People Development & Environment MCQ – Objective Question with Answer for All Competition exams Download Free PDF- Telegram Link-https://t.me/EasynotesNTA
People Development & Environment MCQ Question 1
Troposphere and Thermosphere belong to
- Atmosphere
- Lithosphere
- Hydrosphere
- Biosphere
क्षोभमंडल और थर्मोस्फीयर से संबंधित हैं
- वातावरण
- स्थलमंडल
- हीड्रास्फीयर
- बीओस्फिअ
Option 1 : Atmosphere
People Development & Environment MCQ Question 1 Detailed Solution
The correct answer is Atmosphere.
Important Points
Layers of Earth’s Atmosphere:
- Earth’s atmosphere has a series of layers, each with its own specific traits.
- Moving upward from ground level, these layers have named the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere and exosphere.
- The exosphere gradually fades away into the realm of interplanetary space.

- The lithosphere is the rocky outer part of the Earth. It is made up of the brittle crust and the top part of the upper mantle. The lithosphere is the coolest and most rigid part of the Earth.
- The hydrosphere is the layer of water surface on Earth. It comprises all forms of liquid or frozen surface water, groundwater, and water vapor.
- The biosphere is the life-supporting segment of Earth’s surface which extends from few kilometers in the atmosphere to the deep sea shelves of the ocean. It is a global chain of ecosystem consisting of living organism(biotic) and non-living (abiotic) components features which form the energy chain of flow. Telegram Link-https://t.me/EasynotesNTA
सही उत्तर है → वायुमंडल।
महत्वपूर्ण बिंदु
पृथ्वी के वायुमंडल की परतें:
- पृथ्वी के वायुमंडल में परतों की एक श्रृंखला है, जिनमें से प्रत्येक की अपनी विशिष्ट विशेषताएं हैं।
- जमीनी स्तर से ऊपर की ओर बढ़ते हुए, इन परतों ने क्षोभमंडल, समताप मंडल, मध्यमंडल, थर्मोस्फीयर और बहिर्मंडल का नाम दिया है।
- एक्सोस्फीयर धीरे-धीरे इंटरप्लेनेटरी स्पेस के दायरे में फीका पड़ जाता है।

- स्थलमंडल पृथ्वी के चट्टानी बाहरी हिस्सा है। यह भंगुर क्रस्ट और ऊपरी मेंटल के शीर्ष भाग से बना है। स्थलमंडल पृथ्वी के सबसे अच्छे और सबसे कठोर हिस्सा है।
- जलमंडल पृथ्वी पर पानी की सतह की परत है। इसमें सभी प्रकार के तरल या जमे हुए सतही जल, भूजल और जल वाष्प शामिल हैं।
- जीवमंडल पृथ्वी की सतह का जीवनदायी खंड है जो वायुमंडल में कुछ किलोमीटर से लेकर समुद्र के गहरे समुद्र के समतल तक फैला हुआ है। यह पारिस्थितिक तंत्र की एक वैश्विक श्रृंखला है जिसमें जीवित जीव (जैविक) और निर्जीव (अजैविक) घटक शामिल हैं जो प्रवाह की ऊर्जा श्रृंखला बनाते हैं।
People Development & Environment MCQ Question 2
In comparison to pure water, Boiling point of impure water
- is same
- increases
- decreases
- first decreases then Increases
शुद्ध जल की तुलना में अशुद्ध जल का क्वथनांक
- एकजैसा हैं
- बढ़ती है
- कम हो जाती है
- पहले घटता है फिर बढ़ता है
Option 2 : increases
People Development & Environment MCQ Question 2 Detailed Solution
Explanation:
- Sea water is impure water,so adding salt increases the boiling point of water this is because salt is a non-volatile solute which is responsible for boiling point elevation.
- The boiling point of a liquid is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid and the surrounding pressure are equal.
- The original boiling point of water is 100°C. After the addition of 58 grams of salt, the boiling point increases by one half of the degree Celsius
व्याख्या:
- Sea water is impure water, so adding salt raises the boiling point of water because salt is a non-volatile solute that is responsible for the elevation of the boiling point.
- The boiling point of a liquid is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid and the pressure around it are equal.
- The original boiling point of water is 100°C. After adding 58 grams of salt, the boiling point increases by half of °C Telegram Link-https://t.me/EasynotesNTA
People Development & Environment MCQ Question 3
Noise pollution is created if sound is in excess to
- 70-75 dB
- 50-60 dB
- 80-99 dB
- 40-65 dB
ध्वनि से अधिक होने पर ध्वनि प्रदूषण उत्पन्न होता है
- 70-75 डीबी
- 50-60 डीबी
- 80-99 डीबी
- 40-65 डीबी
Option 3 : 80-99 dB
People Development & Environment MCQ Question 3 Detailed Solution
Telegram Link-https://t.me/EasynotesNTA
The correct answer is 80-99 dB.
Important Points
- Grades of ambient noise pollution are as follows according to noise pollution control and regulations Rules 2000;
- Industrial areas: 70-75 dB
- Commercial areas: 55-65 dB
- Residential areas: 45-55 dB
- Silence zone: 40-50 dB
- Indoor limit: <30 dB According to WHO
- Noise greater than 75 dB over long exposure can cause hearing damage.
- Noise above 120 dB can cause biochemical changes in human bodies.

- Section 2 (a) of the Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981, includes noise in the definition of pollutants.
- Noise Pollution Control and regulation Rules, 2000 are framed under the Environment Protection Act, 1986.
- The frequency range between 20-20000 Hz is an audible range for the human ear.
- A firecracker generally generates about 125 dB of noise.
- According to a 2015 report by the European Commission, 1.3 billion people suffer from hearing impairment due to noise exposure.
