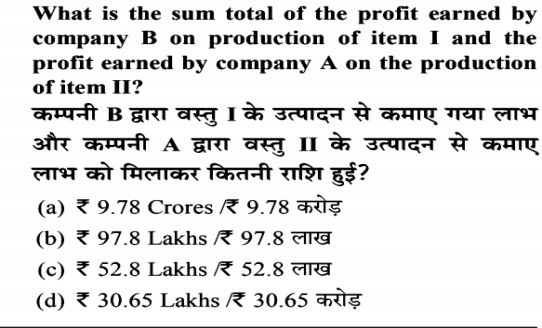
UGC NET 20th September 2022 Question Paper & Exam Analysis for both Shift 1 and Shift 2 will be provided below. UGC NET 12 July 2022 Paper 1 Memory-Based Question Paper will also be provided here.

UGC NET 20th September 2022 Question Paper: Day 4 of UGC NET 2022 examination is being conducted on Tuesday, Sep 20, 2022 while the other days are scheduled for October 2022 .Each day is held in two shifts from 9 AM to 12 PM and 3 PM to 6 PM. Phase 3 of UGC NET examination will be carried out later on October 1-14. UGC NET Phase 1 consists of 2 papers, Paper 1 and Paper 2. Out of these two, Paper 1 is the same for all while Paper 2 is subject-specific, carried out for a total of 82 subjects.
UGC NET 2022 Paper 1 and Paper 2 are conducted together for a duration of 180 minutes and it has a total of 50 questions which are unequally divided into 10 sections, the details of which are provided below along with the analysis UGC NET 12th July 2022. The weightage distribution of these sections is not pre-defined but rather changes from paper to paper. So, we have also included the section-wise number of questions asked in the exam while analyzing the paper.
UGC NET 20th September 2022 Highlights will Updated Soon !
UGC NET 20TH SEPTEMBER QUESTION PAPER & EXAM ANALYSIS
UGC NET 2022 Exam Analysis – Difficulty Level & Topic-wise Weightage
Candidates can refer to the table below to check the UGC NET 2022 exam analysis:
| UGC NET 2022 Exam – September 20, 2022 | ||||
| Subject/Paper | Topics with Maximum Number ofQuestions in UGC NET 2022 Exam | Number of Questions Asked | UGC NET 2022Difficulty Level | Good Attempts |
| Teaching Aptitude | 4-5 | Moderate | To be Announced | |
| Research Aptitude | To be Announced | 4-5 | Moderate | To be Announced |
| Comprehension | To be Announced | 5 | Easy | To be Announced |
| Logical Reasoning | To be Announced | 3-4 | Moderate | To be Announced |
| Data Interpretation | To be Announced | 5 | Moderate | To be Announced |
| Math’s/Reasoning | To be Announced | 3-4 | Moderate | To be Announced |
| Communication | To be Announced | 4-5 | Moderate | To be Announced |
| Environment | To be Announced | 4 | Easy to Moderate | To be Announced |
| Higher Education | To be Announced | 4-5 | Moderate | To be Announced |
| Information Technology | To be Announced | 3-4 | Moderate | To be Announced |
Question Asked in Exam (Memory Based )
Ans this Question in Comment Section or Telegram
Q2 Matching
IGNOU YEAR
NIRF
Q3 What are the advantages of Choice Based Credit System (CBCS) introduced by the UGC for
higher education institutions?
(A) Focuses on student-centric education
(B) Allows students to choose inter-disciplinary and intra-disciplinary courses.
(C) Makes education at par with global standards
(D) Makes it easy to estimate the performance levels of students in terms of marks.
(E) Offers flexibility for students to undertake studies at different times and at different
institutions.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
- (A), (B), (C), (D) only
- (B), (C), (D), (E ) only
- (A), (B), (C), (E) only
- (C), (D), (E), (A) only
उच्च शिक्षा संस्थानों के लिए यूजीसी द्वारा शुरू की गई च्वाइस बेस्ड क्रेडिट सिस्टम (सीबीसीएस) के क्या फायदे हैं ?
(ए) छात्र केंद्रित शिक्षा पर केंद्रित है
(बी) छात्रों को अंतःविषय और अंतःविषय पाठ्यक्रम चुनने की अनुमति देता है।
(सी) शिक्षा को वैश्विक मानकों के बराबर बनाता है
(डी) अंकों के संदर्भ में छात्रों के प्रदर्शन के स्तर का अनुमान लगाना आसान बनाता है।
(ई) छात्रों को अलग-अलग समय और विभिन्न संस्थानों में अध्ययन करने के लिए लचीलापन प्रदान करता है ।
नीचे दिए गए विकल्पों में से सही उत्तर चुनिए:
- (ए), (बी), (सी), (डी) केवल
- (बी), (सी), (डी), (ई) केवल
- (ए), (बी), (सी), (ई) केवल
- (सी), (डी), (ई), (ए) केवल
Option 3 : (A), (B), (C), (E) only
- यूजीसी [विश्वविद्यालय के रूप में संस्थान] विनियम, 2016 , कला, मानविकी के संकायों में गैर-औपचारिक / दूरस्थ शिक्षा के माध्यम से पहली डिग्री का अनुदान ।
- यूजीसी ने डिग्री की विशिष्टता के बारे में अधिसूचित किया (यूजीसी में प्रकाशित (उच्च शिक्षण संस्थानों का अनिवार्य मूल्यांकन और मान्यता ) ।
- मानव संसाधन विकास मंत्रालय (एचआरडी), सरकार। भारत सरकार ने भारतीय शिक्षा प्रणाली में सुधार लाने के लिए हमारे देश में नई शिक्षा नीति (एनईपी) विकसित करने की प्रक्रिया पहले ही शुरू कर दी है।
- विश्वविद्यालय अनुदान आयोग (यूजीसी) हमारे देश में राष्ट्रीय शिक्षा नीति विकसित करने, उसके क्रियान्वयन और उच्च शिक्षा को बढ़ावा देने में अधिक सक्रिय रूप से भाग लेता है।
- यूजीसी ने राष्ट्रीय उच्च शिक्षा प्रणाली में समानता, दक्षता और अकादमिक उत्कृष्टता लाने के लिए पहले ही कई कदम उठाए हैं ।
- महत्वपूर्ण बातों में नवाचार और पाठ्यक्रम में सुधार, पाठ्यक्रम, शिक्षण और शिक्षण अध्यापन, परीक्षा और शिक्षा प्रणाली में प्रतिमान बदलाव की शुरूआत शामिल है।
प्रमुख बिंदु
यूजीसी है, जो पसंद–आधारित क्रेडिट सिस्टम (सीबीसीएस) की प्रणाली की अनुमति देता है ताकि छात्र अपनी रुचियों और उद्देश्यों के आधार पर अंतःविषय, अंतर–अनुशासनात्मक और कौशल–आधारित पाठ्यक्रमों का चयन कर सकें ।
- यह तभी संभव हो सकता है जब एक अंतरराष्ट्रीय स्तर पर स्वीकृत प्रणाली , एक विकल्प-आधारित क्रेडिट प्रणाली (सीबीसीएस) को अपनाया जाए।
- च्वाइस-बेस्ड क्रेडिट सिस्टम न केवल मुख्य विषयों को सीखने के अवसर और रास्ते प्रदान करता है, बल्कि किसी व्यक्ति के समग्र विकास के लिए मुख्य विषयों से परे सीखने के अतिरिक्त रास्ते तलाशता है ।
- सीबीसीएस निस्संदेह हमें सर्वोत्तम अंतरराष्ट्रीय शैक्षणिक प्रथाओं के साथ हमारे पाठ्यक्रमों के लिए एक बेंचमार्क की सुविधा प्रदान करता है।
महत्वपूर्ण बिंदु
च्वाइस बेस्ड क्रेडिट सिस्टम के लाभ:
- शिक्षक–केंद्रित से छात्र–केंद्रित शिक्षा पर ध्यान केंद्रित करना।
- एक छात्र जितने क्रेडिट का सामना कर सकता है उतने क्रेडिट ले सकता है (किसी दिए गए सेमेस्टर में सभी पाठ्यक्रमों को दोहराए बिना यदि वे एक / अधिक पाठ्यक्रमों में असफल होते हैं)।
- सीबीसीएस छात्रों को इंटर–डिसिप्लिनरी, इंट्रा–डिसिप्लिनरी कोर्स, स्किल ओरिएंटेड पेपर (यहां तक कि उनकी सीखने की जरूरतों, रुचियों और योग्यता के अनुसार अन्य विषयों से) और छात्रों के लिए अधिक लचीलेपन का चयन करने की अनुमति देता है।
- सीबीसीएस शिक्षा को व्यापक और वैश्विक मानकों के अनुरूप बनाता है ।
- अद्वितीय संयोजनों को मिलाकर कोई भी क्रेडिट ले सकता है।
- उदाहरण के लिए, अर्थशास्त्र के साथ भौतिकी, रसायन विज्ञान के साथ सूक्ष्म जीव विज्ञान या पर्यावरण विज्ञान आदि।
- सीबीसीएस छात्रों को अलग-अलग समय पर और अलग-अलग संस्थानों में एक कोर्स (छात्रों की गतिशीलता में आसानी) को पूरा करने के लिए लचीलापन प्रदान करता है।
- एक संस्थान में अर्जित क्रेडिट को स्थानांतरित किया जा सकता है।
अतिरिक्त जानकारी
नुकसान :
- शिक्षकों के सटीक अंक और कार्यभार का अनुमान लगाना मुश्किल है जिसमें उतार-चढ़ाव हो सकता है।
- शिक्षा के प्रसार के लिए अच्छे बुनियादी ढांचे की मांग करें।
- सीबीसीएस छात्रों को कोर, वैकल्पिक/मामूली, या कौशल-आधारित पाठ्यक्रमों वाले निर्धारित पाठ्यक्रमों में से पाठ्यक्रम चुनने का अवसर प्रदान करता है ।
- पाठ्यक्रमों का मूल्यांकन ग्रेडिंग प्रणाली का अनुसरण करते हुए किया जा सकता है, जिसे पारंपरिक अंक प्रणाली से बेहतर माना जाता है।
- इसलिए, भारत में संपूर्ण उच्च शिक्षा में एक समान ग्रेडिंग प्रणाली लागू करना आवश्यक है ।
- इससे छात्रों को भारत के भीतर, शुरू में, और पूरे देशों में संस्थानों में जाने में लाभ होगा ।
इसलिए , हम कह सकते हैं कि उच्च शिक्षा संस्थानों के लिए यूजीसी द्वारा शुरू की गई च्वाइस बेस्ड क्रेडिट सिस्टम (सीबीसीएस) के लाभों को निम्नानुसार माना जा सकता है:
(ए) छात्र केंद्रित शिक्षा पर ध्यान केंद्रित करता है।
(बी) छात्रों को अंतःविषय और अंतःविषय पाठ्यक्रम चुनने की अनुमति देता है।
(सी) शिक्षा को वैश्विक मानकों के अनुरूप बनाता है।
(ई) छात्रों को अलग-अलग समय और विभिन्न संस्थानों में अध्ययन करने के लिए लचीलापन प्रदान करता है।
लेकिन विकल्प (डी): यूजीसी या किसी अन्य शैक्षणिक संस्थान का उद्देश्य नहीं होने वाले अंकों के आधार पर एक बच्चे का न्याय करने के लिए कहे गए अंकों के संदर्भ में छात्रों के प्रदर्शन के स्तर का अनुमान लगाना आसान बनाता है ।
Choice Based Credit System (CBCS) MCQ Question Detailed Solution
- UGC [Institutions Deemed to be Universities] Regulations, 2016, grant of first degree though non-formal / distance education in the faculties of Arts, Humanities.
- UGC Notified about Specification of Degrees (published in the UGC (Mandatory Assessment and accreditation of Higher Educational Institutions).
- Ministry of Human Resource Development (HRD), Govt. of India, has already initiated the process for developing New Education Policy (NEP) in our country to bring out reforms in the Indian education system.
- University Grants Commission (UGC) participates more actively in developing National Education Policy, its execution, and the promotion of higher education in our country.
- The UGC has already initiated several steps to bring equity, efficiency, and academic excellence in National Higher Education System.
- The important ones include innovation and improvement in course, curricula, the introduction of paradigm shift in learning and teaching pedagogy, examination and education system.
Key Points
There is UGC, which allows the system of the choice-based credit system (CBCS) so that students depending upon their interests and aims can choose interdisciplinary, intra-disciplinary, and skill-based courses.
- This can only be possible when a choice-based credit system (CBCS), an internationally acknowledged system, is adopted.
- The choice-based credit system not only offers opportunities and avenues to learn core subjects but also exploring additional avenues of learning beyond the core subjects for the holistic development of an individual.
- The CBCS undoubtedly facilitate us a benchmark our courses with the best international academic practices.
Important Points
Advantages of the choice based credit system:
- The shift in focus from the teacher-centric to student-centric education.
- A student may undertake as many credits as they can cope with (without repeating all courses in a given semester if they fail in one/more courses).
- CBCS allows students to choose inter-disciplinary, intra-disciplinary courses, skill oriented papers (even from other disciplines according to their learning needs, interests, and aptitude), and more flexibility for students).
- CBCS makes education broad-based and at par with global standards.
- One can take credits by combining unique combinations.
- For example, Physics with Economics, Microbiology with Chemistry or Environment Science, etc.
- CBCS offers flexibility for students to study at different times and at different institutions to complete one course (ease mobility of students).
- Credits earned at one institution can be transferred.
Additional Information
Disadvantages:
- Difficult to estimate the exact marks and Workload of teachers that may fluctuate.
- Demand good infrastructure for the dissemination of education.
- The CBCS provides an opportunity for the students to choose courses from the prescribed courses comprising core, elective/minor, or skill-based courses.
- The courses can be evaluated following the grading system, which is considered to be better than the conventional marks system.
- Therefore, it is necessary to introduce a uniform grading system in the entire higher education in India.
- This will benefit the students to move across institutions within India, to begin with, and across countries.
Hence, we may say that the advantages of Choice Based Credit System (CBCS) introduced by the UGC for higher education institutions can be considered as follows:
(A) Focuses on student-centric education.
(B) Allows students to choose inter-disciplinary and intra-disciplinary courses.
(C) Makes education at par with global standards.
(E) Offers flexibility for students to undertake studies at different times and at different institutions.
But option (D): Makes it easy to estimate the performance levels of students in terms of marks said to judge a child based on the marks that are not the purpose of UGC or any other educational institution.
Q Hexa decimal to Decimal
Convert (E8B)16 to decimal system.
Solution:
(E8B)16
Here,
E = 14
8 = 8
B = 11
Thus,
(E8B)16 = (14 × 162) + (8 × 161) + (11 × 160)
= (14 × 256) + (8 × 16) + (11 × 1)
= 3584 + 128 + 11
= 3723
Therefore, (E8B)16 = (3723)10
Q Fastest Download Speed
16 GB 64 MB
Q Selective Communication
UGC NET Exam Highlights 2022 (UGC NET 12th July 2022 Paper 1 Question Paper Analysis)
Candidates can check the UGC NET exam highlights for the exam. It is important to know the details that are related to the exam.
- The NTA will administer the UGC NET Exam in online mode.
- The exam will be a computer-based test and the exam shall be conducted in two shifts.
- The UGC NET exam timings 2022 for both the shifts are
- UGC NET exam 2022 – Shift 1: 09:00 AM to 12:00 PM
- UGC NET exam 2022 – Shift 2: 03:00 PM to 06:00 PM
UGC NET 11th July 2022 Paper 1 Question Paper Analysis; Major Highlights
Major highlights of the 11th July examination has been updated here in due time after the conclusion of the exam.
Overall Difficulty Level of Shift 1: Moderate
Overall Difficulty Level of Shift 2: To be Updated
Expected Good Score of Shift 1: 33-35
Expected Good Score of Shift 2: To be Updated Was Shift 1 Paper Time-Consuming? No
Was Shift 2 Paper Time-Consuming? To be Updated
Shift 1 vs Shift 2 Analysis Comparison: To be Updated
UGC NET Exam Analysis Difficulty Level [July 12, 2022]
Check the section-wise difficulty level of UGC NET Paper 1 hereafter the exam. Candidates who have exams in upcoming shifts must check the difficulty level of the exam.
UGC NET 12th July 2022 Paper 1 Question Paper Shift1 & 2 Analysis, Answer Key, Solutions
UGC NET 12th July 2022 Paper 1 Shift 1 & 2 Question Paper Analysis; Major Highlights
Major highlights of the 12th July examination has been updated here in due time after the conclusion of the exam.
