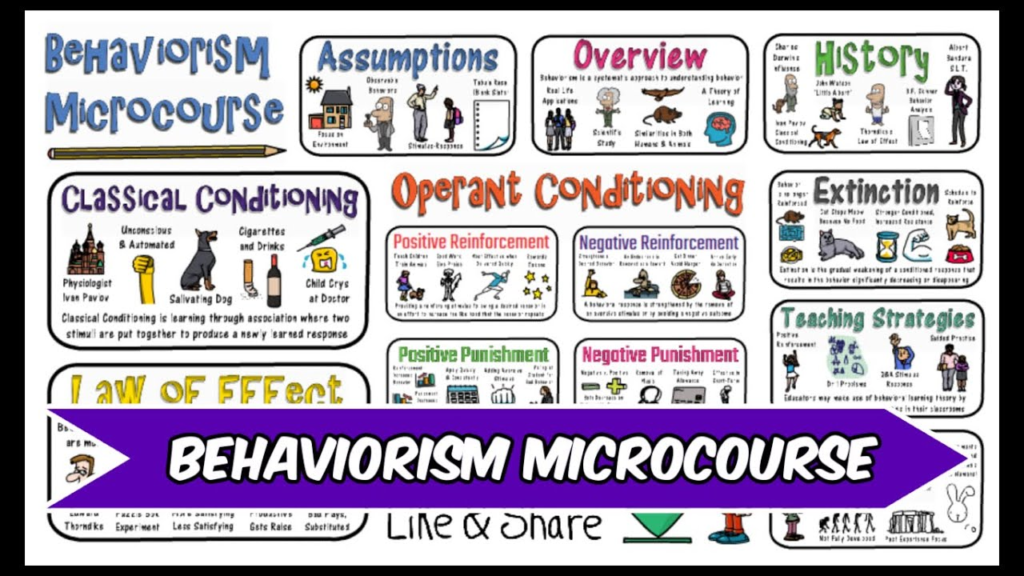
Q1. What is the main focus of Child Development?
Answer: Understanding physical, mental, and emotional growth of a child.
मुख्य ध्यान बच्चे के शारीरिक, मानसिक और भावनात्मक विकास को समझने पर है।
Q2. At what age does cognitive development peak in children?
Answer: Cognitive skills develop significantly from ages 2 to 7.
बच्चों में संज्ञानात्मक कौशल 2 से 7 वर्ष की आयु में तेजी से विकसित होते हैं।
Q3. Who developed the theory of cognitive development?
Answer: Jean Piaget.
संज्ञानात्मक विकास का सिद्धांत किसने विकसित किया? – जीन पियाजे।
Q4. What is the sensitive period in child development?
Answer: A phase when a child is particularly receptive to certain learning.
एक चरण जिसमें बच्चा विशेष प्रकार के सीखने के प्रति अधिक ग्रहणशील होता है।
Q5. What is scaffolding in child development?
Answer: Support provided by teachers to help children achieve goals they can’t reach alone.
शिक्षकों द्वारा बच्चों को ऐसी चीज़ें हासिल करने में मदद करने के लिए दिया गया समर्थन जो वे अकेले नहीं कर सकते।
Q6. What is meant by socialization?
Answer: The process through which children learn norms, values, and culture.
जिस प्रक्रिया से बच्चे मानदंड, मूल्य, और संस्कृति सीखते हैं।
Q7. Who proposed the ‘Zone of Proximal Development’?
Answer: Lev Vygotsky.
‘निकटतम विकास क्षेत्र’ का प्रस्ताव किसने किया? – लेव वायगोत्स्की।
Q8. What is the role of reinforcement in learning?
Answer: It encourages the repetition of a desired behavior.
यह एक वांछित व्यवहार की पुनरावृत्ति को प्रोत्साहित करता है।
Q9. What does ‘Child-Centered Education’ focus on?
Answer: The individual needs and interests of the child.