महत्वपूर्ण बिंदु
- ध्वनि प्रदूषण नियंत्रण और विनियम नियम 2000 के अनुसार परिवेशी ध्वनि प्रदूषण के ग्रेड निम्नानुसार हैं ;
- औद्योगिक क्षेत्र: 70-75 डीबी
- वाणिज्यिक क्षेत्र: 55-65 डीबी
- आवासीय क्षेत्र: 45-55 डीबी
- साइलेंस जोन: 40-50 डीबी
- आंतरिक सीमा: < 30 डीबी डब्ल्यूएचओ के अनुसार
- लंबे समय तक एक्सपोजर में 75 डीबी से अधिक का शोर सुनने की क्षति का कारण बन सकता है ।
- 120 डीबी से ऊपर का शोर मानव शरीर में जैव रासायनिक परिवर्तन का कारण बन सकता है।

अतिरिक्त जानकारी
- वायु (प्रदूषण की रोकथाम और नियंत्रण) अधिनियम, 1981 की धारा 2 (ए) में प्रदूषकों की परिभाषा में शोर शामिल है।
- पर्यावरण संरक्षण अधिनियम, 1986 के तहत ध्वनि प्रदूषण नियंत्रण और विनियमन नियम, 2000 बनाए गए हैं ।
- 20-20000 हर्ट्ज के बीच आवृत्ति रेंज मानव कान के लिए एक श्रव्य सीमा है।
- एक पटाखा आमतौर पर लगभग 125 डीबी शोर उत्पन्न करता है।
- यूरोपीय आयोग की 2015 की एक रिपोर्ट के अनुसार, शोर के संपर्क में आने के कारण 1.3 बिलियन लोग श्रवण दोष से पीड़ित हैं।
Telegram Link-https://t.me/EasynotesNTA Trusted by 2,17,23,979+ Students
People Development & Environment MCQ Question 4
What is the range of the intensity scale used in measuring earthquakes?
- 1 to 12
- 1 to 7
- 1 to 15
- 1 to 5
भूकंप को मापने के लिए उपयोग किए जाने वाले तीव्रता पैमाने की सीमा क्या है?
- 1 से 12
- 1 से 7
- 1 से 15
- 1 से 5
Option 1 : 1 to 12
People Development & Environment MCQ Question 4 Detailed Solution
The correct answer is 1 to 12.

Key Points
- An Earthquake is also called a quake, tremor, or temblor.
- It is the phenomenon of shaking of the surface of the earth that also create seismic wave.
- Seismic waves are the waves that travel through the earth’s layer.
- These waves are the result of earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, magma moment, landslides, and man-made explosion.
- The earthquake produce different types of seismic waves such as P wave, S wave, and Surface waves.
- Seismic activity also increases due to global warming. https://t.me/EasynotesNTA
Important Points
- The instruments used to measure the intensity of the earthquake are Seismograph, Ritcher scale, and Seismograph.
| Ritcher Scale | – The Ritcher scale is also called a magnitude scale – It was developed by Charles F. Ritcher |
| Mercalli Scale | – The Mercalli scale was developed by Giusseppe Mercalli. – The scale ranges between 1 to 12. |
| Seismograph | – A Seismograph consists of a mass attached to a fixed base. – The mass moves during the earthquake. |
Trusted by 2,17,23,979+ Students
सही उत्तर 1 से 12 तक है।

प्रमुख बिंदु
- भूकंप को भूकंप, कंपकंपी या भूकंप भी कहा जाता है ।
- यह पृथ्वी की सतह के हिलने की घटना है जो भूकंपीय तरंग भी पैदा करती है।
- भूकंपीय तरंगें वे तरंगें हैं जो पृथ्वी की परत से होकर गुजरती हैं।
- इन तरंगों का परिणाम है भूकंप, ज्वालामुखी विस्फोट, मेग्मा पल, भूस्खलन, और मानव निर्मित विस्फोट।
- भूकंप विभिन्न प्रकार की भूकंपीय तरंगें जैसे P तरंग, S तरंग और सतह तरंगें उत्पन्न करता है ।
- ग्लोबल वार्मिंग के कारण भूकंपीय गतिविधि भी बढ़ जाती है।
- महत्वपूर्ण बिंदु
- भूकंप की तीव्रता को मापने के लिए इस्तेमाल किए जाने वाले उपकरण सीस्मोग्राफ, रिचर स्केल और सीस्मोग्राफ हैं।
| रिचर स्केल | – रिचर स्केल को परिमाण पैमाना भी कहा जाता है – इसे चार्ल्स एफ. रिचर द्वारा विकसित किया गया था |
| मर्कल्ली स्केल | – मर्कल्ली स्केल को Giusseppe Mercalli द्वारा विकसित किया गया था । – पैमाना 1 से 12 के बीच होता है । |
| भूकंप-सूचक यंत्र | – सीस्मोग्राफ में एक निश्चित आधार से जुड़ा एक द्रव्यमान होता है। – भूकंप के दौरान द्रव्यमान चलता है। |
People Development & Environment MCQ Question 5
Identify the correct sequence of continents in decreasing order of their yearly carbon dioxide emissions, at present
A. Africa
B. Asia
C. Europe
D. North America
Choose the correct answer from the option given below
- B, D, A, C
- B, D, C, A
- D, B, C, A
- D, C, B, A
वर्तमान में उनके वार्षिक कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड उत्सर्जन के घटते क्रम में महाद्वीपों के सही क्रम की पहचान करें
ए अफ्रीका
बी एशिया
सी यूरोप
डी उत्तरी अमेरिका
नीचे दिए गए विकल्पों में से सही उत्तर चुनिए
- बी, डी, ए, सी
- बी, डी, सी, ए
- डी, बी, सी, ए
- डी, सी, बी, ए
Option 2 : B, D, C, A
People Development & Environment MCQ Question 5 Detailed Solution
Carbon dioxide (CO2) makes up the vast majority of greenhouse gas emissions from the sector, but smaller amounts of methane (CH4) and nitrous oxide (N2O) are also emitted. These gases are released during the combustion of fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, to produce electricity.