Overall Difficulty Level of Shift 1: Moderate
Overall Difficulty Level of Shift 2: To be Updated
Expected Good Score of Shift 1: 32-37
Expected Good Score of Shift 2: To be Updated
Was Shift 1 Paper Time-Consuming? No
Was Shift 2 Paper Time-Consuming? To be Updated
Shift 1 vs Shift 2 Analysis Comparison:
UGC NET 12th July 2022 Paper 1 Question Paper Analysis: Shift 1 & 2
The combined analysis of both shifts has been detailed in the table below:
| Section | Difficulty Level | Number of Questions Asked in the Exam | Topics with Highest Weightage |
| Communication | Moderate | 7+8 | Liner Communication,Communication Sequence ,theory of communication , Verbal & Non Verbal ,Classroom communication |
| Data Interpretation | Easy to Moderate | 10 | % Percentage |
| Information and Communication Technology (ICT) | Moderate | 4-5 | Internet Yahoo,Bing Search Engine ,Malicious Software, Cache Memory,Coding ,Firewall Matching,HTTPL |
| Logical Reasoning | Easy | 5-6 | Syllogism, Moods, Figuers, Square of Opposition ,Indian logic assertion Reason, Hetu Related Question ,Contrary ,Sub Contrary |
| Mathematics | Easy | 4-5 | Ratio, Average, Percentage ,Number System,Simple Interest ,Pipeline Related Question |
| People and Environment | Easy | 5-6 | Natural Disaster ,Co2 Emission ,Methane ,Green Hydrozen ,SDG Goal 1.2,3,4 ,Air Pollutants ,Solar Energy ,Carbon Mono oxide ,Green House Effect ,Kyoto Protocol,Bio diversity, Matching -Paris Agreement ,Noise level |
| Reading Comprehension | Easy | 2/1 | |
| Research Aptitude | Easy | 4-5 | Types of Research , Quantitative & Qualitative Research,Hypothesis MODEM ,Sampling ,Type & Step of Research ,Plagiarism ,Hypothesis ,T test |
| Teaching Aptitude | Moderate | 4-5 | Teacher Characteristics ,effective teaching ,teacher centered methods of teaching , |
| Higher Education System: Governance, Polity, Administration, and Current Affairs | Easy | 4-5 | SWAYAM,MOOC Statement Wise ,Kothari Commision Chairmen ,NEP 2020 Assertion Reason ,Stuatory body ,INFLIBNET*E PG pathshala ,Skill development Agency , National E governance ,Online Learning |
Question Asked In Today Session –
Which Chinese visited Nalanda University?
traveller Hiuen Tsang
Chinese traveler memorial Hall. This hall is constructed in memory of a Chinese traveller Hiuen Tsang who visited Nalanda university as a part of his India visit in the period of 633AD. He stayed here for twelve long years during the Gupta dynasty rule and did his research study on Buddhism and mysticism.
Which Chinese scholar came to Nalanda university?
Xuanzang memorial
Xuanzang, the Chinese Buddhist monk reached India to learn about the tenets propagated by Chinese philosopher Confucius (551-479 BC). He spent five years as a student at Nalanda and taught here for a year.
| Rabindra Nath Tagore’s Legacy for Inclusive Education, Ecological Awareness & Intercultural Understanding |
Firewall-
Spy Ware-
Bluetooth-
Sequence RAM Installation
Choose Option Which is One Way Communication
Mass Media
Work of GateKeeper
Which is not Affective Domain
Formative & Summative Statement
Diagnostic /Peer Based
Curriculam
Anuman ,Nyaya
All deposits received under National Saving Schemes are credited to the National Small Saving Fund (NSSF) – a public account established w.e.f 1.4. 1999. All withdrawals by the depositors are made out of the accumulations in the fund.
राष्ट्रीय बचत योजनाओं के तहत प्राप्त सभी जमाराशियों को राष्ट्रीय लघु बचत कोष (एनएसएसएफ) में जमा किया जाता है – एक सार्वजनिक खाता जिसे 1.4.2014 से स्थापित किया गया था। 1999. जमाकर्ताओं द्वारा सभी निकासी फंड में जमा राशि से की जाती है।
Which type of communiation has the least possible chance of making errors ?
Written Communication
Communication Barrier Matching
Blog -Matching Social media
SWAYAM full form ?
SWAYAM (Study Webs of Active–Learning for Young Aspiring Minds) is a programme initiated by Government of India and designed to achieve the three cardinal principles of Education Policy viz., access, equity and quality.
Countries That Are Not Part Of The Paris Climate Agreement
- There are 8 countries that are not currently a part of the Paris Climate Agreement.
- Lebanon and Kyrgyzstan are the most recent countries to ratify the agreement as of February, 2020.
- Turkey is now the only G20 member to not be a member of the Paris Climate Agreement.
Which is not in Affective Domain ?
National Skill Development Agency (NSDA)
National Skill Development Agency (NSDA) is an autonomous body registered as a society under the Societies Registration Act, 1860, under the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship. It anchors the National Skills Qualifications Framework (NSQF) and allied quality assurance mechanisms for synergizing skill initiatives in the country.
As per the Gazette Notification dated June 6, 2013, NSDA is mandated to discharge the following functions:
- Take all possible steps to meet skilling targets as envisaged in the 12th Five Year Plan and beyond.
- Coordinate and harmonize the approach to skill development among various Central Ministries/Department, State Governments, NSDC and the private sector.
- Anchor and operationalize the NSQF to ensure that quality and standards meet sector specific requirements.
- Be the nodal agency for State Skill Development Missions.
- Raise extra-budgetary resources for skill development from various sources such as international agencies, including multi-lateral agencies, and the private sector.
- Evaluate existing skill development schemes with a view to assessing their efficacy and suggest corrective action to make them more effective.
- Create and maintain a national data base related to skill development including development of a dynamic Labour Market Information System (LMIS).
- Take affirmative action for advocacy.
- Ensure that the skilling needs of the disadvantaged and the marginalized groups like SCs, STs, OBCs, minorities, women and differently abled persons are taken care of.
- Discharge any other function as may be assigned to it by the Government of India.
National Skills Qualifications Framework (NSQF)
The National Skills Qualifications Framework (NSQF) gazette notification dated 27th Dec 2013 defines Qualification as ‘a formal outcome of an assessment & validation process which is obtained when a competent body determines that an individual has achieved learning outcomes to given standards’.
The NSQF is anchored in National Skill Development Agency (NSDA) and is implemented through the National Skill Qualification Committee (NSQC). A permanent secretariat for NSQC is set up in NSDA.
राष्ट्रीय कौशल विकास एजेंसी (एनएसडीए)
राष्ट्रीय कौशल विकास एजेंसी (NSDA) कौशल विकास और उद्यमिता मंत्रालय के तहत सोसायटी पंजीकरण अधिनियम, 1860 के तहत एक सोसायटी के रूप में पंजीकृत एक स्वायत्त निकाय है। यह देश में कौशल पहलों के तालमेल के लिए राष्ट्रीय कौशल योग्यता फ्रेमवर्क (एनएसक्यूएफ) और संबद्ध गुणवत्ता आश्वासन तंत्र की एंकरिंग करता है।
6 जून 2013 की राजपत्र अधिसूचना के अनुसार, एनएसडीए को निम्नलिखित कार्यों का निर्वहन करना अनिवार्य है:
- 12वीं पंचवर्षीय योजना और उसके बाद के परिकल्पित कौशल लक्ष्यों को पूरा करने के लिए सभी संभव कदम उठाएं।
- विभिन्न केंद्रीय मंत्रालयों/विभागों, राज्य सरकारों, एनएसडीसी और निजी क्षेत्र के बीच कौशल विकास के दृष्टिकोण में समन्वय और सामंजस्य स्थापित करना।
- यह सुनिश्चित करने के लिए कि गुणवत्ता और मानक क्षेत्र विशेष की आवश्यकताओं को पूरा करते हैं, एनएसक्यूएफ का संचालन और संचालन करना।
- राज्य कौशल विकास मिशनों के लिए नोडल एजेंसी बनें।
- बहु-पक्षीय एजेंसियों और निजी क्षेत्र सहित अंतरराष्ट्रीय एजेंसियों जैसे विभिन्न स्रोतों से कौशल विकास के लिए अतिरिक्त बजटीय संसाधन जुटाएं।
- मौजूदा कौशल विकास योजनाओं की प्रभावशीलता का आकलन करने की दृष्टि से उनका मूल्यांकन करना और उन्हें अधिक प्रभावी बनाने के लिए सुधारात्मक कार्रवाई का सुझाव देना।
- एक गतिशील श्रम बाजार सूचना प्रणाली (एलएमआईएस) के विकास सहित कौशल विकास से संबंधित एक राष्ट्रीय डेटा बेस बनाना और बनाए रखना।
- वकालत के लिए सकारात्मक कार्रवाई करें।
- अनुसूचित जाति, अनुसूचित जनजाति, अन्य पिछड़ा वर्ग, अल्पसंख्यकों, महिलाओं और अलग-अलग विकलांग व्यक्तियों जैसे वंचित और हाशिए के समूहों की कौशल आवश्यकताओं का ध्यान रखना सुनिश्चित करें।
- भारत सरकार द्वारा सौंपे गए किसी अन्य कार्य का निर्वहन करना।
राष्ट्रीय कौशल योग्यता फ्रेमवर्क (एनएसक्यूएफ)
राष्ट्रीय कौशल योग्यता फ्रेमवर्क (एनएसक्यूएफ) राजपत्र अधिसूचना दिनांक 27 दिसंबर 2013 योग्यता को ‘एक मूल्यांकन और सत्यापन प्रक्रिया के औपचारिक परिणाम के रूप में परिभाषित करती है जो तब प्राप्त होती है जब एक सक्षम निकाय यह निर्धारित करता है कि किसी व्यक्ति ने दिए गए मानकों के लिए सीखने के परिणाम प्राप्त किए हैं’।
NSQF को राष्ट्रीय कौशल विकास एजेंसी (NSDA) में शामिल किया गया है और इसे राष्ट्रीय कौशल योग्यता समिति (NSQC) के माध्यम से कार्यान्वित किया जाता है। एनएसडीए में एनएसक्यूसी के लिए एक स्थायी सचिवालय स्थापित किया गया है।
What is HTTP L?
This technique is called “pipelining in HTTP. HTTP/l. 1 also enables transport compression of data types so those clients can retrieve HTML (or other) uncompressed documents using data compression; HTTP/l
HTTP एल क्या है?
इस तकनीक को “HTTP में पाइपलाइनिंग” कहा जाता है। एचटीटीपी/एल. 1 डेटा प्रकारों के परिवहन संपीड़न को भी सक्षम बनाता है ताकि वे क्लाइंट डेटा संपीड़न का उपयोग करके HTML (या अन्य) असम्पीडित दस्तावेज़ों को पुनः प्राप्त कर सकें ; एचटीटीपी/एल.
What is use of HTTP protocol?
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is an application-layer protocol for transmitting hypermedia documents, such as HTML. It was designed for communication between web browsers and web servers, but it can also be used for other purposes
HTTP प्रोटोकॉल का उपयोग क्या है?
हाइपरटेक्स्ट ट्रांसफर प्रोटोकॉल (HTTP) हाइपरमीडिया दस्तावेज़ों को प्रसारित करने के लिए एक एप्लिकेशन–लेयर प्रोटोकॉल है, जैसे कि HTML । इसे वेब ब्राउज़र और वेब सर्वर के बीच संचार के लिए डिज़ाइन किया गया था, लेकिन इसका उपयोग अन्य उद्देश्यों के लिए भी किया जा सकता है
What is E PG pathshala?
What is E Pg Pathshala e-PGPathshala is a one portal under which High quality, curriculum- based,interactive content in different subjects across all disciplines of social sciences, arts, fine arts & humanities, natural & mathematical sciences, linguistics and languages is being developed.
ई पीजी पाठशाला क्या है?
ई पीजी पाठशाला क्या है ई-पीजीपाठशाला एक पोर्टल है जिसके तहत सामाजिक विज्ञान, कला, ललित कला और मानविकी, प्राकृतिक और गणितीय विज्ञान, भाषा विज्ञान और भाषाओं के सभी विषयों में विभिन्न विषयों में उच्च गुणवत्ता, पाठ्यक्रम-आधारित, इंटरैक्टिव सामग्री उपलब्ध कराई जा रही है
Who started e pathshala?
E-Pathshala has been developed by NCERT for showcasing and disseminating all educational e-resources including textbooks, audio, video, periodicals and a variety of other print and non-print materials through website and mobile app
ई पाठशाला किसने शुरू की?
वेबसाइट और मोबाइल ऐप के माध्यम से पाठ्यपुस्तकों, ऑडियो, वीडियो, पत्रिकाओं और विभिन्न प्रकार की अन्य प्रिंट और गैर-प्रिंट सामग्री सहित सभी शैक्षिक ई-संसाधनों को प्रदर्शित और प्रसारित करने के लिए एनसीईआरटी द्वारा ई-पाठशाला विकसित की गई है
Types of Evaluation:
| Placement Evaluation | Formative Evaluation | Diagnostic Evaluation | Summative Evaluation |
| It is conducted before the teaching-learning process to analyse the previous knowledge of learners. | It is conducted more than once during the teaching-learning process to improve and enhance learning. | It is conducted along with the formative assessment to solve student’s problems relate to learning. | It is conducted at the end/terminal point of the teaching-learning process to grade or rank the learners. |
| This assessment can be done through various entrance tests such as GMAT, CAT, etc. | This assessment is done through class tests, field trips, quiz, debate, discussions, role plays, etc. | This assessment is done through a diagnostic remedial test. | The ways of conducting such assessments include a written exam at the end of the term. |
मूल्यांकन के प्रकार:
| प्लेसमेंट मूल्यांकन | निर्माणात्मक मूल्यांकन | नैदानिक मूल्यांकन | योगात्मक मूल्यांकन |
| यह शिक्षार्थियों के पिछले ज्ञान का विश्लेषण करने के लिए शिक्षण–अधिगम प्रक्रिया से पहले आयोजित किया जाता है। | यह सीखने-सिखाने की प्रक्रिया के दौरान सीखने को बेहतर बनाने और बढ़ाने के लिए एक से अधिक बार आयोजित किया जाता है। | यह सीखने से संबंधित छात्र की समस्याओं को हल करने के लिए रचनात्मक मूल्यांकन के साथ आयोजित किया जाता है। | यह शिक्षार्थियों को ग्रेड या रैंक देने के लिए शिक्षण–अधिगम प्रक्रिया के अंत/टर्मिनल बिंदु पर आयोजित किया जाता है । |
| यह मूल्यांकन विभिन्न प्रवेश परीक्षाओं जैसे जीमैट, कैट, आदि के माध्यम से किया जा सकता है। | यह मूल्यांकन कक्षा परीक्षण, फील्ड ट्रिप, प्रश्नोत्तरी, वाद-विवाद, चर्चा, रोल प्ले आदि के माध्यम से किया जाता है। | यह मूल्यांकन एक नैदानिक उपचारात्मक परीक्षण के माध्यम से किया जाता है। | इस तरह के आकलन करने के तरीकों में कार्यकाल के अंत में एक लिखित परीक्षा शामिल है |
सितंबर 2015 में, महासभा ने सतत विकास के लिए 2030 एजेंडा को अपनाया जिसमें 17 सतत विकास लक्ष्य (एसडीजी) शामिल हैं। “किसी को पीछे नहीं छोड़ना” के सिद्धांत पर निर्माण, नया एजेंडा सभी के लिए सतत विकास प्राप्त करने के लिए एक समग्र दृष्टिकोण पर जोर देता है।
एसडीजी में स्पष्ट रूप से विकलांगता और विकलांग व्यक्तियों को 11 बार शामिल किया गया है । विकलांगता को एसडीजी के कई हिस्सों में संदर्भित किया जाता है, विशेष रूप से शिक्षा, विकास और रोजगार, असमानता, मानव बस्तियों की पहुंच, साथ ही डेटा संग्रह और एसडीजी की निगरानी से संबंधित भागों में।
हालांकि, “विकलांगता” शब्द को सभी लक्ष्यों में सीधे तौर पर उद्धृत नहीं किया गया है, लक्ष्य वास्तव में विकलांग व्यक्तियों के समावेश और विकास को सुनिश्चित करने के लिए प्रासंगिक हैं।
सतत विकास के लिए नव कार्यान्वित 2030 एजेंडा हर जगह विकलांग व्यक्तियों के लिए एक गहरा वादा रखता है।
वर्ष 2016 एसडीजी के कार्यान्वयन का पहला वर्ष है। इस महत्वपूर्ण बिंदु पर, #Envision2030 निम्नलिखित उद्देश्यों के साथ विकलांगता की मुख्य धारा को बढ़ावा देने और एसडीजी के 15 साल के जीवनकाल में कार्यान्वयन को बढ़ावा देने के लिए काम करेगा:
- 2030 एजेंडा और विकलांग व्यक्तियों के लिए एसडीजी की उपलब्धि के बारे में जागरूकता बढ़ाना;
- विकलांग व्यक्तियों के लिए एक बेहतर दुनिया बनाने की दृष्टि से एसडीजी पर हितधारकों के बीच सक्रिय संवाद को बढ़ावा देना; तथा
- प्रत्येक एसडीजी और विकलांगता पर एक सतत लाइव वेब संसाधन स्थापित करें।
In September 2015, the General Assembly adopted the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development that includes 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Building on the principle of “leaving no one behind”, the new Agenda emphasizes a holistic approach to achieving sustainable development for all.