बच्चे की व्यक्तिगत जरूरतों और रुचियों पर ध्यान केंद्रित करता है।
Q10. Who is known for the theory of multiple intelligences?
Answer: Howard Gardner.
कौन बहु-बुद्धिमत्ता सिद्धांत के लिए जाना जाता है? – हॉवर्ड गार्डनर।
Q11. At what age does a child typically begin to speak?
Answer: Around 12-18 months.
लगभग 12-18 महीने की उम्र में।
Q12. What does the term ‘cognitive development’ refer to?
Answer: The development of thinking, reasoning, and understanding.
सोचने, तर्क करने और समझने के विकास को संदर्भित करता है।
Q13. What are ‘fine motor skills’?
Answer: Skills that involve small muscle movements, like holding a pencil.
छोटी मांसपेशियों की गतिविधियाँ, जैसे पेंसिल पकड़ना।
Q14. What is the main characteristic of the preoperational stage?
Answer: Egocentrism and symbolic thinking.
अहंकारी और प्रतीकात्मक सोच।
Q15. Who introduced the concept of ‘classical conditioning’?
Answer: Ivan Pavlov.
‘शास्त्रीय अनुबंधन’ की अवधारणा किसने दी? – इवान पावलोव।
Q16. What does ‘schema’ mean in cognitive development?
Answer: A framework or concept to organize and interpret information.
जानकारी को व्यवस्थित और व्याख्या करने के लिए एक ढांचा।
Q17. At what stage does a child develop object permanence?
Answer: Sensorimotor stage.
संवेदी-मोटर चरण में।
Q18. What is the importance of play in child development?
Answer: It fosters creativity, social skills, and cognitive development.
यह रचनात्मकता, सामाजिक कौशल और संज्ञानात्मक विकास को बढ़ावा देता है।
Q19. What is operant conditioning?
Answer: A learning process through rewards and punishments.
इनाम और दंड के माध्यम से सीखने की प्रक्रिया।
Q20. What is ‘positive reinforcement’?
Answer: Rewarding desired behavior to encourage its repetition.
वांछित व्यवहार को पुरस्कृत करके उसकी पुनरावृत्ति को प्रोत्साहित करना।
Q21. What is the purpose of formative assessment?
Answer: To monitor student learning and provide ongoing feedback.
छात्रों के सीखने की निगरानी और निरंतर प्रतिक्रिया देना।
Q22. What does the term ‘metacognition’ mean?
Answer: Awareness of one’s own thought processes.
अपने विचार प्रक्रियाओं की जागरूकता।
Q23. Who introduced the ‘Hierarchy of Needs’?
Answer: Abraham Maslow.
जरूरतों के पदानुक्रम का परिचय किसने दिया? – अब्राहम मैस्लो।
Q24. What is observational learning?
Answer: Learning by observing others.
दूसरों को देखकर सीखना।
Q25. What is intrinsic motivation?
Answer: Motivation driven by internal rewards and satisfaction.
आंतरिक इनाम और संतोष द्वारा संचालित प्रेरणा।
Q26. What is self-regulation in child development?
Answer: The ability to control one’s emotions, behavior, and thoughts.
अपनी भावनाओं, व्यवहार और विचारों को नियंत्रित करने की क्षमता।
Q27. At what age do children usually develop empathy?
Answer: Around age 4-5.
लगभग 4-5 वर्ष की उम्र में।
Q28. Who proposed the theory of moral development?
Answer: Lawrence Kohlberg.
नैतिक विकास का सिद्धांत किसने प्रस्तावित किया? – लॉरेंस कोहलबर्ग।
Q29. What is the main focus of Vygotsky’s theory?
Answer: The social context of learning.
सीखने का सामाजिक संदर्भ।
Q30. What is the concept of ‘readiness to learn’?
Answer: A state where the child is developmentally prepared to acquire new skills.