According to World Green House Gas Emission Data, the correct sequence of countries in decreasing order of their contribution to global carbon dioxide emissions is Asia, North America, Europe, and Africa. Telegram Link-https://t.me/EasynotesNTA
कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड (CO2) क्षेत्र से ग्रीनहाउस गैस उत्सर्जन का विशाल बहुमत बनाता है , लेकिन कम मात्रा में मीथेन (CH4) और नाइट्रस ऑक्साइड (N2O) भी उत्सर्जित होते हैं। ये गैसें बिजली पैदा करने के लिए कोयला, तेल और प्राकृतिक गैस जैसे जीवाश्म ईंधन के दहन के दौरान निकलती हैं ।
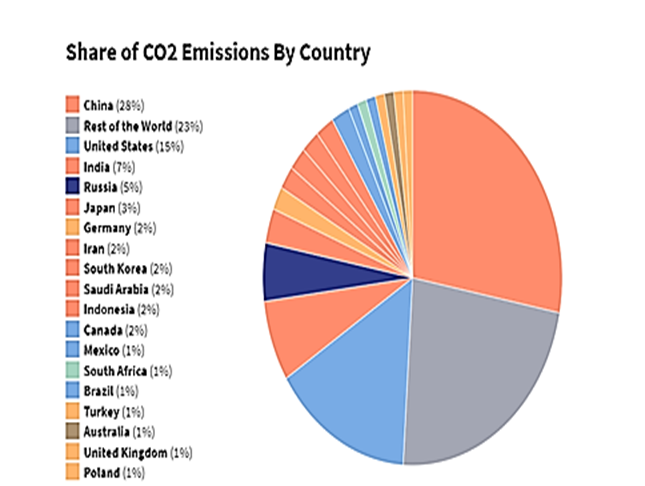
विश्व ग्रीन हाउस गैस उत्सर्जन डेटा के अनुसार, वैश्विक कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड उत्सर्जन में उनके योगदान के घटते क्रम में देशों का सही क्रम एशिया, उत्तरी अमेरिका, यूरोप और अफ्रीका है।
People Development & Environment MCQ Question 6
Noise pollution is measured in –
- Ohm
- Decibel
- Joule
- Ampere
ध्वनि प्रदूषण को मापा जाता है –
- ओम
- डेसिबल
- जौल
- एम्पेयर
Option 2 : Decibel
People Development & Environment MCQ Question 6 Detailed Solution
Noise pollution is measured in Decibel.
- The decibel (dB) is a logarithmic unit used to measure sound level.
- It is also widely used in electronics, signals and communication.
- In ordinary usage, specification of the intensity of a sound implies a comparison of the intensity of the sound with that of a sound just perceptible to the human ear.
- In simple terms, the dB is the ratio between two power levels expressed in logarithmic terms with relation to some reference level.
- For example, if given two known power levels, P2 and P1, the relative value of P2 with respect to P1 in dB is given by:
- dB = 10 log 10 (P2/P1)
- Noise levels below 35–40 dB are usually necessary for a good night’s sleep.
- A busy office may be about 60 dB while the noise level on a footpath beside a busy road might be approximately 75 dB.
- A departing jumbo jet may result in 120 dB being recorded along the runway.
- Ohm is the SI unit of electrical resistance, transmitting a current of one ampere when subjected to a potential difference of one volt.
- Joule, unit of work or energy in the International System of Units (SI); it is equal to the work done by a force of one newton acting through one metre.
- Ampere is a unit of electric current equal to a flow of one coulomb per second.

ध्वनि प्रदूषण डेसीबल में मापा जाता है ।
- डेसिबल (dB) एक लघुगणक इकाई है जिसका उपयोग ध्वनि स्तर को मापने के लिए किया जाता है ।
- यह इलेक्ट्रॉनिक्स, सिग्नल और संचार में भी व्यापक रूप से उपयोग किया जाता है ।
- सामान्य उपयोग में, ध्वनि की तीव्रता के विनिर्देशन में ध्वनि की तीव्रता की तुलना उस ध्वनि से की जाती है जो मानव कान के लिए बोधगम्य है।
- सरल शब्दों में, डीबी कुछ संदर्भ स्तर के संबंध में लघुगणकीय शब्दों में व्यक्त दो शक्ति स्तरों के बीच का अनुपात है।
- उदाहरण के लिए, यदि दो ज्ञात शक्ति स्तर, P2 और P1 दिए गए हैं, तो dB में P1 के संबंध में P2 का सापेक्ष मान निम्न द्वारा दिया गया है:
- डीबी = 10 लॉग 10 (पी 2 / पी 1 )
- अच्छी रात की नींद के लिए आमतौर पर 35-40 डीबी से नीचे के शोर का स्तर आवश्यक होता है ।
- एक व्यस्त कार्यालय लगभग 60 डीबी हो सकता है जबकि एक व्यस्त सड़क के किनारे फुटपाथ पर शोर का स्तर लगभग 75 डीबी हो सकता है ।
- एक प्रस्थान करने वाले जंबो जेट के परिणामस्वरूप रनवे के साथ 120 डीबी दर्ज किया जा सकता है । Telegram Link-https://t.me/EasynotesNTA
- ओम विद्युत प्रतिरोध की एसआई इकाई है , जो एक वोल्ट के संभावित अंतर के अधीन होने पर एक एम्पीयर की धारा को संचारित करता है।
- जूल , इंटरनेशनल सिस्टम ऑफ़ यूनिट्स (SI) में कार्य या ऊर्जा की इकाई; यह एक मीटर के माध्यम से अभिनय करने वाले एक न्यूटन के बल द्वारा किए गए कार्य के बराबर है।
- एम्पीयर एक कूलम्ब प्रति सेकंड के प्रवाह के बराबर विद्युत प्रवाह की एक इकाई है।
People Development & Environment MCQ Question 7
Environmental studies aims at developing
- Understanding local environment/environmental issues
- Understanding global environment/environmental issues
- To develop positive attitude towards environment
- All of the above
पर्यावरण अध्ययन का उद्देश्य विकास करना है
- स्थानीय पर्यावरण/पर्यावरणीय मुद्दों को समझना
- वैश्विक पर्यावरण/पर्यावरणीय मुद्दों को समझना
- पर्यावरण के प्रति सकारात्मक दृष्टिकोण विकसित करना
- ऊपर के सभी
Option 4 : All of the above
People Development & Environment MCQ Question 7 Detailed Solution
The correct answer is All of the above.