The SDGs also explicitly include disability and persons with disabilities 11 times. Disability is referenced in multiple parts of the SDGs, specifically in the parts related to education, growth and employment, inequality, accessibility of human settlements, as well as data collection and the monitoring of the SDGs.
Although, the word “disability” is not cited directly in all goals, the goals are indeed relevant to ensure the inclusion and development of persons with disabilities.
The newly implemented 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development holds a deep promise for persons with disabilities everywhere.
The year 2016 marks the first year of the implementation of the SDGs. At this critical point, #Envision2030 will work to promote the mainstreaming of disability and the implementation of the SDGs throughout its 15-year lifespan with objectives to:
- Raise awareness of the 2030 Agenda and the achievement of the SDGs for persons with disabilities;
- Promote an active dialogue among stakeholders on the SDGs with a view to create a better world for persons with disabilities; and
- Establish an ongoing live web resource on each SDG and disability.
हमारी दुनिया को बदलने के लिए 17 सतत विकास लक्ष्य (एसडीजी):
लक्ष्यों को
- 2030 तक, हर जगह सभी लोगों के लिए अत्यधिक गरीबी का उन्मूलन, वर्तमान में 1.25 डॉलर प्रतिदिन से कम पर जीने वाले लोगों के रूप में मापा जाता है।
- 2030 तक, राष्ट्रीय परिभाषाओं के अनुसार गरीबी में जीवन यापन करने वाले सभी उम्र के पुरुषों, महिलाओं और बच्चों के अनुपात को कम से कम आधा कर दें।
- फर्श सहित सभी के लिए राष्ट्रीय स्तर पर उपयुक्त सामाजिक सुरक्षा प्रणालियों और उपायों को लागू करें , और 2030 तक गरीबों और कमजोर लोगों के लिए पर्याप्त कवरेज प्राप्त करें ।
- 2030 तक, सुनिश्चित करें कि सभी पुरुषों और महिलाओं, विशेष रूप से गरीब और कमजोर लोगों के पास आर्थिक संसाधनों के समान अधिकार हैं , साथ ही साथ बुनियादी सेवाओं तक पहुंच, भूमि पर स्वामित्व और नियंत्रण और 13 संपत्ति, विरासत, प्राकृतिक संसाधनों के अन्य रूपों, सूक्ष्म वित्त सहित उपयुक्त नई प्रौद्योगिकी और वित्तीय सेवाएं।
- 2030 तक, गरीबों और कमजोर परिस्थितियों में उनके लचीलेपन का निर्माण करें और जलवायु से संबंधित चरम घटनाओं और अन्य आर्थिक, सामाजिक और पर्यावरणीय झटकों और आपदाओं के लिए उनके जोखिम और भेद्यता को कम करें।
- विकासशील देशों, विशेष रूप से कम से कम विकसित देशों के लिए, सभी आयामों में गरीबी को समाप्त करने के लिए कार्यक्रमों और नीतियों को लागू करने के लिए पर्याप्त और अनुमानित साधन प्रदान करने के लिए, विभिन्न प्रकार के स्रोतों से संसाधनों की महत्वपूर्ण गतिशीलता सुनिश्चित करना, जिसमें विकास सहयोग शामिल है।
- गरीबी उन्मूलन कार्यों में त्वरित निवेश का समर्थन करने के लिए, गरीब-समर्थक और लिंग-संवेदनशील विकास रणनीतियों के आधार पर राष्ट्रीय, क्षेत्रीय और अंतर्राष्ट्रीय स्तर पर ठोस नीतिगत ढांचे का निर्माण करना।
लक्ष्यों को
- 2030 तक, भूख को समाप्त करना और सभी लोगों, विशेष रूप से गरीबों और शिशुओं सहित कमजोर परिस्थितियों में लोगों तक पूरे वर्ष सुरक्षित, पौष्टिक और पर्याप्त भोजन तक पहुंच सुनिश्चित करना।
- 2030 तक, 5 वर्ष से कम उम्र के बच्चों में स्टंटिंग और वेस्टिंग पर अंतरराष्ट्रीय स्तर पर सहमत लक्ष्यों को प्राप्त करने सहित, कुपोषण के सभी रूपों को समाप्त करना, और किशोर लड़कियों, गर्भवती और स्तनपान कराने वाली महिलाओं और वृद्ध व्यक्तियों की पोषण संबंधी जरूरतों को पूरा करना।
- 2030 तक, कृषि उत्पादकता और छोटे पैमाने के खाद्य उत्पादकों, विशेष रूप से महिलाओं, स्वदेशी लोगों, परिवार के किसानों, चरवाहों और मछुआरों की आय को दोगुना करना, जिसमें भूमि तक सुरक्षित और समान पहुंच, अन्य उत्पादक संसाधन और इनपुट, ज्ञान, वित्तीय सेवाएं शामिल हैं। मूल्यवर्धन और गैर-कृषि रोजगार के लिए बाजार और अवसर
- 2030 तक, स्थायी खाद्य उत्पादन प्रणाली सुनिश्चित करें और उत्पादकता और उत्पादन बढ़ाने वाली लचीली कृषि प्रथाओं को लागू करें, जो पारिस्थितिक तंत्र को बनाए रखने में मदद करें, जो जलवायु परिवर्तन, चरम मौसम, सूखा, बाढ़ और अन्य आपदाओं के अनुकूलन की क्षमता को मजबूत करें और जो भूमि और मिट्टी की गुणवत्ता में उत्तरोत्तर सुधार करें।
- 2020 तक, राष्ट्रीय, क्षेत्रीय और अंतर्राष्ट्रीय स्तरों पर अच्छी तरह से प्रबंधित और विविध बीज और पौधों के बैंकों के माध्यम से बीजों, खेती वाले पौधों और खेती और पालतू जानवरों और उनकी संबंधित जंगली प्रजातियों की आनुवंशिक विविधता को बनाए रखें, और निष्पक्ष और न्यायसंगत पहुंच को बढ़ावा दें। आनुवंशिक संसाधनों और संबद्ध पारंपरिक ज्ञान के उपयोग से उत्पन्न होने वाले लाभों को साझा करना, जैसा कि अंतरराष्ट्रीय स्तर पर सहमति है
- विकासशील देशों, विशेष रूप से कम विकसित देशों में कृषि उत्पादन क्षमता बढ़ाने के लिए ग्रामीण बुनियादी ढांचे, कृषि अनुसंधान और विस्तार सेवाओं, प्रौद्योगिकी विकास और संयंत्र और पशुधन जीन बैंकों में अंतर्राष्ट्रीय सहयोग के माध्यम से निवेश बढ़ाना, व्यापार प्रतिबंधों और विकृतियों को ठीक करना और रोकना दोहा विकास दौर के जनादेश के अनुसार, कृषि निर्यात सब्सिडी के सभी रूपों के समानांतर उन्मूलन और समान प्रभाव वाले सभी निर्यात उपायों सहित विश्व कृषि बाजार
- खाद्य जिंस बाजारों और उनके डेरिवेटिव के उचित कामकाज को सुनिश्चित करने के उपायों को अपनाना और खाद्य भंडार सहित बाजार की जानकारी तक समय पर पहुंच की सुविधा प्रदान करना, ताकि अत्यधिक खाद्य मूल्य अस्थिरता को सीमित करने में मदद मिल सके।
लक्ष्य 3: अच्छा स्वास्थ्य और कल्याण
लक्ष्यों को
- 2030 तक, वैश्विक मातृ मृत्यु अनुपात को कम करके प्रति 100,000 जीवित जन्मों पर 70 से कम करना
- 2030 तक, नवजात शिशुओं और 5 वर्ष से कम उम्र के बच्चों की रोकी जा सकने वाली मौतों को समाप्त करें, सभी देशों का लक्ष्य नवजात मृत्यु दर को कम से कम प्रति 1,000 जीवित जन्मों पर कम से कम 12 और 5 वर्ष से कम उम्र के बच्चों की मृत्यु दर को कम से कम 25 प्रति 1,000 जीवित पर लाना है। जन्मों
- 2030 तक, एड्स, तपेदिक, मलेरिया और उपेक्षित उष्णकटिबंधीय रोगों की महामारियों को समाप्त करना और हेपेटाइटिस, जल जनित रोगों और अन्य संचारी रोगों का मुकाबला करना
- 2030 तक, रोकथाम और उपचार के माध्यम से गैर-संचारी रोगों से समय से पहले होने वाली मृत्यु दर को एक तिहाई तक कम करना और मानसिक स्वास्थ्य और कल्याण को बढ़ावा देना
- मादक द्रव्यों के सेवन और शराब के हानिकारक उपयोग सहित मादक द्रव्यों के सेवन की रोकथाम और उपचार को सुदृढ़ बनाना
- 2020 तक, सड़क यातायात दुर्घटनाओं से होने वाली वैश्विक मौतों और चोटों की संख्या को आधा कर दें 3.7
- 2030 तक, परिवार नियोजन, सूचना और शिक्षा, और राष्ट्रीय रणनीतियों और कार्यक्रमों में प्रजनन स्वास्थ्य के एकीकरण सहित यौन और प्रजनन स्वास्थ्य देखभाल सेवाओं तक सार्वभौमिक पहुंच सुनिश्चित करें।
- वित्तीय जोखिम संरक्षण, गुणवत्तापूर्ण आवश्यक स्वास्थ्य देखभाल सेवाओं तक पहुंच और सभी के लिए सुरक्षित, प्रभावी, गुणवत्ता और सस्ती आवश्यक दवाओं और टीकों तक पहुंच सहित सार्वभौमिक स्वास्थ्य कवरेज प्राप्त करना
- 2030 तक, खतरनाक रसायनों और वायु, जल और मृदा प्रदूषण और संदूषण से होने वाली मौतों और बीमारियों की संख्या को काफी हद तक कम करना
- तंबाकू नियंत्रण पर विश्व स्वास्थ्य संगठन फ्रेमवर्क कन्वेंशन के कार्यान्वयन को सभी देशों में, जैसा उपयुक्त हो, मजबूत बनाना
- प्राथमिक रूप से विकासशील देशों को प्रभावित करने वाले संचारी और गैर-संचारी रोगों के लिए टीकों और दवाओं के अनुसंधान और विकास का समर्थन करना, ट्रिप्स समझौते और सार्वजनिक स्वास्थ्य पर दोहा घोषणा के अनुसार सस्ती आवश्यक दवाओं और टीकों तक पहुंच प्रदान करना, जो विकास के अधिकार की पुष्टि करता है। देशों को सार्वजनिक स्वास्थ्य की रक्षा के लिए लचीलेपन के संबंध में बौद्धिक संपदा अधिकारों के व्यापार संबंधी पहलुओं पर समझौते के प्रावधानों का पूरा उपयोग करने के लिए, और विशेष रूप से, सभी के लिए दवाओं तक पहुंच प्रदान करना
- विकासशील देशों, विशेष रूप से कम विकसित देशों और छोटे द्वीप विकासशील राज्यों में स्वास्थ्य वित्त पोषण और भर्ती, विकास, प्रशिक्षण और स्वास्थ्य कर्मचारियों की अवधारण में पर्याप्त वृद्धि
- राष्ट्रीय और वैश्विक स्वास्थ्य जोखिमों की पूर्व चेतावनी, जोखिम में कमी और प्रबंधन के लिए सभी देशों, विशेष रूप से विकासशील देशों की क्षमता को मजबूत करना
लक्ष्य 4: गुणवत्तापूर्ण शिक्षा
लक्ष्यों को
- 2030 तक, सुनिश्चित करें कि सभी लड़कियां और लड़के मुफ्त, समान और गुणवत्ता वाली प्राथमिक और माध्यमिक शिक्षा पूरी करें, जिससे प्रासंगिक और लक्ष्य-4 प्रभावी शिक्षण परिणाम प्राप्त करें।
- 2030 तक, सुनिश्चित करें कि सभी लड़कियों और लड़कों की गुणवत्ता प्रारंभिक बचपन के विकास, देखभाल और प्रारंभिक शिक्षा तक पहुंच हो ताकि वे प्राथमिक शिक्षा के लिए तैयार हो सकें।
- 2030 तक, विश्वविद्यालय सहित सभी महिलाओं और पुरुषों के लिए सस्ती और गुणवत्तापूर्ण तकनीकी, व्यावसायिक और तृतीयक शिक्षा तक समान पहुंच सुनिश्चित करना
- 2030 तक, रोजगार, अच्छी नौकरियों और उद्यमिता के लिए तकनीकी और व्यावसायिक कौशल सहित प्रासंगिक कौशल रखने वाले युवाओं और वयस्कों की संख्या में पर्याप्त वृद्धि करना।
- 2030 तक, शिक्षा में लैंगिक असमानताओं को समाप्त करना और विकलांग व्यक्तियों, स्वदेशी लोगों और कमजोर परिस्थितियों में बच्चों सहित कमजोर लोगों के लिए शिक्षा और व्यावसायिक प्रशिक्षण के सभी स्तरों तक समान पहुंच सुनिश्चित करना।
- 2030 तक, सुनिश्चित करें कि सभी युवा और वयस्कों का पर्याप्त अनुपात, दोनों पुरुष और महिलाएं, साक्षरता और संख्यात्मकता प्राप्त करें
- 2030 तक, सुनिश्चित करें कि सभी शिक्षार्थी सतत विकास को बढ़ावा देने के लिए आवश्यक ज्ञान और कौशल प्राप्त करें , जिसमें अन्य के अलावा, सतत विकास और सतत जीवन शैली, मानव अधिकार, लैंगिक समानता, शांति और अहिंसा की संस्कृति को बढ़ावा देने के लिए शिक्षा के माध्यम से, वैश्विक नागरिकता और सांस्कृतिक विविधता और सतत विकास में संस्कृति के योगदान की सराहना
- ऐसी शिक्षा सुविधाओं का निर्माण और उन्नयन करना जो बच्चे, विकलांगता और लिंग संवेदनशील हों और सभी के लिए सुरक्षित, अहिंसक, समावेशी और प्रभावी शिक्षण वातावरण प्रदान करें।
- 2020 तक, व्यावसायिक प्रशिक्षण और सूचना और संचार प्रौद्योगिकी, तकनीकी, इंजीनियरिंग और वैज्ञानिक कार्यक्रमों सहित उच्च शिक्षा में नामांकन के लिए विकासशील देशों, विशेष रूप से कम विकसित देशों, छोटे द्वीप विकासशील राज्यों और अफ्रीकी देशों के लिए उपलब्ध छात्रवृत्ति की संख्या का विश्व स्तर पर विस्तार करें। , विकसित देशों और अन्य विकासशील देशों में
- 2030 तक, विकासशील देशों, विशेष रूप से कम विकसित देशों और छोटे द्वीप विकासशील राज्यों में शिक्षक प्रशिक्षण के लिए अंतर्राष्ट्रीय सहयोग सहित योग्य शिक्षकों की आपूर्ति में पर्याप्त वृद्धि करना।
लक्ष्यों को
- हर जगह सभी महिलाओं और लड़कियों के प्रति सभी प्रकार के भेदभाव को समाप्त करें
- सार्वजनिक और निजी क्षेत्रों में सभी महिलाओं और लड़कियों के खिलाफ सभी प्रकार की हिंसा को समाप्त करना, जिसमें तस्करी और यौन और अन्य प्रकार के शोषण शामिल हैं।
- सभी हानिकारक प्रथाओं को समाप्त करें, जैसे कि बच्चा, जल्दी और जबरन विवाह और महिला जननांग विकृति
- सार्वजनिक सेवाओं, बुनियादी ढांचे और सामाजिक सुरक्षा नीतियों के प्रावधान के माध्यम से अवैतनिक देखभाल और घरेलू काम को पहचानना और महत्व देना और राष्ट्रीय स्तर पर उपयुक्त के रूप में घर और परिवार के भीतर साझा जिम्मेदारी को बढ़ावा देना
- राजनीतिक, आर्थिक और सार्वजनिक जीवन में निर्णय लेने के सभी स्तरों पर महिलाओं की पूर्ण और प्रभावी भागीदारी और नेतृत्व के लिए समान अवसर सुनिश्चित करना
- जनसंख्या और विकास पर अंतर्राष्ट्रीय सम्मेलन की कार्रवाई के कार्यक्रम और कार्रवाई के लिए बीजिंग प्लेटफॉर्म और उनके समीक्षा सम्मेलनों के परिणाम दस्तावेजों के अनुसार यौन और प्रजनन स्वास्थ्य और प्रजनन अधिकारों के लिए सार्वभौमिक पहुंच सुनिश्चित करें ।
- राष्ट्रीय कानूनों के अनुसार महिलाओं को आर्थिक संसाधनों के समान अधिकार देने के साथ-साथ भूमि और अन्य प्रकार की संपत्ति, वित्तीय सेवाओं, विरासत और प्राकृतिक संसाधनों पर स्वामित्व और नियंत्रण तक पहुंच प्रदान करने के लिए सुधार करना
- महिलाओं के सशक्तिकरण को बढ़ावा देने के लिए, विशेष रूप से सूचना और संचार प्रौद्योगिकी को सक्षम करने वाली प्रौद्योगिकी के उपयोग को बढ़ाना
- लैंगिक समानता को बढ़ावा देने और सभी स्तरों पर सभी महिलाओं और लड़कियों के सशक्तिकरण के लिए ठोस नीतियों और प्रवर्तनीय कानूनों को अपनाना और मजबूत करना
लक्ष्य 6: स्वच्छ जल और स्वच्छता
लक्ष्यों को
- 2030 तक, सभी के लिए सुरक्षित और किफायती पेयजल तक सार्वभौमिक और समान पहुंच प्राप्त करना
- 2030 तक, सभी के लिए पर्याप्त और समान स्वच्छता और स्वच्छता तक पहुंच प्राप्त करना और खुले में शौच को समाप्त करना, महिलाओं और लड़कियों और कमजोर परिस्थितियों में लोगों की जरूरतों पर विशेष ध्यान देना।
- 2030 तक, प्रदूषण को कम करके, खतरनाक रसायनों और सामग्रियों के डंपिंग को समाप्त करके और अनुपचारित अपशिष्ट जल के अनुपात को आधा करके और विश्व स्तर पर रीसाइक्लिंग और सुरक्षित पुन: उपयोग को बढ़ाकर पानी की गुणवत्ता में सुधार करें।
- 2030 तक, सभी क्षेत्रों में जल-उपयोग दक्षता में पर्याप्त वृद्धि करना और पानी की कमी को दूर करने के लिए स्थायी निकासी और मीठे पानी की आपूर्ति सुनिश्चित करना और पानी की कमी से पीड़ित लोगों की संख्या को काफी हद तक कम करना।
- 2030 तक, सभी स्तरों पर एकीकृत जल संसाधन प्रबंधन को लागू करना, जिसमें उपयुक्त के रूप में सीमा पार सहयोग शामिल है
- 2020 तक, पहाड़ों, जंगलों, आर्द्रभूमि, नदियों, जलभृतों और झीलों सहित पानी से संबंधित पारिस्थितिक तंत्रों की रक्षा और उन्हें पुनर्स्थापित करना
- 2030 तक, जल संचयन, विलवणीकरण, जल दक्षता, अपशिष्ट जल उपचार, पुनर्चक्रण और पुन: उपयोग प्रौद्योगिकियों सहित जल और स्वच्छता संबंधी गतिविधियों और कार्यक्रमों में विकासशील देशों के लिए अंतर्राष्ट्रीय सहयोग और क्षमता निर्माण समर्थन का विस्तार करें।
- पानी और स्वच्छता प्रबंधन में सुधार के लिए स्थानीय समुदायों की भागीदारी को समर्थन और मजबूत करना
लक्ष्य 7: वहनीय और स्वच्छ ऊर्जा
लक्ष्यों को
- 2030 तक, सस्ती, विश्वसनीय और आधुनिक ऊर्जा सेवाओं तक सार्वभौमिक पहुंच सुनिश्चित करें
- 2030 तक, वैश्विक ऊर्जा मिश्रण में अक्षय ऊर्जा की हिस्सेदारी में पर्याप्त वृद्धि करें
- 2030 तक, ऊर्जा दक्षता में सुधार की वैश्विक दर को दोगुना करना
- 2030 तक, अक्षय ऊर्जा, ऊर्जा दक्षता और उन्नत और स्वच्छ जीवाश्म-ईंधन प्रौद्योगिकी सहित स्वच्छ ऊर्जा अनुसंधान और प्रौद्योगिकी तक पहुंच को सुविधाजनक बनाने के लिए अंतर्राष्ट्रीय सहयोग बढ़ाना, और ऊर्जा बुनियादी ढांचे और स्वच्छ ऊर्जा प्रौद्योगिकी में निवेश को बढ़ावा देना।
- 2030 तक, विकासशील देशों, विशेष रूप से कम से कम विकसित देशों, छोटे द्वीप विकासशील राज्यों और भूमि-बंद विकासशील देशों में सभी के लिए आधुनिक और टिकाऊ ऊर्जा सेवाओं की आपूर्ति के लिए बुनियादी ढांचे का विस्तार और उन्नयन प्रौद्योगिकी, उनके समर्थन के संबंधित कार्यक्रमों के अनुसार
लक्ष्य 8: अच्छा काम और आर्थिक विकास
लक्ष्यों को
- राष्ट्रीय परिस्थितियों के अनुसार प्रति व्यक्ति आर्थिक विकास को बनाए रखना और, विशेष रूप से, कम से कम विकसित देशों में प्रति वर्ष कम से कम 7 प्रतिशत सकल घरेलू उत्पाद वृद्धि।
- विविधीकरण, तकनीकी उन्नयन और नवाचार के माध्यम से आर्थिक उत्पादकता के उच्च स्तर को प्राप्त करना, जिसमें उच्च मूल्य वर्धित और श्रम प्रधान क्षेत्रों पर ध्यान केंद्रित करना शामिल है।
- विकासोन्मुख नीतियों को बढ़ावा देना जो उत्पादक गतिविधियों, अच्छे रोजगार सृजन, उद्यमिता, रचनात्मकता और नवाचार का समर्थन करती हैं, और वित्तीय सेवाओं तक पहुंच सहित सूक्ष्म, लघु और मध्यम आकार के उद्यमों की औपचारिकता और विकास को प्रोत्साहित करती हैं।