एक अवस्था जिसमें बच्चा नए कौशल सीखने के लिए विकासात्मक रूप से तैयार होता है।
Q31. What is divergent thinking?
Answer: The ability to generate multiple solutions to a problem.
किसी समस्या के कई समाधान उत्पन्न करने की क्षमता।
Q32. What does the term ‘holistic development’ refer to?
Answer: Development that encompasses physical, cognitive, and social-emotional growth.
शारीरिक, संज्ञानात्मक और सामाजिक-भावनात्मक विकास को समाहित करने वाला विकास।
Q33. What is a constructivist approach to learning?
Answer: Learning through active exploration and building one’s own knowledge.
सक्रिय अन्वेषण और अपनी जानकारी बनाने के माध्यम से सीखना।
Q34. What is peer learning?
Answer: Learning through interaction and collaboration with peers.
साथियों के साथ बातचीत और सहयोग के माध्यम से सीखना।
Q35. What is the role of curiosity in child development?
Answer: It drives exploration and learning.
यह अन्वेषण और सीखने को प्रेरित करता है।
Q36. What is the primary mode of learning in the sensorimotor stage?
Answer: Through senses and physical interactions.
इंद्रियों और शारीरिक बातचीत के माध्यम से।
Q37. What is the concept of ‘assimilation’ in Piaget’s theory?
Answer: Integrating new information into existing cognitive structures.
नई जानकारी को मौजूदा संज्ञानात्मक संरचनाओं में शामिल करना।
Q38. What does the term ‘zone of proximal development’ mean?
Answer: The gap between what a learner can do alone and what they can do with help.
जो एक शिक्षार्थी अकेले कर सकता है और जो सहायता से कर सकता है उसके बीच का अंतर।
Q39. What is the importance of routine for young children?
Answer: It provides structure, security, and helps in time management.
यह संरचना, सुरक्षा प्रदान करता है और समय प्रबंधन में मदद करता है।
Q40. What does the term ‘self-efficacy’ refer to?
Answer: Belief in one’s abilities to succeed.
अपने सफल होने की क्षमताओं में विश्वास।
Q41. What is observational learning based on?
Answer: Learning by observing the behavior of others.
दूसरों के व्यवहार का अवलोकन करके सीखना।
Q42. What is the impact of positive reinforcement?
Answer: It increases the likelihood of the desired behavior.
यह वांछित व्यवहार की संभावना को बढ़ाता है।
Q43. What is the role of a teacher in cooperative learning?
Answer: Facilitating and guiding group activities.
समूह गतिविधियों का संचालन और मार्गदर्शन करना।
Q44. What is the critical period in language development?
Answer: The phase during which language acquisition occurs most easily.
वह चरण जिसमें भाषा सीखना सबसे आसान होता है।
Q45. What is the concept of multiple intelligences?
Answer: Theory that suggests people have different kinds of intelligences.
सिद्धांत जो कहता है कि लोगों में अलग-अलग प्रकार की बुद्धिमत्ता होती है।
Q46. Who proposed the social learning theory?
Answer: Albert Bandura.
सामाजिक अधिगम सिद्धांत का प्रस्ताव किसने दिया? – अल्बर्ट बंडुरा।
Q47. What is intrinsic motivation?
Answer: Motivation that comes from internal satisfaction.
आंतरिक संतुष्टि से उत्पन्न प्रेरणा।
Q48. What is the purpose of assessment in learning?
Answer: To evaluate student understanding and progress.
छात्र की समझ और प्रगति का मूल्यांकन करना।
Q49. What does developmental psychology study?
Answer: It studies the growth and changes across the lifespan.
यह जीवनकाल में होने वाली वृद्धि और बदलावों का अध्ययन करता है।
Q50. How does environment affect child development?
Answer: It influences physical, emotional, and cognitive growth.
यह शारीरिक, भावनात्मक, और संज्ञानात्मक विकास को प्रभावित करता है।