Key Points
Environmental studies aim at the following-
- Creating awareness about the environment as a whole as well as its related problems.
- Gaining experiences and acquiring a basic understanding of the environment and its allied problems.
- Skill acquisition for identifying and solving environmental problems.
- Protection of the environment through participation.
- Acquiring an attitude of concern towards the environment and solving its problems.
- Developing an ability to evaluate and analyze measures to protect the environment. Telegram Link-https://t.me/EasynotesNTA
- Raise consciousness about the environment.
- Creating environmental ethics and environmentally sensitive society.
- Teaching environmentally appropriate behaviour.
सही उत्तर उपरोक्त सभी है।
प्रमुख बिंदु

पर्यावरण अध्ययन का उद्देश्य निम्नलिखित है-
- संपूर्ण पर्यावरण के साथ-साथ उससे संबंधित समस्याओं के बारे में जागरूकता पैदा करना ।
- अनुभव प्राप्त करना और पर्यावरण और उससे जुड़ी समस्याओं की बुनियादी समझ हासिल करना ।
- पर्यावरणीय समस्याओं की पहचान और समाधान के लिए कौशल अधिग्रहण ।
- भागीदारी के माध्यम से पर्यावरण की सुरक्षा ।
- पर्यावरण के प्रति सरोकार का दृष्टिकोण प्राप्त करना और उसकी समस्याओं का समाधान करना।
- विकास एक का मूल्यांकन करने और विश्लेषण करने की क्षमता पर्यावरण की रक्षा के उपाय।
- पर्यावरण के प्रति जागरूकता बढ़ाएं ।
- पर्यावरण नैतिकता और पर्यावरण के प्रति संवेदनशील समाज का निर्माण करना ।
- पर्यावरण के अनुकूल व्यवहार सिखाना।
People Development & Environment MCQ Question 8
Which of the following is the central aim to strengthen the global response to the threat of climate change by keeping global temperature rise this century well below 2 degrees Celcius of _________ conference?
- Kyoto Protocol
- Paris Agreement
- Montreal Protocol
- RIO Summit
निम्नलिखित में से कौन सा _________ सम्मेलन के इस सदी में वैश्विक तापमान वृद्धि को 2 डिग्री सेल्सियस से नीचे रखकर जलवायु परिवर्तन के खतरे के लिए वैश्विक प्रतिक्रिया को मजबूत करने का केंद्रीय उद्देश्य है?
- क्योटो प्रोटोकोल
- पेरिस समझौता
- मॉन्ट्रियल प्रोटोकॉल
- रियो शिखर सम्मेलन
Option 2 : Paris Agreement
People Development & Environment MCQ Question 8 Detailed Solution
Paris Agreement

- It is also known as COP 21 Conference which led to an international climate agreement to keep global warming below 2 degrees centigrade prior pre-industrial level.
- 196 negotiating parties agreed on 12 December 2015 and entered into force on 4 November 2016 to draw a long-term greenhouse gas emission development strategy.
- It is a legally binding rule to the parties involved.
- the obligation for developed countries to provide financial support to the developing countries in order to enable them to improvise their existing technologies to implement the agreement is been a constituent of this agreement.
- It aims to reduce Greenhouse gas emissions by 2025-2030.
Montreal Protocol
- It is a global agreement to protect the Earth’s ozone layer by phasing out the ozone-depleting chemicals.
- It includes both production and consumption of ozone-depleting chemicals.
- It was signed in 1987 and enacted in 1989.
- The parties to the protocol meet annually to make a decision and review the execution of its operations to date.
- Kigali agreement is the recent amendment to the material protocol which envisages the phase-down of HFCs in 2016. Telegram Link-https://t.me/EasynotesNTA
Kyoto Protocol
- It is a United Nations agreement that binds the signatory nations to reduce their greenhouse gas emissions.
- The protocol was drafted and agreed upon in Kyoto, Japan in December 1997 thereby getting its name for the conference.
- It was signed by most nations at the 1997 Earth Summit.
- The United States of America is nonsignatory to this agreement.
- It provides mandatory reduction targets for 6 key greenhouse gases by 2012.
Rio Summit
- also known as Earth Summit was United Nations Conference on Environment and development.
- It produced long-range reports and execution plans that continue to serve as guidelines for international actions on environmental issues which include the World summit on sustainable development(Earth Summit 2002) and the Kyoto protocol.
- It leads to the establishment of the Convention on Biological Diversity and the United Nations Framework on climate change(UNFCCC).
- It mandates the nations to exploit natural resources within their borders without compromising the environmental concerns of other nations.
- It calls on all nations & local governments to develop and execute plans to preserve the environment and natural resources for future generations.
Therefore, the Paris Agreement is the central aim to strengthen the global response to the threat of climate change by keeping global temperature rise this century well below 2 degrees Celcius prior pre-industrial level.