- 2030 के माध्यम से, उपभोग और उत्पादन में वैश्विक संसाधन दक्षता में उत्तरोत्तर सुधार करें और विकसित देशों के नेतृत्व में सतत खपत और उत्पादन पर कार्यक्रमों के 10-वर्षीय ढांचे के अनुसार, पर्यावरणीय गिरावट से आर्थिक विकास को अलग करने का प्रयास करें।
- 2030 तक, युवा लोगों और विकलांग व्यक्तियों सहित सभी महिलाओं और पुरुषों के लिए पूर्ण और उत्पादक रोजगार और सभ्य कार्य प्राप्त करना, और समान मूल्य के काम के लिए समान वेतन प्राप्त करना
- 2020 तक, रोजगार, शिक्षा या प्रशिक्षण में नहीं रहने वाले युवाओं के अनुपात को काफी हद तक कम करना
- जबरन श्रम को समाप्त करने, आधुनिक दासता और मानव तस्करी को समाप्त करने के लिए तत्काल और प्रभावी उपाय करें और बाल सैनिकों की भर्ती और उपयोग सहित बाल श्रम के सबसे खराब रूपों का निषेध और उन्मूलन सुनिश्चित करें, और 2025 तक बाल श्रम के सभी रूपों को समाप्त करें।
- श्रमिक अधिकारों की रक्षा करना और प्रवासी श्रमिकों, विशेष रूप से महिला प्रवासियों, और अनिश्चित रोजगार वाले सभी श्रमिकों सहित सभी श्रमिकों के लिए सुरक्षित और सुरक्षित कार्य वातावरण को बढ़ावा देना।
- 2030 तक, स्थायी पर्यटन को बढ़ावा देने के लिए नीतियां तैयार और कार्यान्वित करें जो रोजगार पैदा करती हैं और स्थानीय संस्कृति और उत्पादों को बढ़ावा देती हैं
- सभी के लिए बैंकिंग, बीमा और वित्तीय सेवाओं तक पहुंच को प्रोत्साहित और विस्तारित करने के लिए घरेलू वित्तीय संस्थानों की क्षमता को मजबूत करना
- विकासशील देशों, विशेष रूप से कम विकसित देशों के लिए व्यापार सहायता के लिए सहायता बढ़ाना, जिसमें कम से कम विकसित देशों को व्यापार से संबंधित तकनीकी सहायता के लिए उन्नत एकीकृत ढांचे के माध्यम से शामिल है।
- 2020 तक, युवा रोजगार के लिए एक वैश्विक रणनीति का विकास और संचालन करना और अंतर्राष्ट्रीय श्रम संगठन के ग्लोबल जॉब्स पैक्ट को लागू करना
लक्ष्य 9: उद्योग, नवाचार और बुनियादी ढांचा
लक्ष्यों को
- सभी के लिए वहनीय और समान पहुंच पर ध्यान देने के साथ, आर्थिक विकास और मानव कल्याण का समर्थन करने के लिए क्षेत्रीय और सीमा पार बुनियादी ढांचे सहित गुणवत्ता, विश्वसनीय, टिकाऊ और लचीला बुनियादी ढांचे का विकास करना।
- समावेशी और सतत औद्योगीकरण को बढ़ावा देना और, 2030 तक, राष्ट्रीय परिस्थितियों के अनुरूप, रोजगार और सकल घरेलू उत्पाद में उद्योग की हिस्सेदारी को महत्वपूर्ण रूप से बढ़ाना, और कम से कम विकसित देशों में अपनी हिस्सेदारी को दोगुना करना
- छोटे पैमाने के औद्योगिक और अन्य उद्यमों, विशेष रूप से विकासशील देशों में, वित्तीय सेवाओं तक पहुंच बढ़ाना, जिसमें किफायती ऋण शामिल है, और मूल्य श्रृंखलाओं और बाजारों में उनका एकीकरण
- 2030 तक, सभी देशों द्वारा अपनी-अपनी क्षमताओं के अनुसार कार्रवाई करने के साथ, संसाधन-उपयोग दक्षता में वृद्धि और स्वच्छ और पर्यावरणीय रूप से ध्वनि प्रौद्योगिकियों और औद्योगिक प्रक्रियाओं को अधिक से अधिक अपनाने के साथ, उन्हें टिकाऊ बनाने के लिए बुनियादी ढांचे और रेट्रोफिट उद्योगों को अपग्रेड करें।
- वैज्ञानिक अनुसंधान में वृद्धि, सभी देशों में औद्योगिक क्षेत्रों की तकनीकी क्षमताओं का उन्नयन, विशेष रूप से विकासशील देशों में, 2030 तक, नवाचार को प्रोत्साहित करना और प्रति 1 मिलियन लोगों पर अनुसंधान और विकास श्रमिकों की संख्या में वृद्धि करना और सार्वजनिक और निजी अनुसंधान और विकास खर्च।
- अफ्रीकी देशों, कम से कम विकसित देशों, भूमि से घिरे विकासशील देशों और छोटे द्वीप विकासशील राज्यों को उन्नत वित्तीय, तकनीकी और तकनीकी सहायता के माध्यम से विकासशील देशों में टिकाऊ और लचीला बुनियादी ढांचे के विकास की सुविधा 18
- विकासशील देशों में घरेलू प्रौद्योगिकी विकास, अनुसंधान और नवाचार का समर्थन करना, जिसमें अन्य बातों के साथ-साथ, औद्योगिक विविधीकरण और वस्तुओं के मूल्यवर्धन के लिए एक अनुकूल नीति वातावरण सुनिश्चित करना शामिल है।
- सूचना और संचार प्रौद्योगिकी तक पहुंच को महत्वपूर्ण रूप से बढ़ाएं और 2020 तक कम से कम विकसित देशों में इंटरनेट तक सार्वभौमिक और सस्ती पहुंच प्रदान करने का प्रयास करें
लक्ष्यों को
- 2030 तक, राष्ट्रीय औसत से अधिक दर पर जनसंख्या के निचले 40 प्रतिशत की आय वृद्धि को उत्तरोत्तर प्राप्त करना और बनाए रखना
- 2030 तक, उम्र, लिंग, विकलांगता, नस्ल, जातीयता, मूल, धर्म या आर्थिक या अन्य स्थिति के बावजूद सभी के सामाजिक, आर्थिक और राजनीतिक समावेश को सशक्त और बढ़ावा देना
- भेदभावपूर्ण कानूनों, नीतियों और प्रथाओं को समाप्त करने और इस संबंध में उपयुक्त कानून, नीतियों और कार्रवाई को बढ़ावा देने सहित, समान अवसर सुनिश्चित करें और परिणाम की असमानताओं को कम करें।
- नीतियों, विशेष रूप से वित्तीय, वेतन और सामाजिक सुरक्षा नीतियों को अपनाना, और उत्तरोत्तर अधिक समानता प्राप्त करना
- वैश्विक वित्तीय बाजारों और संस्थानों के विनियमन और निगरानी में सुधार और ऐसे नियमों के कार्यान्वयन को मजबूत करना
- अधिक प्रभावी, विश्वसनीय, जवाबदेह और वैध संस्थानों को वितरित करने के लिए वैश्विक अंतरराष्ट्रीय आर्थिक और वित्तीय संस्थानों में निर्णय लेने में विकासशील देशों के लिए बढ़ाया प्रतिनिधित्व और आवाज सुनिश्चित करना
- नियोजित और अच्छी तरह से प्रबंधित प्रवासन नीतियों के कार्यान्वयन सहित लोगों के व्यवस्थित, सुरक्षित, नियमित और जिम्मेदार प्रवास और गतिशीलता को सुगम बनाना
- विश्व व्यापार संगठन समझौतों के अनुसार विकासशील देशों, विशेष रूप से कम विकसित देशों के लिए विशेष और विभेदक उपचार के सिद्धांत को लागू करें
- आधिकारिक विकास सहायता और वित्तीय प्रवाह को प्रोत्साहित करना, जिसमें प्रत्यक्ष विदेशी निवेश भी शामिल है, उन राज्यों में जहां आवश्यकता सबसे अधिक है, विशेष रूप से सबसे कम विकसित देशों, अफ्रीकी देशों, छोटे द्वीप विकासशील राज्यों और भूमि से घिरे विकासशील देशों में, उनकी राष्ट्रीय योजनाओं और कार्यक्रमों के अनुसार
- 2030 तक, प्रवासी प्रेषण की लेनदेन लागत को 3 प्रतिशत से कम करना और 5 प्रतिशत से अधिक लागत वाले प्रेषण गलियारों को समाप्त करना
लक्ष्यों को
- 2030 तक, सभी के लिए पर्याप्त, सुरक्षित और किफायती आवास और बुनियादी सेवाओं तक पहुंच सुनिश्चित करें और मलिन बस्तियों का उन्नयन करें
- 2030 तक, सभी के लिए सुरक्षित, सस्ती, सुलभ और टिकाऊ परिवहन प्रणाली तक पहुंच प्रदान करना, सड़क सुरक्षा में सुधार करना, विशेष रूप से सार्वजनिक परिवहन का विस्तार करके, कमजोर परिस्थितियों में लोगों, महिलाओं, बच्चों, विकलांग व्यक्तियों और वृद्ध व्यक्तियों की जरूरतों पर विशेष ध्यान देना।
- 2030 तक, सभी देशों में समावेशी और टिकाऊ शहरीकरण और भागीदारी, एकीकृत और टिकाऊ मानव निपटान योजना और प्रबंधन की क्षमता बढ़ाना
- विश्व की सांस्कृतिक और प्राकृतिक विरासत की रक्षा और सुरक्षा के प्रयासों को सुदृढ़ बनाना
- 2030 तक, मौतों की संख्या और प्रभावित लोगों की संख्या में उल्लेखनीय रूप से कमी लाना और पानी से संबंधित आपदाओं सहित आपदाओं के कारण वैश्विक सकल घरेलू उत्पाद के सापेक्ष प्रत्यक्ष आर्थिक नुकसान को काफी हद तक कम करना, गरीबों और कमजोर परिस्थितियों में लोगों की सुरक्षा पर ध्यान केंद्रित करना।
- 2030 तक, शहरों के प्रतिकूल प्रति व्यक्ति पर्यावरणीय प्रभाव को कम करना, जिसमें वायु गुणवत्ता और नगरपालिका और अन्य अपशिष्ट प्रबंधन पर विशेष ध्यान देना शामिल है।
- 2030 तक, सुरक्षित, समावेशी और सुलभ, हरे और सार्वजनिक स्थानों तक सार्वभौमिक पहुंच प्रदान करना, विशेष रूप से महिलाओं और बच्चों, वृद्ध व्यक्तियों और विकलांग व्यक्तियों के लिए
- राष्ट्रीय और क्षेत्रीय विकास योजना को मजबूत करके शहरी, उपनगरीय और ग्रामीण क्षेत्रों के बीच सकारात्मक आर्थिक, सामाजिक और पर्यावरणीय संबंधों का समर्थन करें
- 2020 तक, आपदा जोखिम के लिए सेंडाई फ्रेमवर्क के अनुरूप, समावेश, संसाधन दक्षता, शमन और जलवायु परिवर्तन के अनुकूलन, आपदाओं के प्रति लचीलापन, और विकसित और कार्यान्वित करने के लिए एकीकृत नीतियों और योजनाओं को अपनाने और लागू करने वाले शहरों और मानव बस्तियों की संख्या में पर्याप्त वृद्धि करना। कमी 2015-2030, सभी स्तरों पर समग्र आपदा जोखिम प्रबंधन
- स्थानीय सामग्रियों का उपयोग करके टिकाऊ और लचीला भवनों के निर्माण में वित्तीय और तकनीकी सहायता सहित कम से कम विकसित देशों का समर्थन करें
लक्ष्य 12: जिम्मेदार खपत और उत्पादन
लक्ष्यों को
- विकासशील देशों के विकास और क्षमताओं को ध्यान में रखते हुए, विकसित देशों के नेतृत्व में, सतत खपत और उत्पादन पर कार्यक्रमों के 10-वर्षीय ढांचे को लागू करें, सभी देश कार्रवाई करें।
- 2030 तक, प्राकृतिक संसाधनों के स्थायी प्रबंधन और कुशल उपयोग को प्राप्त करना
- 2030 तक, खुदरा और उपभोक्ता स्तरों पर प्रति व्यक्ति वैश्विक खाद्य अपशिष्ट को आधा करना और फसल के बाद के नुकसान सहित उत्पादन और आपूर्ति श्रृंखलाओं के साथ खाद्य नुकसान को कम करना।
- 2020 तक, सहमत अंतरराष्ट्रीय ढांचे के अनुसार, अपने पूरे जीवन चक्र में रसायनों और सभी कचरे के पर्यावरणीय रूप से ध्वनि प्रबंधन को प्राप्त करें, और मानव स्वास्थ्य और पर्यावरण पर उनके प्रतिकूल प्रभावों को कम करने के लिए हवा, पानी और मिट्टी में उनकी रिहाई को काफी कम करें।
- 2030 तक, रोकथाम, कमी, पुनर्चक्रण और पुन: उपयोग के माध्यम से अपशिष्ट उत्पादन को काफी हद तक कम करें
- कंपनियों, विशेष रूप से बड़ी और अंतरराष्ट्रीय कंपनियों को टिकाऊ प्रथाओं को अपनाने और स्थिरता की जानकारी को अपने रिपोर्टिंग चक्र में एकीकृत करने के लिए प्रोत्साहित करें
- सार्वजनिक खरीद प्रथाओं को बढ़ावा देना जो राष्ट्रीय नीतियों और प्राथमिकताओं के अनुसार टिकाऊ हों
- 2030 तक, सुनिश्चित करें कि हर जगह लोगों के पास प्रकृति के अनुरूप सतत विकास और जीवन शैली के लिए प्रासंगिक जानकारी और जागरूकता है
- खपत और उत्पादन के अधिक टिकाऊ पैटर्न की ओर बढ़ने के लिए विकासशील देशों को उनकी वैज्ञानिक और तकनीकी क्षमता को मजबूत करने में सहायता करना
- रोजगार सृजित करने और स्थानीय संस्कृति और उत्पादों को बढ़ावा देने वाले स्थायी पर्यटन के लिए सतत विकास प्रभावों की निगरानी के लिए उपकरण विकसित और कार्यान्वित करें
- अकुशल जीवाश्म-ईंधन सब्सिडी को युक्तिसंगत बनाना, जो राष्ट्रीय परिस्थितियों के अनुसार बाजार की विकृतियों को दूर करके बेकार खपत को प्रोत्साहित करती है, जिसमें कराधान का पुनर्गठन और उन हानिकारक सब्सिडी को चरणबद्ध करना शामिल है, जहां वे मौजूद हैं, उनके पर्यावरणीय प्रभावों को प्रतिबिंबित करने के लिए, विशिष्ट आवश्यकताओं को पूरी तरह से ध्यान में रखते हुए और विकासशील देशों की स्थिति और उनके विकास पर संभावित प्रतिकूल प्रभावों को इस तरह से कम करना जिससे गरीबों और प्रभावित समुदायों की रक्षा हो
लक्ष्यों को
- सभी देशों में जलवायु संबंधी खतरों और प्राकृतिक आपदाओं के प्रति लचीलापन और अनुकूली क्षमता को मजबूत करना
- राष्ट्रीय नीतियों, रणनीतियों और योजना में जलवायु परिवर्तन के उपायों को एकीकृत करना
- जलवायु परिवर्तन शमन, अनुकूलन, प्रभाव में कमी और प्रारंभिक चेतावनी पर शिक्षा, जागरूकता बढ़ाने और मानव और संस्थागत क्षमता में सुधार
- अर्थपूर्ण शमन कार्यों और कार्यान्वयन पर पारदर्शिता के संदर्भ में विकासशील देशों की जरूरतों को पूरा करने के लिए 2020 तक सभी स्रोतों से संयुक्त रूप से 100 बिलियन डॉलर सालाना जुटाने के लक्ष्य के लिए जलवायु परिवर्तन पर संयुक्त राष्ट्र फ्रेमवर्क कन्वेंशन के लिए विकसित देशों की पार्टियों द्वारा की गई प्रतिबद्धता को लागू करें। और जितनी जल्दी हो सके हरित जलवायु कोष को इसके पूंजीकरण के माध्यम से पूरी तरह से चालू करना
- महिलाओं, युवाओं और स्थानीय और हाशिए के समुदायों पर ध्यान केंद्रित करने सहित कम से कम विकसित देशों और छोटे द्वीप विकासशील राज्यों में प्रभावी जलवायु परिवर्तन से संबंधित योजना और प्रबंधन के लिए क्षमता बढ़ाने के लिए तंत्र को बढ़ावा देना
लक्ष्यों को
- 2025 तक, सभी प्रकार के समुद्री प्रदूषण को रोकें और महत्वपूर्ण रूप से कम करें, विशेष रूप से भूमि-आधारित गतिविधियों से, जिसमें समुद्री मलबे और पोषक तत्व प्रदूषण शामिल हैं।
- 2020 तक, महत्वपूर्ण प्रतिकूल प्रभावों से बचने के लिए समुद्री और तटीय पारिस्थितिकी प्रणालियों का स्थायी प्रबंधन और संरक्षण करना, जिसमें उनके लचीलेपन को मजबूत करना शामिल है, और स्वस्थ और उत्पादक महासागरों को प्राप्त करने के लिए उनकी बहाली के लिए कार्रवाई करना।
- समुद्र के अम्लीकरण के प्रभावों को कम करना और उनका समाधान करना, जिसमें सभी स्तरों पर वैज्ञानिक सहयोग बढ़ाना शामिल है
- 2020 तक, कटाई को प्रभावी ढंग से विनियमित करें और अत्यधिक मछली पकड़ने, अवैध, गैर-रिपोर्टेड और अनियमित मछली पकड़ने और विनाशकारी मछली पकड़ने की प्रथाओं को समाप्त करें और विज्ञान-आधारित प्रबंधन योजनाओं को लागू करें, ताकि कम से कम संभव समय में मछली के स्टॉक को बहाल किया जा सके, कम से कम उस स्तर तक जो अधिकतम टिकाऊ उपज पैदा कर सके। जैसा कि उनकी जैविक विशेषताओं द्वारा निर्धारित किया जाता है
- 2020 तक, राष्ट्रीय और अंतर्राष्ट्रीय कानून के अनुरूप और सर्वोत्तम उपलब्ध वैज्ञानिक जानकारी के आधार पर कम से कम 10 प्रतिशत तटीय और समुद्री क्षेत्रों का संरक्षण करें।
- 2020 तक, मत्स्य पालन सब्सिडी के कुछ रूपों को प्रतिबंधित करें जो अति क्षमता और अधिक मछली पकड़ने में योगदान करते हैं, उन सब्सिडी को समाप्त करते हैं जो अवैध, गैर-रिपोर्टेड और अनियमित मछली पकड़ने में योगदान करते हैं और नई ऐसी सब्सिडी शुरू करने से बचते हैं, जो विकासशील और कम से कम विकसित देशों के लिए उपयुक्त और प्रभावी विशेष और अंतर उपचार को पहचानते हैं। विश्व व्यापार संगठन मत्स्य पालन सब्सिडी वार्ता का एक अभिन्न अंग होना चाहिए
- 2030 तक, मत्स्य पालन, जलीय कृषि और पर्यटन के सतत प्रबंधन सहित समुद्री संसाधनों के सतत उपयोग से छोटे द्वीप विकासशील राज्यों और कम से कम विकसित देशों को आर्थिक लाभ बढ़ाना
- समुद्र के स्वास्थ्य में सुधार लाने और विकासशील देशों के विकास में समुद्री जैव विविधता के योगदान को बढ़ाने के लिए वैज्ञानिक ज्ञान में वृद्धि, अनुसंधान क्षमता विकसित करना और समुद्री प्रौद्योगिकी के अंतर सरकारी समुद्र विज्ञान आयोग मानदंड और समुद्री प्रौद्योगिकी के हस्तांतरण पर दिशानिर्देशों को ध्यान में रखते हुए समुद्री प्रौद्योगिकी को स्थानांतरित करना, विशेष रूप से छोटे द्वीप विकासशील राज्यों और कम से कम विकसित देशों में
- छोटे पैमाने के कारीगर मछुआरों को समुद्री संसाधनों और बाजारों तक पहुंच प्रदान करें
- यूएनसीएलओएस में परिलक्षित अंतरराष्ट्रीय कानून को लागू करके महासागरों और उनके संसाधनों के संरक्षण और टिकाऊ उपयोग को बढ़ाना, जो महासागरों और उनके संसाधनों के संरक्षण और टिकाऊ उपयोग के लिए कानूनी ढांचा प्रदान करता है, जैसा कि द फ्यूचर वी वांट के पैराग्राफ 158 में याद किया गया है।
लक्ष्यों को
- 2020 तक, अंतरराष्ट्रीय समझौतों के तहत दायित्वों के अनुरूप स्थलीय और अंतर्देशीय मीठे पानी के पारिस्थितिक तंत्र और उनकी सेवाओं, विशेष रूप से जंगलों, आर्द्रभूमि, पहाड़ों और शुष्क भूमि के संरक्षण, बहाली और स्थायी उपयोग को सुनिश्चित करें।
- 2020 तक, सभी प्रकार के वनों के सतत प्रबंधन के कार्यान्वयन को बढ़ावा देना, वनों की कटाई को रोकना, नष्ट हुए वनों को बहाल करना और विश्व स्तर पर वनीकरण और वनों की कटाई में काफी वृद्धि करना।
- 2030 तक, मरुस्थलीकरण का मुकाबला करना, मरुस्थलीकरण, सूखे और बाढ़ से प्रभावित भूमि सहित, खराब भूमि और मिट्टी को बहाल करना, और भूमि क्षरण-तटस्थ दुनिया को प्राप्त करने का प्रयास करना
- 2030 तक, सतत विकास के लिए आवश्यक लाभ प्रदान करने की उनकी क्षमता को बढ़ाने के लिए, उनकी जैव विविधता सहित पर्वतीय पारिस्थितिकी प्रणालियों के संरक्षण को सुनिश्चित करना
- प्राकृतिक आवासों के क्षरण को कम करने, जैव विविधता के नुकसान को रोकने और 2020 तक संकटग्रस्त प्रजातियों के विलुप्त होने की रक्षा और रोकथाम के लिए तत्काल और महत्वपूर्ण कार्रवाई करें।
- आनुवंशिक संसाधनों के उपयोग से होने वाले लाभों के उचित और समान बंटवारे को बढ़ावा देना और अंतरराष्ट्रीय स्तर पर सहमत ऐसे संसाधनों तक उचित पहुंच को बढ़ावा देना
- वनस्पतियों और जीवों की संरक्षित प्रजातियों के अवैध शिकार और तस्करी को समाप्त करने के लिए तत्काल कार्रवाई करें और अवैध वन्यजीव उत्पादों की मांग और आपूर्ति दोनों को संबोधित करें।
- 2020 तक, भूमि और जल पारिस्थितिक तंत्र पर आक्रामक विदेशी प्रजातियों के प्रभाव को कम करने और प्रारंभिक प्रजातियों को नियंत्रित करने या उन्मूलन करने के लिए उपायों को पेश करना।