पेरिस समझौता
- इसे COP 21 सम्मेलन के रूप में भी जाना जाता है, जिसके कारण ग्लोबल वार्मिंग को पूर्व-औद्योगिक स्तर से पहले 2 डिग्री सेंटीग्रेड से नीचे रखने के लिए एक अंतर्राष्ट्रीय जलवायु समझौता हुआ।
- 196 वार्ता पक्ष 12 दिसंबर 2015 को सहमत हुए और दीर्घकालिक ग्रीनहाउस गैस उत्सर्जन विकास रणनीति तैयार करने के लिए 4 नवंबर 2016 को लागू हुए।
- यह शामिल पक्षों के लिए कानूनी रूप से बाध्यकारी नियम है।
- विकासशील देशों को वित्तीय सहायता प्रदान करने के लिए विकसित देशों का दायित्व, ताकि वे समझौते को लागू करने के लिए अपनी मौजूदा प्रौद्योगिकियों में सुधार कर सकें, इस समझौते का एक घटक रहा है।
- इसका उद्देश्य 2025-2030 तक ग्रीनहाउस गैस उत्सर्जन को कम करना है।
मॉन्ट्रियल प्रोटोकॉल
- यह ओजोन-क्षयकारी रसायनों को चरणबद्ध तरीके से समाप्त करके पृथ्वी की ओजोन परत की रक्षा के लिए एक वैश्विक समझौता है।
- इसमें ओजोन-क्षयकारी रसायनों का उत्पादन और खपत दोनों शामिल हैं।
- इसे 1987 में हस्ताक्षरित किया गया था और 1989 में अधिनियमित किया गया था।
- प्रोटोकॉल के पक्षकार निर्णय लेने के लिए सालाना मिलते हैं और इसके संचालन के निष्पादन की समीक्षा करते हैं।
- किगाली समझौता सामग्री प्रोटोकॉल में हालिया संशोधन है जो 2016 में एचएफसी के चरण-डाउन की परिकल्पना करता है।
क्योटो प्रोटोकोल
- यह एक संयुक्त राष्ट्र समझौता है जो हस्ताक्षरकर्ता देशों को अपने ग्रीनहाउस गैस उत्सर्जन को कम करने के लिए बाध्य करता है।
- दिसंबर 1997 में क्योटो, जापान में प्रोटोकॉल का मसौदा तैयार किया गया था और इस पर सहमति बनी थी, जिससे सम्मेलन के लिए इसका नाम मिला।
- 1997 के पृथ्वी शिखर सम्मेलन में अधिकांश देशों द्वारा इस पर हस्ताक्षर किए गए थे।
- संयुक्त राज्य अमेरिका इस समझौते के लिए गैर-हस्ताक्षरकर्ता है।
- यह 2012 तक 6 प्रमुख ग्रीनहाउस गैसों के लिए अनिवार्य कमी लक्ष्य प्रदान करता है।
रियो शिखर सम्मेलन
- पर्यावरण और विकास पर संयुक्त राष्ट्र सम्मेलन को पृथ्वी शिखर सम्मेलन के रूप में भी जाना जाता है।
- इसने लंबी दूरी की रिपोर्ट और निष्पादन योजनाएं तैयार कीं जो पर्यावरणीय मुद्दों पर अंतर्राष्ट्रीय कार्यों के लिए दिशा-निर्देश के रूप में काम करना जारी रखती हैं जिसमें सतत विकास पर विश्व शिखर सम्मेलन (पृथ्वी शिखर सम्मेलन 2002) और क्योटो प्रोटोकॉल शामिल हैं।
- यह जैव विविधता पर कन्वेंशन और जलवायु परिवर्तन पर संयुक्त राष्ट्र फ्रेमवर्क (यूएनएफसीसीसी) की स्थापना की ओर जाता है।
- यह राष्ट्रों को अन्य देशों की पर्यावरणीय चिंताओं से समझौता किए बिना अपनी सीमाओं के भीतर प्राकृतिक संसाधनों का दोहन करने का आदेश देता है।
- यह सभी राष्ट्रों और स्थानीय सरकारों से भविष्य की पीढ़ियों के लिए पर्यावरण और प्राकृतिक संसाधनों के संरक्षण के लिए योजनाओं को विकसित और निष्पादित करने का आह्वान करता है।
इसलिए, पेरिस समझौता इस सदी में वैश्विक तापमान वृद्धि को पूर्व-औद्योगिक स्तर से पहले 2 डिग्री सेल्सियस से नीचे रखकर जलवायु परिवर्तन के खतरे के लिए वैश्विक प्रतिक्रिया को मजबूत करने का केंद्रीय उद्देश्य है।
People Development & Environment MCQ Question 9
The Kyoto protocol was entered into force in the year:
A. 2005
B. 1997
C. 2000
D. 2002
- C
- B
- D
- A
क्योटो प्रोटोकॉल किस वर्ष लागू हुआ था:
ए. 2005
बी 1997
सी 2000
डी. 2002
- सी
- बी
- डी
- ए
Option 4 : A
People Development & Environment MCQ Question 9 Detailed Solution
Option 4 is the correct answer: the Kyoto Protocol came into force in 2005.
- Kyoto Protocol is a mechanism which set limits for the industrialised nations to reduce the greenhouse gases emissions as aimed by the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
- It was adopted in 1997 but did not come into force as the process required ratification by 55% member states.
- After the ratification by Russia in 2004, it came into force in 2005.
- The flexible market mechanism of the Kyoto protocol talks about the trading of emission permits
- It laid three mechanisms by which countries can reduce their emissions:
- Joint Implementation.
- The Clean Development Mechanism.
- Emission Trading.
विकल्प 4 सही उत्तर है: क्योटो प्रोटोकॉल 2005 में लागू हुआ ।
- क्योटो प्रोटोकॉल एक ऐसा तंत्र है जो संयुक्त राष्ट्र फ्रेमवर्क कन्वेंशन ऑन क्लाइमेट चेंज (यूएनएफसीसीसी) के उद्देश्य से औद्योगिक राष्ट्रों के लिए ग्रीनहाउस गैसों के उत्सर्जन को कम करने की सीमा निर्धारित करता है।
- इसे 1997 में अपनाया गया था लेकिन यह लागू नहीं हुआ क्योंकि इस प्रक्रिया को 55% सदस्य राज्यों द्वारा अनुसमर्थन की आवश्यकता थी ।
- 2004 में रूस द्वारा अनुसमर्थन के बाद , यह 2005 में लागू हुआ ।
- क्योटो प्रोटोकॉल का लचीला बाजार तंत्र उत्सर्जन परमिट के व्यापार के बारे में बात करता है Telegram Link-https://t.me/EasynotesNTA
- इसने तीन तंत्र रखे जिनके द्वारा देश अपने उत्सर्जन को कम कर सकते हैं:
- संयुक्त कार्यान्वयन।
- स्वच्छ विकास तंत्र।
- उत्सर्जन व्यापार।
People Development & Environment MCQ Question 10
The global emissions (by weight) of following primary pollutants from natural sources are maximum in the case of
- Nitric oxide
- Carbon monoxide
- Methane
- Carbon dioxide
प्राकृतिक स्रोतों से निम्नलिखित प्राथमिक प्रदूषकों का वैश्विक उत्सर्जन (वजन के अनुसार) अधिकतम है?
- नाइट्रिक ऑक्साइड
- कार्बन मोनोआक्साइड
- मीथेन
- कार्बन डाइआक्साइड
Option 4 : Carbon dioxide
People Development & Environment MCQ Question 10 Detailed Solution
The global emissions (by weight) of the following primary pollutants from natural sources are maximum in the case of Carbon dioxide.
Greenhouse gases:
- They can absorb and emit radiant energy within the thermal infrared range
- Some of the major greenhouse gases are water vapor, carbon dioxide, Methane, CFC, etc.
- Some GHG from industrial sources are,
- Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs)
- Perfluorocarbons (PFCs)
- Sulfur hexafluoride (SF6)
- Nitrogen trifluoride (NF3)
- GHG block the earth’s heat going to space by terrestrial radiation
- So this effect traps the heat energy and gradually cause global warming
- GHG emission is an effect of economic activity, energy use, population size, technology, lifestyle, land use patterns, and climate policy.
Telegram Link-https://t.me/EasynotesNTA

Share of GHGs in global warming:
- Carbon dioxide:
- About 76 percent of global human-caused emissions, carbon dioxide (CO2) sticks around for quite a while.
- Once it’s emitted into the atmosphere, 40 percent still remains after 100 years, 20 percent after 1,000 years, and 10 percent as long as 10,000 years later.
- Methane (CH4):
- It is much more potent in terms of the greenhouse effect.
- Its global warming impact is 25 times greater than that of carbon dioxide over a 100-year period.
- Globally it accounts for approximately 16 percent of human-generated greenhouse gas emissions.
- Nitrous oxide (N2O):
- It is a powerful greenhouse gas that has a GWP 300 times that of carbon dioxide on a 100-year time scale
- It accounts for about 6 percent of human-caused greenhouse gas emissions worldwide.
- Fluorinated gases:
- These are man-made and mainly generated through industrial activities.
- hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), perfluorocarbons (PFCs), sulfur hexafluoride (SF6), and nitrogen trifluoride (NF3) are four main fluorinated gases
- They can trap substantially more heat.
- CFCs are responsible for Ozone depletion and HFCs ahs high global warming capacity
- Water vapor:
- they can absorb more heat
- They are abandoned in the atmosphere
प्राकृतिक स्रोतों से निम्नलिखित प्राथमिक प्रदूषकों का वैश्विक उत्सर्जन (वजन के अनुसार) कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड के मामले में अधिकतम है ।
ग्रीन हाउस गैसें:
- वे थर्मल इन्फ्रारेड रेंज के भीतर उज्ज्वल ऊर्जा को अवशोषित और उत्सर्जित कर सकते हैं
- कुछ प्रमुख ग्रीनहाउस गैसें जल वाष्प, कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड, मीथेन, सीएफ़सी आदि हैं।
- औद्योगिक स्रोतों से कुछ GHG हैं,
- हाइड्रोफ्लोरोकार्बन (एचएफसी)
- पेरफ्लूरोकार्बन (पीएफसी)
- सल्फर हेक्साफ्लोराइड (SF6)
- नाइट्रोजन ट्राइफ्लोराइड (NF3)

- जीएचजी स्थलीय विकिरण द्वारा अंतरिक्ष में जाने वाली पृथ्वी की गर्मी को रोकता है
- तो यह प्रभाव ऊष्मा ऊर्जा को फँसाता है और धीरे-धीरे ग्लोबल वार्मिंग का कारण बनता है
- जीएचजी उत्सर्जन का प्रभाव है आर्थिक गतिविधि, ऊर्जा का उपयोग, पी opulation आकार, प्रौद्योगिकी, जीवन शैली, भूमि उपयोग पैटर्न, और जलवायु नीति।
ग्लोबल वार्मिंग में जीएचजी का हिस्सा:
- कार्बन डाइआक्साइड:
- के बारे में 76 प्रतिशत वैश्विक मानव का कारण उत्सर्जन की, कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड (सीओ 2 ) काफी देर के लिए चारों ओर चिपक।
- एक बार जब यह वायुमंडल में उत्सर्जित हो जाता है, तो 40 प्रतिशत 100 साल बाद भी, 20 प्रतिशत 1,000 साल बाद और 10 प्रतिशत 10,000 साल बाद तक बना रहता है।
- मीथेन (सीएच 4 ):
- यह ग्रीनहाउस प्रभाव के मामले में बहुत अधिक शक्तिशाली है।