- 2020 तक, पारिस्थितिकी तंत्र और जैव विविधता मूल्यों को राष्ट्रीय और स्थानीय नियोजन, विकास प्रक्रियाओं, गरीबी कम करने की रणनीतियों और खातों में एकीकृत करें
- जैव विविधता और पारिस्थितिक तंत्र के संरक्षण और स्थायी रूप से उपयोग करने के लिए सभी स्रोतों से वित्तीय संसाधनों को जुटाना और महत्वपूर्ण रूप से बढ़ाना
- टिकाऊ वन प्रबंधन को वित्तपोषित करने के लिए सभी स्रोतों और सभी स्तरों से महत्वपूर्ण संसाधन जुटाएं और विकासशील देशों को ऐसे प्रबंधन को आगे बढ़ाने के लिए पर्याप्त प्रोत्साहन प्रदान करें, जिसमें संरक्षण और वनीकरण शामिल है।
- स्थायी आजीविका के अवसरों का पीछा करने के लिए स्थानीय समुदायों की क्षमता में वृद्धि सहित संरक्षित प्रजातियों के अवैध शिकार और तस्करी से निपटने के प्रयासों के लिए वैश्विक समर्थन बढ़ाना
लक्ष्य 16: शांति और न्याय मजबूत संस्थाएं
लक्ष्यों को
- हर जगह सभी प्रकार की हिंसा और संबंधित मृत्यु दर को महत्वपूर्ण रूप से कम करें।
- बच्चों के साथ दुर्व्यवहार, शोषण, तस्करी और सभी प्रकार की हिंसा और उत्पीड़न को समाप्त करें।
- राष्ट्रीय और अंतर्राष्ट्रीय स्तर पर कानून के शासन को बढ़ावा देना और सभी के लिए न्याय तक समान पहुंच सुनिश्चित करना।
- 2030 तक, अवैध वित्तीय और हथियारों के प्रवाह को महत्वपूर्ण रूप से कम करना, चोरी की गई संपत्ति की वसूली और वापसी को मजबूत करना और सभी प्रकार के संगठित अपराध का मुकाबला करना।
- उनके सभी रूपों में भ्रष्टाचार और रिश्वतखोरी को पर्याप्त रूप से कम करें।
- सभी स्तरों पर प्रभावी, जवाबदेह और पारदर्शी संस्थानों का विकास करना।
- सभी स्तरों पर उत्तरदायी, समावेशी, सहभागी और प्रतिनिधि निर्णय लेना सुनिश्चित करें।
- वैश्विक शासन के संस्थानों में विकासशील देशों की भागीदारी को व्यापक और मजबूत करना।
- 2030 तक, जन्म पंजीकरण सहित सभी के लिए कानूनी पहचान प्रदान करें।
- राष्ट्रीय कानून और अंतरराष्ट्रीय समझौतों के अनुसार सूचना तक सार्वजनिक पहुंच सुनिश्चित करना और मौलिक स्वतंत्रता की रक्षा करना।
- हिंसा को रोकने और आतंकवाद और अपराध का मुकाबला करने के लिए, विशेष रूप से विकासशील देशों में, सभी स्तरों पर क्षमता निर्माण के लिए अंतरराष्ट्रीय सहयोग सहित प्रासंगिक राष्ट्रीय संस्थानों को मजबूत करना।
- सतत विकास के लिए गैर-भेदभावपूर्ण कानूनों और नीतियों को बढ़ावा देना और लागू करना।
लक्ष्य 17: लक्ष्य प्राप्त करने के लिए भागीदारी
लक्ष्यों को
वित्त
- कर और अन्य राजस्व संग्रह के लिए घरेलू क्षमता में सुधार करने के लिए विकासशील देशों को अंतरराष्ट्रीय समर्थन के माध्यम से घरेलू संसाधन जुटाने को मजबूत करना
- विकसित देशों को अपनी आधिकारिक विकास सहायता प्रतिबद्धताओं को पूरी तरह से लागू करने के लिए, कई विकसित देशों द्वारा विकासशील देशों के लिए ओडीए/जीएनआई के 0.7 प्रतिशत और कम से कम विकसित देशों को ओडीए/जीएनआई के 0.15 से 0.20 प्रतिशत के लक्ष्य को प्राप्त करने की प्रतिबद्धता सहित ओडीए प्रदाता हैं। कम से कम विकसित देशों को कम से कम 0.20 प्रतिशत ओडीए/जीएनआई प्रदान करने का लक्ष्य निर्धारित करने पर विचार करने के लिए प्रोत्साहित किया गया
- विकासशील देशों के लिए अनेक स्रोतों से अतिरिक्त वित्तीय संसाधन जुटाना
- ऋण वित्तपोषण, ऋण राहत और ऋण पुनर्गठन को बढ़ावा देने के उद्देश्य से समन्वित नीतियों के माध्यम से दीर्घकालिक ऋण स्थिरता प्राप्त करने में विकासशील देशों की सहायता करना, और ऋण संकट को कम करने के लिए अत्यधिक ऋणी गरीब देशों के बाहरी ऋण को संबोधित करना।
- कम से कम विकसित देशों के लिए निवेश प्रोत्साहन व्यवस्था को अपनाना और लागू करना
तकनीकी
- विज्ञान, प्रौद्योगिकी और नवोन्मेष पर उत्तर-दक्षिण, दक्षिण-दक्षिण और त्रिकोणीय क्षेत्रीय और अंतर्राष्ट्रीय सहयोग बढ़ाना और परस्पर सहमत शर्तों पर ज्ञान साझा करना बढ़ाना, जिसमें मौजूदा तंत्रों के बीच बेहतर समन्वय के माध्यम से, विशेष रूप से संयुक्त राष्ट्र स्तर पर, और के माध्यम से एक वैश्विक प्रौद्योगिकी सुविधा तंत्र
- पारस्परिक रूप से सहमत रियायती और तरजीही शर्तों सहित अनुकूल शर्तों पर विकासशील देशों के लिए पर्यावरणीय रूप से सुदृढ़ प्रौद्योगिकियों के विकास, हस्तांतरण, प्रसार और प्रसार को बढ़ावा देना
- 2017 तक कम से कम विकसित देशों के लिए प्रौद्योगिकी बैंक और विज्ञान, प्रौद्योगिकी और नवाचार क्षमता निर्माण तंत्र को पूरी तरह से चालू करना और विशेष रूप से सूचना और संचार प्रौद्योगिकी में सक्षम प्रौद्योगिकी के उपयोग को बढ़ाना
क्षमता निर्माण
- उत्तर-दक्षिण, दक्षिण-दक्षिण और त्रिकोणीय सहयोग सहित सभी सतत विकास लक्ष्यों को लागू करने के लिए राष्ट्रीय योजनाओं का समर्थन करने के लिए विकासशील देशों में प्रभावी और लक्षित क्षमता निर्माण को लागू करने के लिए अंतर्राष्ट्रीय समर्थन बढ़ाना
व्यापार
- विश्व व्यापार संगठन के तहत एक सार्वभौमिक, नियम-आधारित, खुला, गैर-भेदभावपूर्ण और न्यायसंगत बहुपक्षीय व्यापार प्रणाली को बढ़ावा देना, जिसमें इसके दोहा विकास एजेंडा के तहत वार्ता के समापन के माध्यम से शामिल है।
- विकासशील देशों के निर्यात में उल्लेखनीय वृद्धि, विशेष रूप से 2020 तक वैश्विक निर्यात में सबसे कम विकसित देशों की हिस्सेदारी को दोगुना करने की दृष्टि से
- विश्व व्यापार संगठन के निर्णयों के अनुरूप, कम से कम विकसित देशों के लिए स्थायी आधार पर शुल्क-मुक्त और कोटा-मुक्त बाजार पहुंच के समय पर कार्यान्वयन को महसूस करना, जिसमें यह सुनिश्चित करना शामिल है कि कम से कम विकसित देशों से आयात के लिए लागू मूल के अधिमान्य नियम पारदर्शी और सरल हैं, और बाजार पहुंच को सुगम बनाने में योगदान करें
The 17 sustainable development goals (SDGs) to transform our world:
Targets
- By 2030, eradicate extreme poverty for all people everywhere, currently measured as people living on less than $1.25 a day.
- By 2030, reduce at least by half the proportion of men, women and children of all ages living in poverty in all its dimensions according to national definitions.
- Implement nationally appropriate social protection systems and measures for all, including floors, and by 2030 achieve substantial coverage of the poor and the vulnerable.
- By 2030, ensure that all men and women, in particular the poor and the vulnerable, have equal rights to economic resources, as well as access to basic services, ownership and control over land and other forms of 13 property, inheritance, natural resources, appropriate new technology and financial services, including micro-finance.
- By 2030, build the resilience of the poor and those in vulnerable situations and reduce their exposure and vulnerability to climate-related extreme events and other economic, social and environmental shocks and disasters.
- Ensure significant mobilization of resources from a variety of sources, including through enhanced development cooperation, in order to provide adequate and predictable means for developing countries, in particular least developed countries, to implement programmes and policies to end poverty in all its dimensions.
- Create sound policy frameworks at the national, regional and international levels, based on pro-poor and gender-sensitive development strategies, to support accelerated investment in poverty eradication actions
Targets
- By 2030, end hunger and ensure access by all people, in particular the poor and people in vulnerable situations, including infants, to safe, nutritious and sufficient food all year round.
- By 2030, end all forms of malnutrition, including achieving, by 2025, the internationally agreed targets on stunting and wasting in children under 5 years of age, and address the nutritional needs of adolescent girls, pregnant and lactating women and older persons
- By 2030, double the agricultural productivity and incomes of small-scale food producers, in particular women, indigenous peoples, family farmers, pastoralists and fishers, including through secure and equal access to land, other productive resources and inputs, knowledge, financial services, markets and opportunities for value addition and non-farm employment
- By 2030, ensure sustainable food production systems and implement resilient agricultural practices that increase productivity and production, that help maintain ecosystems, that strengthen capacity for adaptation to climate change, extreme weather, drought, flooding and other disasters and that progressively improve land and soil quality
- By 2020, maintain the genetic diversity of seeds, cultivated plants and farmed and domesticated animals and their related wild species, including through soundly managed and diversified seed and plant banks at the national, regional and international levels, and promote access to and fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising from the utilization of genetic resources and associated traditional knowledge, as internationally agreed
- Increase investment, including through enhanced international cooperation, in rural infrastructure, agricultural research and extension services, technology development and plant and livestock gene banks in order to enhance agricultural productive capacity in developing countries, in particular least developed countriesCorrect and prevent trade restrictions and distortions in world agricultural markets, including through the parallel elimination of all forms of agricultural export subsidies and all export measures with equivalent effect, in accordance with the mandate of the Doha Development Round
- Adopt measures to ensure the proper functioning of food commodity markets and their derivatives and facilitate timely access to market information, including on food reserves, in order to help limit extreme food price volatility
GOAL 3: Good Health and Well-being
Targets
- By 2030, reduce the global maternal mortality ratio to less than 70 per 100,000 live births
- By 2030, end preventable deaths of newborns and children under 5 years of age, with all countries aiming to reduce neonatal mortality to at least as low as 12 per 1,000 live births and under-5 mortality to at least as low as 25 per 1,000 live births
- By 2030, end the epidemics of AIDS, tuberculosis, malaria and neglected tropical diseases and combat hepatitis, water-borne diseases and other communicable diseases
- By 2030, reduce by one third premature mortality from non-communicable diseases through prevention and treatment and promote mental health and well-being
- Strengthen the prevention and treatment of substance abuse, including narcotic drug abuse and harmful use of alcohol
- By 2020, halve the number of global deaths and injuries from road traffic accidents 3.7
- By 2030, ensure universal access to sexual and reproductive health-care services, including for family planning, information and education, and the integration of reproductive health into national strategies and programmes
- Achieve universal health coverage, including financial risk protection, access to quality essential health-care services and access to safe, effective, quality and affordable essential medicines and vaccines for all
- By 2030, substantially reduce the number of deaths and illnesses from hazardous chemicals and air, water and soil pollution and contamination
- Strengthen the implementation of the World Health Organization Framework Convention on Tobacco Control in all countries, as appropriate
- Support the research and development of vaccines and medicines for the communicable and noncommunicable diseases that primarily affect developing countries, provide access to affordable essential medicines and vaccines, in accordance with the Doha Declaration on the TRIPS Agreement and Public Health, which affirms the right of developing countries to use to the full the provisions in the Agreement on Trade Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights regarding flexibilities to protect public health, and, in particular, provide access to medicines for all
- Substantially increase health financing and the recruitment, development, training and retention of the health workforce in developing countries, especially in least developed countries and small island developing States
- Strengthen the capacity of all countries, in particular developing countries, for early warning, risk reduction and management of national and global health risks
Targets
- By 2030, ensure that all girls and boys complete free, equitable and quality primary and secondary education leading to relevant and Goal-4 effective learning outcomes
- By 2030, ensure that all girls and boys have access to quality early childhood development, care and preprimary education so that they are ready for primary education
- By 2030, ensure equal access for all women and men to affordable and quality technical, vocational and tertiary education, including university
- By 2030, substantially increase the number of youth and adults who have relevant skills, including technical and vocational skills, for employment, decent jobs and entrepreneurship
- By 2030, eliminate gender disparities in education and ensure equal access to all levels of education and vocational training for the vulnerable, including persons with disabilities, indigenous peoples and children in vulnerable situations
- By 2030, ensure that all youth and a substantial proportion of adults, both men and women, achieve literacy and numeracy
- By 2030, ensure that all learners acquire the knowledge and skills needed to promote sustainable development, including, among others, through education for sustainable development and sustainable lifestyles, human rights, gender equality, promotion of a culture of peace and non-violence, global citizenship and appreciation of cultural diversity and of culture’s contribution to sustainable development
- Build and upgrade education facilities that are child, disability and gender sensitive and provide safe, nonviolent, inclusive and effective learning environments for all
- By 2020, substantially expand globally the number of scholarships available to developing countries, in particular least developed countries, small island developing States and African countries, for enrolment in higher education, including vocational training and information and communications technology, technical, engineering and scientific programmes, in developed countries and other developing countries
- By 2030, substantially increase the supply of qualified teachers, including through international cooperation for teacher training in developing countries, especially least developed countries and small island developing states
Targets
- End all forms of discrimination against all women and girls everywhere
- Eliminate all forms of violence against all women and girls in the public and private spheres, including trafficking and sexual and other types of exploitation