- इसका ग्लोबल वार्मिंग प्रभाव 100 साल की अवधि में कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड की तुलना में 25 गुना अधिक है ।
- विश्व स्तर पर यह मानव जनित ग्रीनहाउस गैस उत्सर्जन का लगभग 16 प्रतिशत हिस्सा है।
- नाइट्रस ऑक्साइड (एन 2 ओ):
- यह एक शक्तिशाली ग्रीनहाउस गैस है जिसमें 100 साल के समय के पैमाने पर कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड की तुलना में 300 गुना GWP है
- यह दुनिया भर में मानव जनित ग्रीनहाउस गैस उत्सर्जन का लगभग 6 प्रतिशत हिस्सा है।
- फ्लोरीनेटेड गैसें:
- ये मानव निर्मित हैं और मुख्य रूप से औद्योगिक गतिविधियों के माध्यम से उत्पन्न होते हैं।
- हाइड्रोफ्लोरोकार्बन (एचएफसी), पेरफ्लूरोकार्बन (पीएफसी), सल्फर हेक्साफ्लोराइड (एसएफ 6 ) और नाइट्रोजन ट्राइफ्लोराइड (एनएफ 3 ) चार मुख्य फ्लोराइडयुक्त गैसें हैं।
- वे काफी अधिक गर्मी में फंस सकते हैं।
- ओजोन रिक्तीकरण के लिए सीएफ़सी जिम्मेदार हैं और एचएफसी उच्च ग्लोबल वार्मिंग क्षमता के लिए जिम्मेदार हैं
- भाप:
- वे अधिक गर्मी अवशोषित कर सकते हैं
- उन्हें वातावरण में छोड़ दिया जाता है
People Development & Environment MCQ Question 11
Which one of the following is most sensitive to environmental change?
- Amphibian
- Reptile
- Mammal
- Insect
निम्नलिखित में से कौन पर्यावरण परिवर्तन के प्रति सर्वाधिक संवेदनशील है?
- उभयचर
- साँप
- सस्तन प्राणी
- कीट
Option 1 : Amphibian
People Development & Environment MCQ Question 11 Detailed Solution

Amphibians are small vertebrates that need water, or a moist environment, to survive. The species in this group include frogs, toads, salamanders, and newts.
They are sometimes called “indicators.” They are called indicators because they are very sensitive to change in their environment.
- They breathe through their skin and breathe toxic and non-toxic components with it too.
- Nearly 33% of the amphibian species of the world are categorized as threatened on the Red List.
- Amphibians are dependent for their survival on a plentiful supply of fresh water that is free of chemical contaminants and harmful microbes.
Extra Info-
Reptiles
- These are cold-blooded vertebrates. (Vertebrates have backbones.)
- They have dry skin covered with scales or bony plates and usually lay soft-shelled eggs. It usually refers to lizards, snakes, turtles, alligators, and crocodiles.
Mammals
- Mammals include humans and all other animals that are warm-blooded vertebrates (vertebrates have backbones) with hair.
- They feed their young with milk and have a more well-developed brain than other types of animals.
Insects
- All insects belong to the phylum Arthropoda.
- Insects live in nearly every habitat, and it’s estimated that there are currently 10 quintillion insects on the globe.
- So far scientists who study bugs, called entomologists, have named one million insect species but studies estimate that four million are still uncategorized.
Hence, it is clear from the above points that Amphibian is most sensitive to environmental change. Telegram Link-https://t.me/EasynotesNTA
उभयचर छोटे कशेरुकी होते हैं जिन्हें जीवित रहने के लिए पानी या नम वातावरण की आवश्यकता होती है। इस समूह की प्रजातियों में मेंढक, टोड, सैलामैंडर और न्यूट्स शामिल हैं।
उन्हें कभी-कभी “संकेतक” कहा जाता है। उन्हें संकेतक कहा जाता है क्योंकि वे अपने वातावरण में परिवर्तन के प्रति बहुत संवेदनशील होते हैं।
- वे अपनी त्वचा से सांस लेते हैं और इसके साथ जहरीले और गैर विषैले घटकों को भी सांस लेते हैं।
- दुनिया की लगभग 33% उभयचर प्रजातियों को रेड लिस्ट में खतरे के रूप में वर्गीकृत किया गया है।
- उभयचर अपने अस्तित्व के लिए ताजे पानी की भरपूर आपूर्ति पर निर्भर हैं जो रासायनिक संदूषकों और हानिकारक रोगाणुओं से मुक्त है।
अतिरिक्त जानकारी-
सरीसृप
- ये ठंडे खून वाले कशेरुकी हैं। (कशेरुकों में रीढ़ की हड्डी होती है।)
- उनकी सूखी त्वचा होती है जो तराजू या बोनी प्लेटों से ढकी होती है और आमतौर पर नरम-खोल वाले अंडे देती है। यह आमतौर पर छिपकलियों, सांपों, कछुओं, मगरमच्छों और मगरमच्छों को संदर्भित करता है।
स्तनधारियों
- स्तनधारियों में मानव और अन्य सभी जानवर शामिल होते हैं जो बालों के साथ गर्म रक्त वाले कशेरुकी (कशेरुकों की रीढ़ की हड्डी) होते हैं।
- वे अपने बच्चों को दूध पिलाते हैं और अन्य प्रकार के जानवरों की तुलना में अधिक विकसित मस्तिष्क रखते हैं।
कीड़े
- सभी कीट फ़ाइलम आर्थ्रोपोडा के हैं।
- कीड़े लगभग हर आवास में रहते हैं, और यह अनुमान लगाया गया है कि वर्तमान में दुनिया में 10 क्विंटल कीड़े हैं।
- अब तक कीड़े का अध्ययन करने वाले वैज्ञानिकों, जिन्हें कीटविज्ञानी कहा जाता है, ने कीटों की एक मिलियन प्रजातियों का नाम दिया है, लेकिन अध्ययनों का अनुमान है कि चार मिलियन अभी भी अवर्गीकृत हैं।
अतः उपरोक्त बिन्दुओं से स्पष्ट है कि उभयचर पर्यावरण परिवर्तन के प्रति सर्वाधिक संवेदनशील है।
People Development & Environment MCQ Question 12
Which of the following disasters belong to the category of nuclear disasters?