- Eliminate all harmful practices, such as child, early and forced marriage and female genital mutilation
- Recognize and value unpaid care and domestic work through the provision of public services, infrastructure and social protection policies and the promotion of shared responsibility within the household and the family as nationally appropriate
- Ensure women’s full and effective participation and equal opportunities for leadership at all levels of decision making in political, economic and public life
- Ensure universal access to sexual and reproductive health and reproductive rights as agreed in accordance with the Programme of Action of the International Conference on Population and Development and the Beijing Platform for Action and the outcome documents of their review conferences
- Undertake reforms to give women equal rights to economic resources, as well as access to ownership and control over land and other forms of property, financial services, inheritance and natural resources, in accordance with national laws
- Enhance the use of enabling technology, in particular information and communications technology, to promote the empowerment of women
- Adopt and strengthen sound policies and enforceable legislation for the promotion of gender equality and the empowerment of all women and girls at all levels
GOAL 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
Targets
- By 2030, achieve universal and equitable access to safe and affordable drinking water for all
- By 2030, achieve access to adequate and equitable sanitation and hygiene for all and end open defecation, paying special attention to the needs of women and girls and those in vulnerable situations
- By 2030, improve water quality by reducing pollution, eliminating dumping and minimizing release of hazardous chemicals and materials, halving the proportion of untreated wastewater and substantially increasing recycling and safe reuse globally
- By 2030, substantially increase water-use efficiency across all sectors and ensure sustainable withdrawals and supply of freshwater to address water scarcity and substantially reduce the number of people suffering from water scarcity
- By 2030, implement integrated water resources management at all levels, including through transboundary cooperation as appropriate
- By 2020, protect and restore water-related ecosystems, including mountains, forests, wetlands, rivers, aquifers and lakes
- By 2030, expand international cooperation and capacity-building support to developing countries in water- and sanitation-related activities and programmes, including water harvesting, desalination, water efficiency, wastewater treatment, recycling and reuse technologies
- Support and strengthen the participation of local communities in improving water and sanitation management
GOAL 7: Affordable and Clean Energy
Targets
- By 2030, ensure universal access to affordable, reliable and modern energy services
- By 2030, increase substantially the share of renewable energy in the global energy mix
- By 2030, double the global rate of improvement in energy efficiency
- By 2030, enhance international cooperation to facilitate access to clean energy research and technology, including renewable energy, energy efficiency and advanced and cleaner fossil-fuel technology, and promote investment in energy infrastructure and clean energy technology
- By 2030, expand infrastructure and upgrade technology for supplying modern and sustainable energy services for all in developing countries, in particular least developed countries, small island developing States, and land-locked developing countries, in accordance with their respective programmes of support
GOAL 8: Decent Work and Economic Growth
Targets
- Sustain per capita economic growth in accordance with national circumstances and, in particular, at least 7 per cent gross domestic product growth per annum in the least developed countries
- Achieve higher levels of economic productivity through diversification, technological upgrading and innovation, including through a focus on high-value added and labour-intensive sectors
- Promote development-oriented policies that support productive activities, decent job creation, entrepreneurship, creativity and innovation, and encourage the formalization and growth of micro-, small- and medium-sized enterprises, including through access to financial services
- Improve progressively, through 2030, global resource efficiency in consumption and production and endeavour to decouple economic growth from environmental degradation, in accordance with the 10-year framework of programmes on sustainable consumption and production, with developed countries taking the lead
- By 2030, achieve full and productive employment and decent work for all women and men, including for young people and persons with disabilities, and equal pay for work of equal value
- By 2020, substantially reduce the proportion of youth not in employment, education or training
- Take immediate and effective measures to eradicate forced labour, end modern slavery and human trafficking and secure the prohibition and elimination of the worst forms of child labour, including recruitment and use of child soldiers, and by 2025 end child labour in all its forms
- Protect labour rights and promote safe and secure working environments for all workers, including migrant workers, in particular women migrants, and those in precarious employment
- By 2030, devise and implement policies to promote sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products
- Strengthen the capacity of domestic financial institutions to encourage and expand access to banking, insurance and financial services for all
- Increase Aid for Trade support for developing countries, in particular least developed countries, including through the Enhanced Integrated Framework for Trade-Related Technical Assistance to Least Developed Countries
- By 2020, develop and operationalize a global strategy for youth employment and implement the Global Jobs Pact of the International Labour Organization
GOAL 9: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure
Targets
- Develop quality, reliable, sustainable and resilient infrastructure, including regional and transborder infrastructure, to support economic development and human well-being, with a focus on affordable and equitable access for all
- Promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization and, by 2030, significantly raise industry’s share of employment and gross domestic product, in line with national circumstances, and double its share in least developed countries
- Increase the access of small-scale industrial and other enterprises, in particular in developing countries, to financial services, including affordable credit, and their integration into value chains and markets
- By 2030, upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies and industrial processes, with all countries taking action in accordance with their respective capabilities
- Enhance scientific research, upgrade the technological capabilities of industrial sectors in all countries, in particular developing countries, including, by 2030, encouraging innovation and substantially increasing the number of research and development workers per 1 million people and public and private research and development spending
- Facilitate sustainable and resilient infrastructure development in developing countries through enhanced financial, technological and technical support to African countries, least developed countries, landlocked developing countries and small island developing States 18
- Support domestic technology development, research and innovation in developing countries, including by ensuring a conducive policy environment for, inter alia, industrial diversification and value addition to commodities
- Significantly increase access to information and communications technology and strive to provide universal and affordable access to the Internet in least developed countries by 2020
Targets
- By 2030, progressively achieve and sustain income growth of the bottom 40 per cent of the population at a rate higher than the national average
- By 2030, empower and promote the social, economic and political inclusion of all, irrespective of age, sex, disability, race, ethnicity, origin, religion or economic or other status
- Ensure equal opportunity and reduce inequalities of outcome, including by eliminating discriminatory laws, policies and practices and promoting appropriate legislation, policies and action in this regard
- Adopt policies, especially fiscal, wage and social protection policies, and progressively achieve greater equality
- Improve the regulation and monitoring of global financial markets and institutions and strengthen the implementation of such regulations
- Ensure enhanced representation and voice for developing countries in decision-making in global international economic and financial institutions in order to deliver more effective, credible, accountable and legitimate institutions
- Facilitate orderly, safe, regular and responsible migration and mobility of people, including through the implementation of planned and well-managed migration policies
- Implement the principle of special and differential treatment for developing countries, in particular least developed countries, in accordance with World Trade Organization agreements
- Encourage official development assistance and financial flows, including foreign direct investment, to States where the need is greatest, in particular least developed countries, African countries, small island developing States and landlocked developing countries, in accordance with their national plans and programmes
- By 2030, reduce to less than 3 per cent the transaction costs of migrant remittances and eliminate remittance corridors with costs higher than 5 per cent
GOAL 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
Targets
- By 2030, ensure access for all to adequate, safe and affordable housing and basic services and upgrade slums
- By 2030, provide access to safe, affordable, accessible and sustainable transport systems for all, improving road safety, notably by expanding public transport, with special attention to the needs of those in vulnerable situations, women, children, persons with disabilities and older persons
- By 2030, enhance inclusive and sustainable urbanization and capacity for participatory, integrated and sustainable human settlement planning and management in all countries
- Strengthen efforts to protect and safeguard the world’s cultural and natural heritage
- By 2030, significantly reduce the number of deaths and the number of people affected and substantially decrease the direct economic losses relative to global gross domestic product caused by disasters, including water-related disasters, with a focus on protecting the poor and people in vulnerable situations
- By 2030, reduce the adverse per capita environmental impact of cities, including by paying special attention to air quality and municipal and other waste management
- By 2030, provide universal access to safe, inclusive and accessible, green and public spaces, in particular for women and children, older persons and persons with disabilities
- Support positive economic, social and environmental links between urban, peri-urban and rural areas by strengthening national and regional development planning
- By 2020, substantially increase the number of cities and human settlements adopting and implementing integrated policies and plans towards inclusion, resource efficiency, mitigation and adaptation to climate change, resilience to disasters, and develop and implement, in line with the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015-2030, holistic disaster risk management at all levels
- Support least developed countries, including through financial and technical assistance, in building sustainable and resilient buildings utilizing local materials
GOAL 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
Targets
- Implement the 10-year framework of programmes on sustainable consumption and production, all countries taking action, with developed countries taking the lead, taking into account the development and capabilities of developing countries
- By 2030, achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources
- By 2030, halve per capita global food waste at the retail and consumer levels and reduce food losses along production and supply chains, including post-harvest losses
- By 2020, achieve the environmentally sound management of chemicals and all wastes throughout their life cycle, in accordance with agreed international frameworks, and significantly reduce their release to air, water and soil in order to minimize their adverse impacts on human health and the environment
- By 2030, substantially reduce waste generation through prevention, reduction, recycling and reuse
- Encourage companies, especially large and transnational companies, to adopt sustainable practices and to integrate sustainability information into their reporting cycle
- Promote public procurement practices that are sustainable, in accordance with national policies and priorities
- By 2030, ensure that people everywhere have the relevant information and awareness for sustainable development and lifestyles in harmony with nature
- Support developing countries to strengthen their scientific and technological capacity to move towards more sustainable patterns of consumption and production
- Develop and implement tools to monitor sustainable development impacts for sustainable tourism that creates jobs and promotes local culture and products
- Rationalize inefficient fossil-fuel subsidies that encourage wasteful consumption by removing market distortions, in accordance with national circumstances, including by restructuring taxation and phasing out those harmful subsidies, where they exist, to reflect their environmental impacts, taking fully into account the specific needs and conditions of developing countries and minimizing the possible adverse impacts on their development in a manner that protects the poor and the affected communities
Targets
- Strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards and natural disasters in all countries
- Integrate climate change measures into national policies, strategies and planning
- Improve education, awareness-raising and human and institutional capacity on climate change mitigation, adaptation, impact reduction and early warning
- Implement the commitment undertaken by developed-country parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change to a goal of mobilizing jointly $100 billion annually by 2020 from all sources to address the needs of developing countries in the context of meaningful mitigation actions and transparency on implementation and fully operationalize the Green Climate Fund through its capitalization as soon as possible
- Promote mechanisms for raising capacity for effective climate change-related planning and management in least developed countries and small island developing States, including focusing on women, youth and local and marginalized communities
Targets
- By 2025, prevent and significantly reduce marine pollution of all kinds, in particular from land-based activities, including marine debris and nutrient pollution
- By 2020, sustainably manage and protect marine and coastal ecosystems to avoid significant adverse impacts, including by strengthening their resilience, and take action for their restoration in order to achieve healthy and productive oceans
- Minimize and address the impacts of ocean acidification, including through enhanced scientific cooperation at all levels
- By 2020, effectively regulate harvesting and end overfishing, illegal, unreported and unregulated fishing and destructive fishing practices and implement science-based management plans, in order to restore fish stocks in the shortest time feasible, at least to levels that can produce maximum sustainable yield as determined by their biological characteristics
- By 2020, conserve at least 10 per cent of coastal and marine areas, consistent with national and international law and based on the best available scientific information
- By 2020, prohibit certain forms of fisheries subsidies which contribute to overcapacity and overfishing, eliminate subsidies that contribute to illegal, unreported and unregulated fishing and refrain from introducing new such subsidies, recognizing that appropriate and effective special and differential treatment for developing and least developed countries should be an integral part of the World Trade Organization fisheries subsidies negotiation
- By 2030, increase the economic benefits to Small Island developing States and least developed countries from the sustainable use of marine resources, including through sustainable management of fisheries, aquaculture and tourism
- Increase scientific knowledge, develop research capacity and transfer marine technology, taking into account the Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission Criteria and Guidelines on the Transfer of Marine Technology, in order to improve ocean health and to enhance the contribution of marine biodiversity to the development of developing countries, in particular small island developing States and least developed countries
- Provide access for small-scale artisanal fishers to marine resources and markets
- Enhance the conservation and sustainable use of oceans and their resources by implementing international law as reflected in UNCLOS, which provides the legal framework for the conservation and sustainable use of oceans and their resources, as recalled in paragraph 158 of The Future We Want
Targets
- By 2020, ensure the conservation, restoration and sustainable use of terrestrial and inland freshwater ecosystems and their services, in particular forests, wetlands, mountains and drylands, in line with obligations under international agreements
- By 2020, promote the implementation of sustainable management of all types of forests, halt deforestation, restore degraded forests and substantially increase afforestation and reforestation globally
- By 2030, combat desertification, restore degraded land and soil, including land affected by desertification, drought and floods, and strive to achieve a land degradation-neutral world
- By 2030, ensure the conservation of mountain ecosystems, including their biodiversity, in order to enhance their capacity to provide benefits that are essential for sustainable development
- Take urgent and significant action to reduce the degradation of natural habitats, halt the loss of biodiversity and, by 2020, protect and prevent the extinction of threatened species
- Promote fair and equitable sharing of the benefits arising from the utilization of genetic resources and promote appropriate access to such resources, as internationally agreed
- Take urgent action to end poaching and trafficking of protected species of flora and fauna and address both demand and supply of illegal wildlife products
- By 2020, introduce measures to prevent the introduction and significantly reduce the impact of invasive alien species on land and water ecosystems and control or eradicate the priority species
- By 2020, integrate ecosystem and biodiversity values into national and local planning, development processes, poverty reduction strategies and accounts
- Mobilize and significantly increase financial resources from all sources to conserve and sustainably use biodiversity and ecosystems
- Mobilize significant resources from all sources and at all levels to finance sustainable forest management and provide adequate incentives to developing countries to advance such management, including for conservation and reforestation
- Enhance global support for efforts to combat poaching and trafficking of protected species, including by increasing the capacity of local communities to pursue sustainable livelihood opportunities
GOAL 16: Peace and Justice Strong Institutions
Targets
- Significantly reduce all forms of violence and related death rates everywhere.
- End abuse, exploitation, trafficking and all forms of violence against and torture of children.
- Promote the rule of law at the national and international levels and ensure equal access to justice for all.
- By 2030, significantly reduce illicit financial and arms flows, strengthen the recovery and return of stolen assets and combat all forms of organised crime.
- Substantially reduce corruption and bribery in all their forms.
- Develop effective, accountable and transparent institutions at all levels.
- Ensure responsive, inclusive, participatory and representative decision-making at all levels.
- Broaden and strengthen the participation of developing countries in the institutions of global governance.
- By 2030, provide legal identity for all, including birth registration.
- Ensure public access to information and protect fundamental freedoms, in accordance with national legislation and international agreements.
- Strengthen relevant national institutions, including through international cooperation, for building capacity at all levels, in particular in developing countries, to prevent violence and combat terrorism and crime.
- Promote and enforce non-discriminatory laws and policies for sustainable development.
GOAL 17: Partnerships to achieve the Goal
Targets
Finance
- Strengthen domestic resource mobilization, including through international support to developing countries, to improve domestic capacity for tax and other revenue collection
- Developed countries to implement fully their official development assistance commitments, including the commitment by many developed countries to achieve the target of 0.7 per cent of ODA/GNI to developing countries and 0.15 to 0.20 per cent of ODA/GNI to least developed countries ODA providers are encouraged to consider setting a target to provide at least 0.20 per cent of ODA/GNI to least developed countries
- Mobilize additional financial resources for developing countries from multiple sources
- Assist developing countries in attaining long-term debt sustainability through coordinated policies aimed at fostering debt financing, debt relief and debt restructuring, as appropriate, and address the external debt of highly indebted poor countries to reduce debt distress
- Adopt and implement investment promotion regimes for least developed countries
Technology
- Enhance North-South, South-South and triangular regional and international cooperation on and access to science, technology and innovation and enhance knowledge sharing on mutually agreed terms, including through improved coordination among existing mechanisms, in particular at the United Nations level, and through a global technology facilitation mechanism
- Promote the development, transfer, dissemination and diffusion of environmentally sound technologies to developing countries on favourable terms, including on concessional and preferential terms, as mutually agreed
- Fully operationalize the technology bank and science, technology and innovation capacity-building mechanism for least developed countries by 2017 and enhance the use of enabling technology, in particular information and communications technology
Capacity building
- Enhance international support for implementing effective and targeted capacity-building in developing countries to support national plans to implement all the sustainable development goals, including through North-South, South-South and triangular cooperation
Trade
- Promote a universal, rules-based, open, non-discriminatory and equitable multilateral trading system under the World Trade Organization, including through the conclusion of negotiations under its Doha Development Agenda
- Significantly increase the exports of developing countries, in particular with a view to doubling the least developed countries’ share of global exports by 2020
- Realize timely implementation of duty-free and quota-free market access on a lasting basis for all least developed countries, consistent with World Trade Organization decisions, including by ensuring that preferential rules of origin applicable to imports from least developed countries are transparent and simple, and contribute to facilitating market access
we generally make use of parametric and non-parametric tests for making inferences about various population values (parameters). Many methods and techniques are used in statistics. These have been grouped under parametric and non-parametric statistics.
| Parametric | Non-Parametric Statistics |
| It involves data expressed in absolute numbers or values rather than ranks.An example is the Student’s t-test.The parametric statistical test operates under certain conditions. Since the conditions are not ordinarily tested, they are assumed to hold valid.Tests like t, z, and F are called parametrical statistical tests.Multiple Regression, Two-way ANOVA. | In this, the statistics are based on the ranks of observations.It does not depend on any distribution of the population.It deals with small sample sizes.These are not bound by any assumptions.These are user friendly compared with parametric statistics and economical in time.Tests like chi-square test, Kruskal-Wallis test, median test, Man-Whitney U test, sign test, and Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-ranks test tests are examples of non-parametrical statistics tests. |
हम आम तौर पर विभिन्न जनसंख्या मूल्यों (पैरामीटर) के बारे में अनुमान लगाने के लिए पैरामीट्रिक और गैर-पैरामीट्रिक परीक्षणों का उपयोग करते हैं । सांख्यिकी में अनेक विधियों और तकनीकों का प्रयोग किया जाता है। इन्हें पैरामीट्रिक और गैर–पैरामीट्रिक आंकड़ों के तहत समूहीकृत किया गया है ।
| पैरामीट्रिक | गैर–पैरामीट्रिक सांख्यिकी |
| इसमें रैंक के बजाय निरपेक्ष संख्या या मूल्यों में व्यक्त डेटा शामिल है।एक उदाहरण विद्यार्थी का t-परीक्षण है।पैरामीट्रिक सांख्यिकीय परीक्षण कुछ शर्तों के तहत संचालित होता है। चूंकि शर्तों का सामान्य रूप से परीक्षण नहीं किया जाता है, इसलिए उन्हें वैध माना जाता है।टी, जेड और एफ जैसे परीक्षणों को पैरामीट्रिक सांख्यिकीय परीक्षण कहा जाता है।मल्टीपल रिग्रेशन, टू–वे एनोवा। | इसमें आँकड़े प्रेक्षणों की श्रेणी पर आधारित होते हैं।यह जनसंख्या के किसी वितरण पर निर्भर नहीं करता है।यह छोटे नमूना आकारों से संबंधित है।ये किसी धारणा से बंधे नहीं हैं।ये पैरामीट्रिक आँकड़ों की तुलना में उपयोगकर्ता के अनुकूल हैं और समय में किफायती हैं।ची–स्क्वायर टेस्ट , क्रुस्कल –वालिस टेस्ट, मीडियन टेस्ट, मैन-व्हिटनी यू टेस्ट, साइन टेस्ट, और विलकॉक्सन मिलान-जोड़ी साइन-रैंक टेस्ट टेस्ट जैसे टेस्ट गैर-पैरामीट्रिक सांख्यिकी परीक्षणों के उदाहरण हैं। |
पैरामीट्रिक परीक्षणों के लिए अनुमान:
- डेटा का सामान्य : पैरामीट्रिक परीक्षणों के लिए पी–मान सामान्य नमूना वितरण पर निर्भर करता है। यदि नमूना आकार काफी बड़ा है और वास्तविक नमूना डेटा बिंदु मान लगभग सामान्य रूप से वितरित किया जाता है, तो केंद्रीय सीमा प्रमेय सामान्य रूप से वितरित नमूना वितरण सुनिश्चित करता है।
- विचरण की समरूपता: यह पूरे डेटा में भिन्नता में समानता की आवश्यकता को संदर्भित करता है। इसका मतलब यह है कि आबादी में जिस चर से नमूने लिए गए थे, इन आबादी में समान भिन्नता है।
- अंतराल डेटा: यह स्पष्ट है कि डेटा बिंदु मान एक संख्यात्मक चर के लिए होना चाहिए और इस स्तर पर मापा जाना चाहिए।
- स्वतंत्रता : विभिन्न समूहों के लिए चर के लिए डेटा बिंदु मान एक दूसरे से स्वतंत्र होने चाहिए। प्रतिगमन विश्लेषण में, त्रुटियाँ भी स्वतंत्र होनी चाहिए।
स्वतंत्र टी – परीक्षण , जिसे दो-नमूना टी – परीक्षण , स्वतंत्र – नमूने टी – परीक्षण, या छात्र का टी – परीक्षण भी कहा जाता है, एक अनुमानित सांख्यिकीय परीक्षण है जो यह निर्धारित करने में मदद करता है कि दो असंबंधित समूहों में साधनों का अंतर सांख्यिकीय रूप से महत्वपूर्ण है या नहीं .