a. Fukushima disaster
b. Chernobyl disaster
c. Three-mile Island incident
d. The love canal disaster
Choose the correct option:
- (a), (b) and (c)
- (a), (b) and (d)
- (a), (c) and (d)
- (b), (c) and (d)
निम्नलिखित में से कौन सी आपदा परमाणु आपदाओं की श्रेणी से संबंधित है?
ए। फुकुशिमा आपदा
बी। चेरनोबिल आपदा
सी। तीन मील द्वीप घटना
डी। प्रेम नहर आपदा
सही विकल्प चुनें:
- (ए), (बी) और (सी)
- (ए), (बी) और (डी)
- (ए), (सी) और (डी)
- (बी), (सी) और (डी)
Option 1 : (a), (b) and (c)
People Development & Environment MCQ Question 12 Detailed Solution
Natural and human-caused disasters affect thousands of people each year. Major adverse events such as these have the potential to cause catastrophic loss of life and physical destruction.
Nuclear Disasters: The main drawback of nuclear energy is the possibility of nuclear disasters. These occur in nuclear power plants. The consequences of such disasters can be extremely serious. A few of these nuclear disasters include:

- The Fukushima Disaster: It took place in 2011 at the Fukushima Daiichi plant in northern Japan. It is the second-worst nuclear accident in the history of nuclear power generation. It is also known as the Fukushima nuclear accident or Fukushima Daiichi nuclear accident.
- The Chernobyl Disaster: The 1986 accident at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant in Ukraine, then part of the former Soviet Union, is the only accident in the history of commercial nuclear power to cause fatalities from radiation. It was the result of a severely flawed reactor design, combined with human error.
- Three-mile Island Incident: The Three Mile Island accident, that took place on March 28, 1979, was a meltdown at a nuclear power plant in Middletown, Pennsylvania. This was the most serious accident in U.S. commercial nuclear power plant operating history. It resulted from a combination of equipment malfunctions, design-related problems and human errors.

NOTE: The Love Canal Disaster: Love Canal is one of the most shocking environmental man-made disasters in American history. It was the first US state of emergency to be declared over a human-made disaster, and it was a thoughtful lesson about the harmful effects of toxic pollution.
Hence, it can be concluded from the given points that the Fukushima, the Chernobyl and the three-mile island incident belong to the category of nuclear disasters.
प्राकृतिक और मानव जनित आपदाएं हर साल हजारों लोगों को प्रभावित करती हैं। इस तरह की प्रमुख प्रतिकूल घटनाओं में जीवन और भौतिक विनाश के विनाशकारी नुकसान की संभावना है।
परमाणु आपदाएं: परमाणु ऊर्जा का मुख्य दोष परमाणु आपदाओं की संभावना है। ये परमाणु ऊर्जा संयंत्रों में होते हैं। ऐसी आपदाओं के परिणाम अत्यंत गंभीर हो सकते हैं। इनमें से कुछ परमाणु आपदाओं में शामिल हैं: Telegram Link-https://t.me/EasynotesNTA
- फुकुशिमा आपदा : यह 2011 में उत्तरी जापान में फुकुशिमा दाइची संयंत्र में हुई थी। यह परमाणु ऊर्जा उत्पादन के इतिहास में दूसरी सबसे बड़ी परमाणु दुर्घटना है । इसे फुकुशिमा परमाणु दुर्घटना या फुकुशिमा दाइची परमाणु दुर्घटना के रूप में भी जाना जाता है ।
- चेरनोबिल आपदा: यूक्रेन में चेरनोबिल परमाणु ऊर्जा संयंत्र में 1986 की दुर्घटना, जो उस समय पूर्व सोवियत संघ का हिस्सा था, वाणिज्यिक परमाणु ऊर्जा के इतिहास में एकमात्र दुर्घटना है जो विकिरण से मृत्यु का कारण बनती है। यह मानवीय त्रुटि के साथ संयुक्त रूप से एक गंभीर रूप से त्रुटिपूर्ण रिएक्टर डिजाइन का परिणाम था।
- थ्री-मील आइलैंड हादसा: 28 मार्च, 1979 को हुई थ्री माइल आइलैंड दुर्घटना, मिडलटाउन, पेनसिल्वेनिया में एक परमाणु ऊर्जा संयंत्र में एक मंदी थी। अमेरिकी वाणिज्यिक परमाणु ऊर्जा संयंत्र के संचालन के इतिहास में यह सबसे गंभीर दुर्घटना थी । यह उपकरण की खराबी, डिजाइन से संबंधित समस्याओं और मानवीय त्रुटियों के संयोजन के परिणामस्वरूप हुआ।
नोट: लव कैनाल डिजास्टर: लव कैनाल अमेरिकी इतिहास की सबसे चौंकाने वाली पर्यावरणीय मानव निर्मित आपदाओं में से एक है। यह मानव निर्मित आपदा पर घोषित होने वाला पहला अमेरिकी आपातकाल था, और यह जहरीले प्रदूषण के हानिकारक प्रभावों के बारे में एक विचारशील सबक था।
इसलिए, दिए गए बिंदुओं से यह निष्कर्ष निकाला जा सकता है कि फुकुशिमा, चेरनोबिल और तीन मील द्वीप की घटना परमाणु आपदाओं की श्रेणी से संबंधित है।