आश्रित t- परीक्षण ( जिसे युग्मित t- परीक्षण या युग्मित-नमूना t- परीक्षण भी कहा जाता है ) यह निर्धारित करने में मदद करता है कि दो असंबंधित समूहों में साधनों का अंतर सांख्यिकीय रूप से महत्वपूर्ण है या नहीं ।
विलकॉक्सन परीक्षण: विलकॉक्सन परीक्षण एक गैर-पैरामीट्रिक सांख्यिकीय परीक्षण है जो यह निर्धारित करने के लिए जोड़े के दो या दो से अधिक सेटों के मध्य की तुलना करता है कि समूह सांख्यिकीय रूप से महत्वपूर्ण तरीके से एक दूसरे से भिन्न हैं या नहीं।
साइन टेस्ट: साइन टेस्ट एक सांख्यिकीय विधि है जो टिप्पणियों के जोड़े के बीच लगातार अंतर का परीक्षण करती है, जैसे कि उपचार से पहले और बाद में विषयों की ऊंचाई।
महत्वपूर्ण बिंदु
चूंकि प्रश्न में, दोनों समूह असंबंधित हैं, हम एक स्वतंत्र टी-परीक्षण का उपयोग करेंगे।
अतिरिक्त जानकारी
युग्मित डेटा वह है जहां प्राकृतिक मिलान या युग्मन संभव है। आम तौर पर यह तब संभव होता है जब डेटा सेट में जहां एक स्वतंत्र नमूने में प्रत्येक डेटा बिंदु को जोड़ा जाएगा – विशिष्ट रूप से – किसी अन्य स्वतंत्र नमूने में डेटा बिंदु पर।
Assumptions for parametric tests:
- Normal distribution of data: The p-value for parametric tests depends upon a normal sampling distribution. If the sample size is large enough and the actual sample data point value is approximately normally distributed, then the central limit theorem ensures a normally distributed sampling distribution.
- Homogeneity of variance: This refers to the need for a similarity in the variance throughout the data. This means that the variable in the populations from which the samples were taken have a similar variance in these populations.
- Interval data: It is obvious that the data point values should be for a numerical variable and measured at this level.
- Independence: Data point values for variables for different groups should be independent of each other. In regression analysis, the errors should likewise be independent.
The independent t–test, also called the two-sample t–test, independent-samples t–test, or student’s t–test is an inferential statistical test that helps to determine whether the difference of the means in two unrelated groups are statistically significant.
The dependent t–test (also called the paired t–test or paired-samples t–test) helps to determine whether the difference of the means in two unrelated groups is statistically significant.
Wilcoxon test: The Wilcoxon test is a nonparametric statistical test that compares the median of two or more sets of pairs to determine whether the groups are different from one another in a statistically significant manner.
Sign test: The sign test is a statistical method to test consistent differences between pairs of observations, such as the height of subjects before and after treatment.
Important Points
Since in question, both the groups are unrelated, we will use an independent t-test.
Additional Information
Paired data is where natural matching or coupling is possible. Generally this is possible when in data sets where every data point in one independent sample would be paired—uniquely—to a data point in another independent sample.
What is ANOVA vs t-test?
The t-test is a method that determines whether two populations are statistically different from each other, whereas ANOVA determines whether three or more populations are statistically different from each other
एनोवा बनाम टी-टेस्ट क्या है?
टी-टेस्ट एक ऐसा तरीका है जो यह निर्धारित करता है कि क्या दो आबादी एक दूसरे से सांख्यिकीय रूप से भिन्न हैं, जबकि एनोवा यह निर्धारित करती है कि तीन या अधिक आबादी एक दूसरे से सांख्यिकीय रूप से भिन्न हैं या नहीं
Also Read –UGC NET 11TH JULY 2022 PAPER 1 QUESTION PAPER ANALYSIS: SHIFT 1 AND 2:
UGC NET 11th July 2022 Paper 1 Shift 1 & 2 Question Paper Analysis; Major Highlights
Major highlights of the 11th July examination has been updated here in due time after the conclusion of the exam.
Overall Difficulty Level of Shift 1: Moderate
Overall Difficulty Level of Shift 2: To be Updated
Expected Good Score of Shift 1: 30-35
Expected Good Score of Shift 2: To be Updated
Was Shift 1 Paper Time-Consuming? No
Was Shift 2 Paper Time-Consuming? To be Updated
Shift 1 vs Shift 2 Analysis Comparison:
UGC NET 11th July 2022 Paper 1 Question Paper Analysis: Shift 1 & 2
The combined analysis of both shifts has been detailed in the table below:
| Section | Difficulty Level | Number of Questions Asked in the Exam | Topics with Highest Weightage |
| Communication | Moderate | 5-6 | Communication Barrier /Mode ,Effective Communication ,Formal ,linear Communication ,Non linear & Interaction Matching ,Oral Communication question & Step of Communication |
| Data Interpretation | Easy to Moderate | 10 | Covid Same PYQ |
| Information and Communication Technology (ICT) | Moderate | 5-6 | Computer Generation ,Circuit Related Question , 16 GB Conversion ,ASCII ,Number system RAM ,JPG Format ,Full form of MOODLE ,Optic Fibre & DVD R & DVD Raw ,Malware Virus |
| Logical Reasoning | Easy | 5-6 | Syllogism, Moods, Figuers, Square of Opposition ,Indian logic assertion Reason, Hetu Related Question ,Arthapatti |
| Mathematics | Easy | 4-5 | Ratio, Average, Percentage ,Number System,Simple Interest |
| People and Environment | Easy | 4-5 | Water Pollution & Treatment (Sludge Treatment ) ,Biomass, Eco-system, Source of Energy & SDG/MDG Goal ,(Govardhan ,Jal Jeevan )Govt Scheme ,Photochemical Smog ,Hurricane Speed ,COVID Virus Name -SARS COV -2 |
| Reading Comprehension | Easy | 5 | |
| Research Aptitude | Easy | 5 | Types of Research , Quantitative & Qualitative Research |
| Teaching Aptitude | Moderate | 7 | Value Education Assertion Reason ,Effective Teaching ,Classroom Teaching & Idealism |
| Higher Education System: Governance, Polity, Administration, and Current Affairs | Easy | 4-5 | New Education Policy, Govt Schemes,Swayam Prabha ,CARE related Question,Copyright Related question,British Education Related ,Pre/Post Independence ,SPSS Full form ,NCVET Full form ,Coordinator of Vocational Education ,SWAYAM Quadrants & Coordinator , Lord Curzen commision Related |
Question Asked In Today Session –
Q -The missing term in the series 1, 4, 27, 16, ?, 36, 343, … is
Logic: Cube of odd number and square of even number
Q 16 GB =2^ =
1 GB = 1024 MB= 2^10 MB
1MB = 1024 KB =2^10 KB
1KB = 1024 bytes= 2^10 bytes
1byte = 8 bits= 2^3bits
therefore
16GB= 16 * 2^10 * 2^10 * 2^10 * 2^3
= 2^4 * 2^10 * 2^10 * 2^10 * 2^3
= 2^(4+10+10+10+3)
Ans = 2^37 bits
Q SCOPUS =Elsevier-Scopus is Elsevier’s abstract and citation database launched in 2004. Scopus covers nearly 36,377 titles from approximately 11,678 publishers, of which 34,346 are peer-reviewed journals in top-level subject fields: life sciences, social sciences, physical sciences and health sciences.
स्कोपस एल्सेवियर का सार और उद्धरण डेटाबेस है जिसे 2004 में लॉन्च किया गया था। स्कोपस में लगभग 11,678 प्रकाशकों के लगभग 36,377 शीर्षक शामिल हैं, जिनमें से 34,346 शीर्ष-स्तरीय विषय क्षेत्रों में सहकर्मी-समीक्षित पत्रिकाएं हैं: जीवन विज्ञान, सामाजिक विज्ञान, भौतिक विज्ञान और स्वास्थ्य विज्ञान
Q Speed Scooter wala
Q AICTE /NPTEL Matching
Q Biomass
Q Psychology ,Cognitive Domain -Piaget
Q Fundamental Research
Q 2nd Shift Boy Girl % DI Question
Q Indian Logic 3 Question 2 Square of Opposition Mood & Figure
Q ICT Input Output Device Matching
Q Swayam MOOC Statement Question
Q Swayam Prabha DTH Channel
Q % Profit
Q Ancient Education
Q Green house Gas
Q Facebook Skype
Q MOOC Full form
Q NEP –The new policy aims in the higher education to improve the Gross Enrollment Ratio from 26.3% to 50% by
2030
2035
2025
2040
Q Which satellite system is used in swayan prabha?
- QUICKBird
- GSAT-15
- LANDSAT-TM
- CARTOSAT
Q Teaching Behaviour ,Evaluation
Q Hurricane Speed
Q SPSS Full Form ?
Software

Description
SPSS Statistics is a statistical software suite developed by IBM for data management, advanced analytics, multivariate analysis, business intelligence, and criminal investigation. Long produced by SPSS Inc., it was acquired by IBM in 2009. Current versions have the brand name: IBM SPSS Statistics
एसपीएसएस
सॉफ़्टवेयर
विवरण
SPSS सांख्यिकी आईबीएम द्वारा डेटा प्रबंधन, उन्नत विश्लेषिकी, बहुभिन्नरूपी विश्लेषण, व्यापार खुफिया और आपराधिक जांच के लिए विकसित एक सांख्यिकीय सॉफ्टवेयर सूट है। एसपीएसएस इंक द्वारा लंबे समय से उत्पादित, इसे 2009 में आईबीएम द्वारा अधिग्रहित किया गया था। वर्तमान संस्करणों का ब्रांड नाम है: आईबीएम एसपीएसएस सांख्यिकी।
Q National Council for Vocational Education and Training (NCVET) | Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship |
SWAYAM (Study Webs of Active-Learning for Young Aspiring Minds) is a MOOC (Massive open online courses ) that offers courses in various fields like engineering, humanities, social sciences, etc.
SWAYAM:
- This program is initiated by the Government of India (i.e it is not a Non-Governmental Organization) and designed to achieve the three cardinal principles of Education Policy viz., access, equity, and quality.
- The objective is to take the best teaching-learning resources to all, including the most disadvantaged.
- It is an open online course (i.e. it is not an online platform)
- All the courses are interactive, prepared by the best teachers in the country, and are available, free of cost to any learner.
- The courses hosted on SWAYAM are in 4 quadrants –
- Video lecture,
- Specially prepared reading material that can be downloaded/printed
- Self-assessment tests through tests and quizzes, and
- An online discussion forum for clearing the doubts.
- Various steps have been taken to enrich the learning experience by using audio-video and multimedia and state of the art pedagogy/technology.

Nine National Coordinators are appointed to ensure that the best quality content is produced and delivered. They are:
- AICTE (All India Council for Technical Education) for self-paced and international courses.
- NPTEL (National Programme on Technology Enhanced Learning) for Engineering.
- UGC (University Grants Commission) for nontechnical post-graduation education.
- CEC (Consortium for Educational Communication) for undergraduate education.
- NCERT (National Council of Educational Research and Training) for school education.
- NIOS (National Institute of Open Schooling) for school education.
- IGNOU (Indira Gandhi National Open University) for out-of-school students.
- IIMB (Indian Institute of Management, Bangalore) for management studies.
- NITTTR (National Institute of Technical Teachers Training and Research) for Teacher Training program.
स्वयं:
- यह कार्यक्रम भारत सरकार द्वारा शुरू किया गया है (अर्थात यह एक गैर-सरकारी संगठन नहीं है) और शिक्षा नीति के तीन प्रमुख सिद्धांतों जैसे पहुंच, समानता और गुणवत्ता को प्राप्त करने के लिए डिज़ाइन किया गया है।
- इसका उद्देश्य सबसे अधिक वंचितों सहित सभी के लिए सर्वोत्तम शिक्षण-अधिगम संसाधन उपलब्ध कराना है।
- यह एक खुला ऑनलाइन पाठ्यक्रम है (अर्थात यह ऑनलाइन प्लेटफॉर्म नहीं है)
- सभी पाठ्यक्रम इंटरैक्टिव हैं, देश के सर्वश्रेष्ठ शिक्षकों द्वारा तैयार किए गए हैं, और किसी भी शिक्षार्थी के लिए निःशुल्क उपलब्ध हैं।
- SWAYAM पर होस्ट किए गए कोर्स 4 क्वाड्रंट में हैं –
- वीडियो व्याख्यान,
- विशेष रूप से तैयार की गई पठन सामग्री जिसे डाउनलोड/मुद्रित किया जा सकता है
- परीक्षण और प्रश्नोत्तरी के माध्यम से स्व-मूल्यांकन परीक्षण, और
- शंकाओं को दूर करने के लिए एक ऑनलाइन चर्चा मंच।
- ऑडियो-वीडियो और मल्टीमीडिया और अत्याधुनिक शिक्षाशास्त्र/प्रौद्योगिकी का उपयोग करके सीखने के अनुभव को समृद्ध करने के लिए विभिन्न कदम उठाए गए हैं।

सर्वोत्तम गुणवत्ता वाली सामग्री का उत्पादन और वितरण सुनिश्चित करने के लिए नौ राष्ट्रीय समन्वयक नियुक्त किए गए हैं । वे हैं:
- स्व–पुस्तक और अंतर्राष्ट्रीय पाठ्यक्रमों के लिए एआईसीटीई (अखिल भारतीय तकनीकी शिक्षा परिषद)।
- इंजीनियरिंग के लिए एनपीटीईएल (नेशनल प्रोग्राम ऑन टेक्नोलॉजी एनहांस्ड लर्निंग)।
- गैर-तकनीकी स्नातकोत्तर शिक्षा के लिए यूजीसी (विश्वविद्यालय अनुदान आयोग)।
- स्नातक शिक्षा के लिए सीईसी (शैक्षणिक संचार के लिए संघ)।
- स्कूली शिक्षा के लिए NCERT (राष्ट्रीय शैक्षिक अनुसंधान और प्रशिक्षण परिषद)।
- स्कूली शिक्षा के लिए एनआईओएस (राष्ट्रीय मुक्त विद्यालयी शिक्षा संस्थान)।
- स्कूल से बाहर के छात्रों के लिए इग्नू (इंदिरा गांधी राष्ट्रीय मुक्त विश्वविद्यालय)।
- प्रबंधन अध्ययन के लिए IIMB (भारतीय प्रबंधन संस्थान, बैंगलोर)।
- शिक्षक प्रशिक्षण कार्यक्रम के लिए NITTTR (राष्ट्रीय तकनीकी शिक्षक प्रशिक्षण और अनुसंधान संस्थान)।
Ministry of Education, Government of India’s, SWAYAM platform for offering MOOCs has how many quadrants for designing courses?
- 2 Quadrants
- 4 Quadrants
- 6 Quadrants
- 8 Quadrants
The Ministry of Education has launched many schemes for promoting e-learning across students in schools and universities.
Key Points
SWAYAM:
- Its full form is ‘Study Web of Active Learning For Young Aspiring Minds’.
- It is an integrated online learning platform for online courses.
- It is an Indian massive open online course platform.
- It was launched on July 9, 2017.
- It was designed to achieve the three-cardinal principle of Education policy, i.e., access, equity, and equality.
- The courses hosted on Swayam are on 4 quadrants as follows:
- Video lecture
- E-Content
- Test and assignments
- Online Discussion forum
| National Coordinators | Course provided by them |
| AICTE (All India Council for Technical Education) | For self-paced and international courses |
| NITTTR (National Institute of Technical Teachers Training & Research) | Teacher Training Program |
| IGNOU (Indira Gandhi National Open University) | Out of school students |
| NIOS (National Institute of Open Schooling) | For school education |
| IIM B(Indian Institute of Management, Bangalore) | Management studies |
| NCERT (National Council for Educational Research Training) | For school education |
| UGC (University Grants Commission) | Non-technical post-graduation education |
| NPTEL (National Program on Technology Enhanced Learning) | Engineering |
| CEC (Consortium for Educational Communication) | For undergraduate education |